Integrating Audio, Visual, and Semantic Information for Enhanced Multimodal Speaker Diarization

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This research paper explores integrating audio, visual, and semantic information to enhance multimodal speaker diarization.
- Multimodal speaker diarization is the process of identifying and tracking different speakers in a multimedia recording that contains both audio and visual data.
- The paper proposes a novel approach that combines multiple modalities to improve the accuracy and robustness of speaker diarization.
Plain English Explanation
Speaker diarization is the task of determining "who spoke when" in an audio recording. Traditionally, this has been done using just the audio information. However, the paper explores the idea that incorporating additional modalities, such as video and semantic cues, can lead to better speaker diarization.
The key insight is that different modalities can provide complementary information. For example, the audio signal alone may not be sufficient to distinguish between two speakers with similar voices, but the visual information from their faces or gestures could help differentiate them. Similarly, semantic information about the context and content of the conversation could also aid in the diarization process.
By integrating these various sources of data, the researchers believe they can create a more accurate and robust speaker diarization system. This could have important applications in areas like meeting transcription, video conferencing, and media analysis, where accurately identifying who is speaking at any given time is crucial.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a multimodal speaker diarization framework that combines audio, visual, and semantic information. The key components of the system include:
- Audio processing: The audio signal is analyzed to extract speaker-specific features, such as voice characteristics and speaker turns.
- Visual processing: The video data is used to detect and track the faces of different speakers, providing visual cues about who is speaking.
- Semantic processing: The text transcripts or other contextual information are analyzed to infer semantic relationships between speakers and the content of their speech.
- Multimodal fusion: The information from the various modalities is integrated using a neural network-based approach to make the final speaker diarization decisions.
The researchers evaluate their approach on several benchmark datasets and compare it to state-of-the-art unimodal and multimodal speaker diarization methods. The results show that the proposed system outperforms the baselines, demonstrating the benefits of integrating audio, visual, and semantic cues for this task.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling approach to enhancing speaker diarization by leveraging multiple modalities. The authors acknowledge that the performance of unimodal speaker diarization systems is often limited by the inherent ambiguities and noise in a single data source. By fusing information from audio, visual, and semantic cues, they are able to address these limitations and achieve better overall results.
However, the paper does not provide a detailed analysis of the robustness of the proposed system to various real-world challenges, such as varying audio quality, occlusions in the video, or the availability of semantic information. Additionally, the paper does not discuss the computational complexity and resource requirements of the multimodal fusion approach, which could be an important consideration for practical deployment.
Further research could explore the generalizability of the proposed framework to different types of multimedia data and settings, as well as investigate ways to make the system more efficient and scalable. Nonetheless, the core idea of leveraging complementary information from multiple modalities is a promising direction for advancing speaker diarization technology.
Conclusion
This research paper presents a novel approach to speaker diarization that integrates audio, visual, and semantic information. By fusing these multiple modalities, the system is able to achieve better performance than traditional unimodal methods.
The proposed framework has the potential to significantly improve the accuracy and robustness of speaker diarization, which is crucial for a wide range of applications, such as meeting transcription, video conferencing, and media analysis. While the paper highlights several important considerations and areas for future research, the core concept of leveraging complementary multimodal cues is a valuable contribution to the field of speaker diarization.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Integrating Audio, Visual, and Semantic Information for Enhanced Multimodal Speaker Diarization
Luyao Cheng, Hui Wang, Siqi Zheng, Yafeng Chen, Rongjie Huang, Qinglin Zhang, Qian Chen, Xihao Li
Speaker diarization, the process of segmenting an audio stream or transcribed speech content into homogenous partitions based on speaker identity, plays a crucial role in the interpretation and analysis of human speech. Most existing speaker diarization systems rely exclusively on unimodal acoustic information, making the task particularly challenging due to the innate ambiguities of audio signals. Recent studies have made tremendous efforts towards audio-visual or audio-semantic modeling to enhance performance. However, even the incorporation of up to two modalities often falls short in addressing the complexities of spontaneous and unstructured conversations. To exploit more meaningful dialogue patterns, we propose a novel multimodal approach that jointly utilizes audio, visual, and semantic cues to enhance speaker diarization. Our method elegantly formulates the multimodal modeling as a constrained optimization problem. First, we build insights into the visual connections among active speakers and the semantic interactions within spoken content, thereby establishing abundant pairwise constraints. Then we introduce a joint pairwise constraint propagation algorithm to cluster speakers based on these visual and semantic constraints. This integration effectively leverages the complementary strengths of different modalities, refining the affinity estimation between individual speaker embeddings. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple multimodal datasets demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art speaker diarization methods.
Read more8/23/2024


0
Audio-Visual Speaker Diarization: Current Databases, Approaches and Challenges
Victoria Mingote, Alfonso Ortega, Antonio Miguel, Eduardo Lleida
Nowadays, the large amount of audio-visual content available has fostered the need to develop new robust automatic speaker diarization systems to analyse and characterise it. This kind of system helps to reduce the cost of doing this process manually and allows the use of the speaker information for different applications, as a huge quantity of information is present, for example, images of faces, or audio recordings. Therefore, this paper aims to address a critical area in the field of speaker diarization systems, the integration of audio-visual content of different domains. This paper seeks to push beyond current state-of-the-art practices by developing a robust audio-visual speaker diarization framework adaptable to various data domains, including TV scenarios, meetings, and daily activities. Unlike most of the existing audio-visual speaker diarization systems, this framework will also include the proposal of an approach to lead the precise assignment of specific identities in TV scenarios where celebrities appear. In addition, in this work, we have conducted an extensive compilation of the current state-of-the-art approaches and the existing databases for developing audio-visual speaker diarization.
Read more9/10/2024
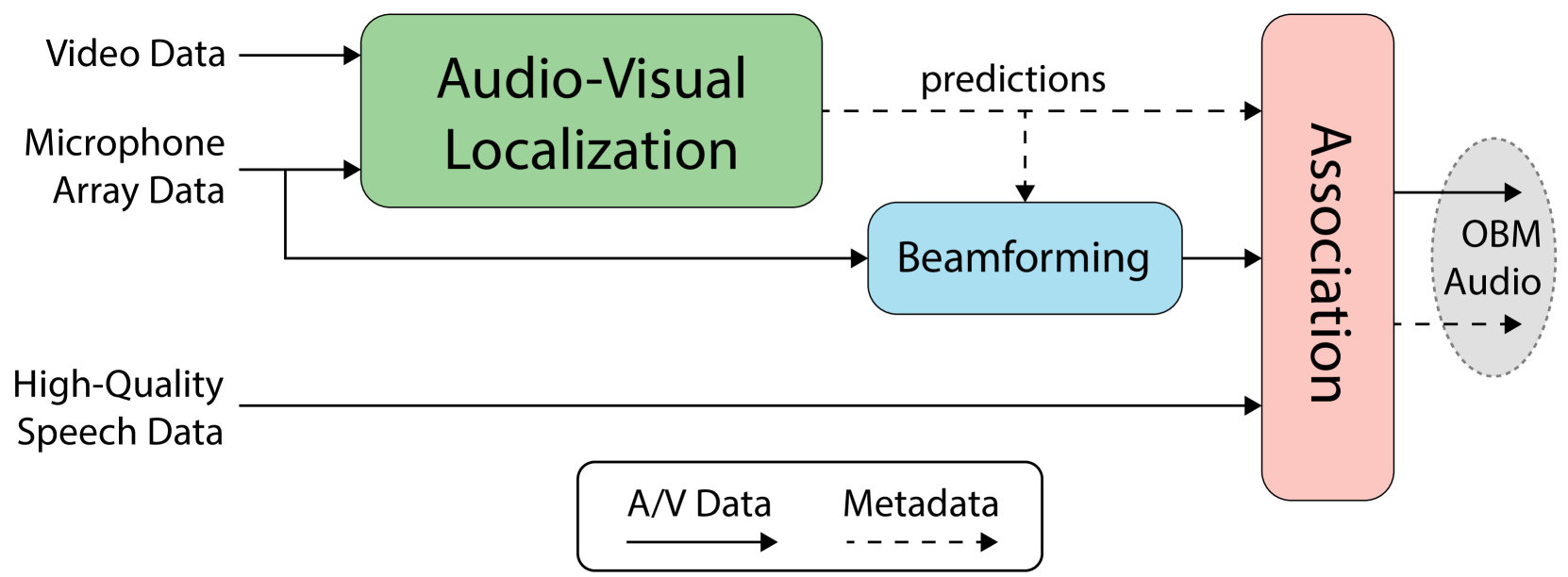

0
Audio-Visual Talker Localization in Video for Spatial Sound Reproduction
Davide Berghi, Philip J. B. Jackson
Object-based audio production requires the positional metadata to be defined for each point-source object, including the key elements in the foreground of the sound scene. In many media production use cases, both cameras and microphones are employed to make recordings, and the human voice is often a key element. In this research, we detect and locate the active speaker in the video, facilitating the automatic extraction of the positional metadata of the talker relative to the camera's reference frame. With the integration of the visual modality, this study expands upon our previous investigation focused solely on audio-based active speaker detection and localization. Our experiments compare conventional audio-visual approaches for active speaker detection that leverage monaural audio, our previous audio-only method that leverages multichannel recordings from a microphone array, and a novel audio-visual approach integrating vision and multichannel audio. We found the role of the two modalities to complement each other. Multichannel audio, overcoming the problem of visual occlusions, provides a double-digit reduction in detection error compared to audio-visual methods with single-channel audio. The combination of multichannel audio and vision further enhances spatial accuracy, leading to a four-percentage point increase in F1 score on the Tragic Talkers dataset. Future investigations will assess the robustness of the model in noisy and highly reverberant environments, as well as tackle the problem of off-screen speakers.
Read more6/4/2024


0
USED: Universal Speaker Extraction and Diarization
Junyi Ao, Mehmet Sinan Y{i}ld{i}r{i}m, Ruijie Tao, Meng Ge, Shuai Wang, Yanmin Qian, Haizhou Li
Speaker extraction and diarization are two enabling techniques for real-world speech applications. Speaker extraction aims to extract a target speaker's voice from a speech mixture, while speaker diarization demarcates speech segments by speaker, annotating `who spoke when'. Previous studies have typically treated the two tasks independently. In practical applications, it is more meaningful to have knowledge about `who spoke what and when', which is captured by the two tasks. The two tasks share a similar objective of disentangling speakers. Speaker extraction operates in the frequency domain, whereas diarization is in the temporal domain. It is logical to believe that speaker activities obtained from speaker diarization can benefit speaker extraction, while the extracted speech offers more accurate speaker activity detection than the speech mixture. In this paper, we propose a unified model called Universal Speaker Extraction and Diarization (USED) to address output inconsistency and scenario mismatch issues. It is designed to manage speech mixture with varying overlap ratios and variable number of speakers. We show that the USED model significantly outperforms the competitive baselines for speaker extraction and diarization tasks on LibriMix and SparseLibriMix datasets. We further validate the diarization performance on CALLHOME, a dataset based on real recordings, and experimental results indicate that our model surpasses recently proposed approaches.
Read more5/10/2024