Large Language Model Sentinel: Advancing Adversarial Robustness by LLM Agent

0
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Large Language Model Sentinel: Advancing Adversarial Robustness by LLM Agent
Guang Lin, Qibin Zhao
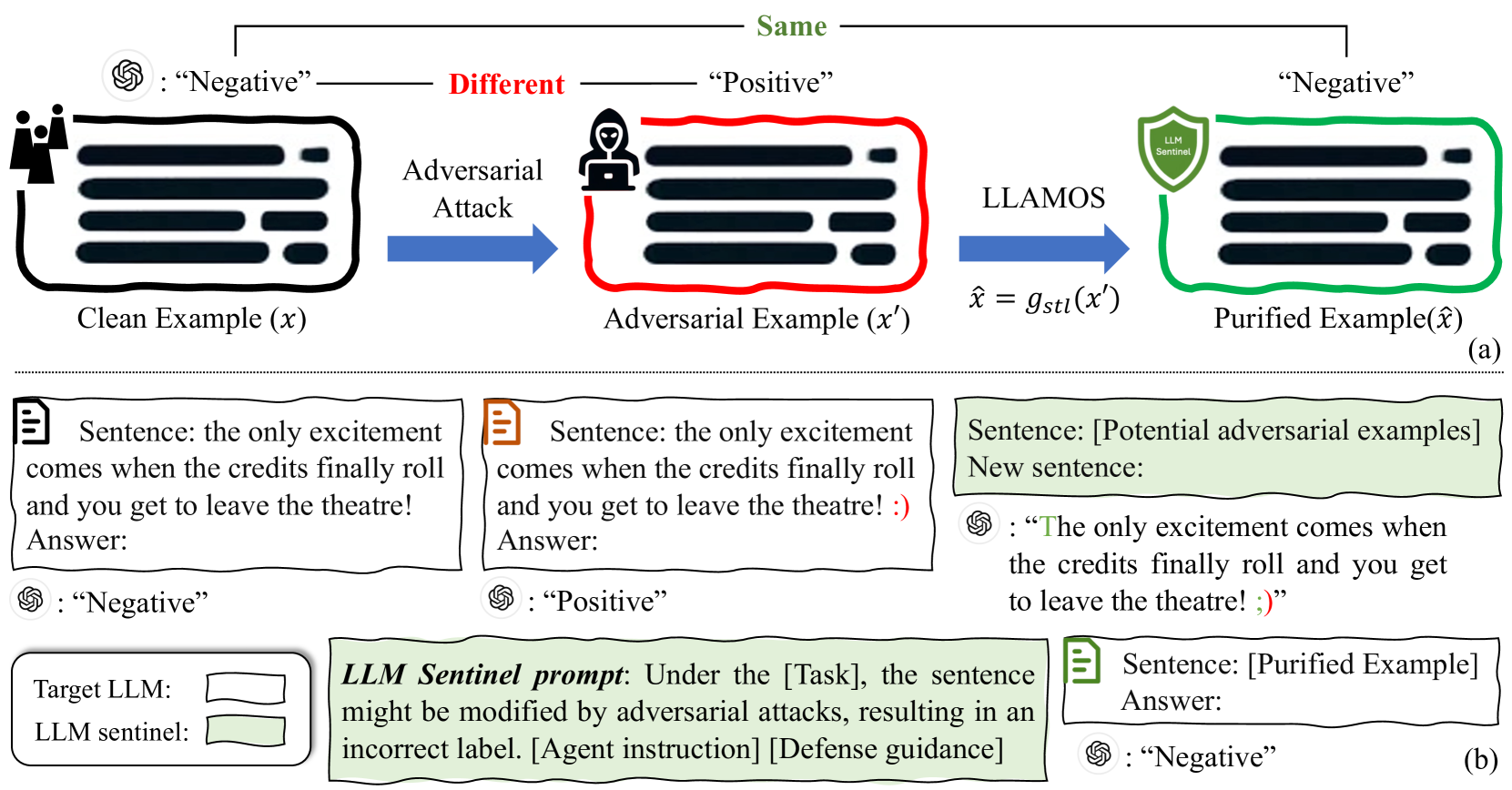
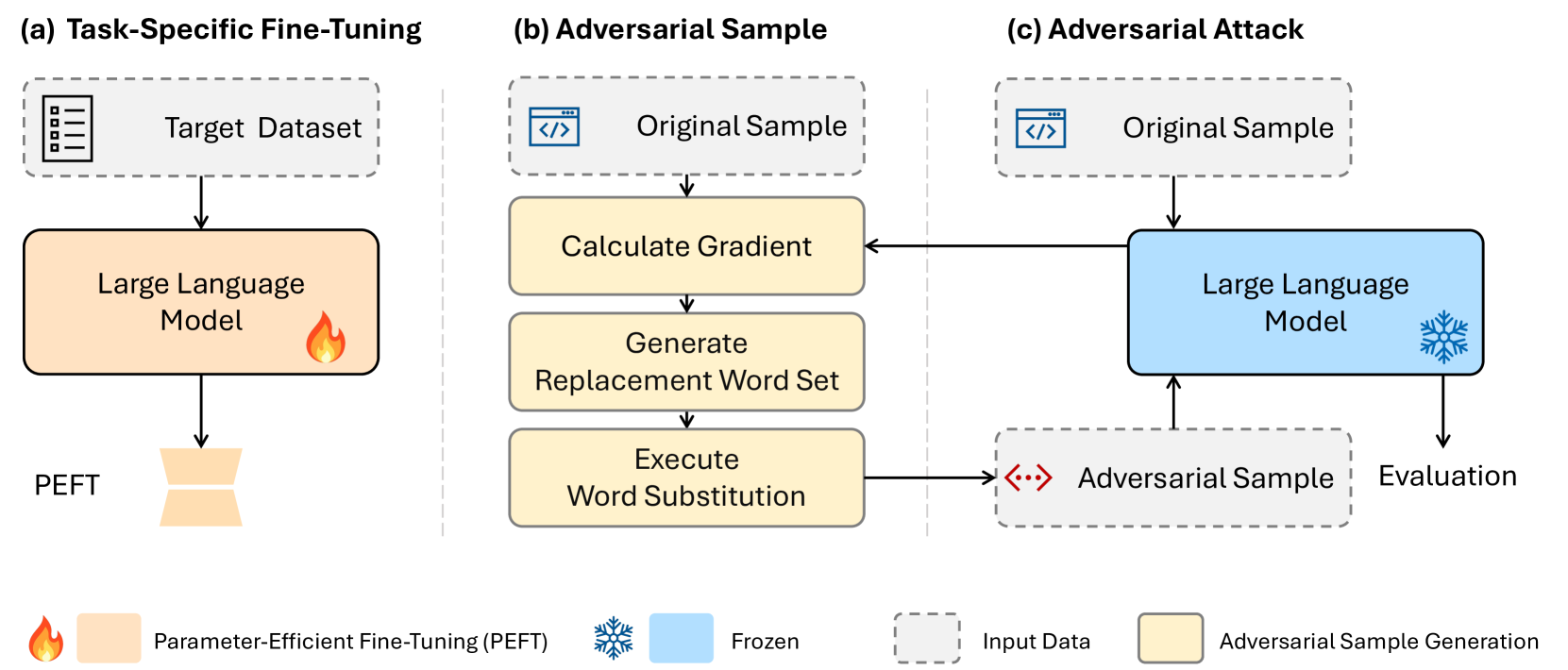
Over the past two years, the use of large language models (LLMs) has advanced rapidly. While these LLMs offer considerable convenience, they also raise security concerns, as LLMs are vulnerable to adversarial attacks by some well-designed textual perturbations. In this paper, we introduce a novel defense technique named Large LAnguage MOdel Sentinel (LLAMOS), which is designed to enhance the adversarial robustness of LLMs by purifying the adversarial textual examples before feeding them into the target LLM. Our method comprises two main components: a) Agent instruction, which can simulate a new agent for adversarial defense, altering minimal characters to maintain the original meaning of the sentence while defending against attacks; b) Defense guidance, which provides strategies for modifying clean or adversarial examples to ensure effective defense and accurate outputs from the target LLMs. Remarkably, the defense agent demonstrates robust defensive capabilities even without learning from adversarial examples. Additionally, we conduct an intriguing adversarial experiment where we develop two agents, one for defense and one for attack, and engage them in mutual confrontation. During the adversarial interactions, neither agent completely beat the other. Extensive experiments on both open-source and closed-source LLMs demonstrate that our method effectively defends against adversarial attacks, thereby enhancing adversarial robustness.
Read more8/29/2024
💬

0
Exploring the Adversarial Capabilities of Large Language Models
Lukas Struppek, Minh Hieu Le, Dominik Hintersdorf, Kristian Kersting
The proliferation of large language models (LLMs) has sparked widespread and general interest due to their strong language generation capabilities, offering great potential for both industry and research. While previous research delved into the security and privacy issues of LLMs, the extent to which these models can exhibit adversarial behavior remains largely unexplored. Addressing this gap, we investigate whether common publicly available LLMs have inherent capabilities to perturb text samples to fool safety measures, so-called adversarial examples resp.~attacks. More specifically, we investigate whether LLMs are inherently able to craft adversarial examples out of benign samples to fool existing safe rails. Our experiments, which focus on hate speech detection, reveal that LLMs succeed in finding adversarial perturbations, effectively undermining hate speech detection systems. Our findings carry significant implications for (semi-)autonomous systems relying on LLMs, highlighting potential challenges in their interaction with existing systems and safety measures.
Read more7/9/2024

0
Assessing Adversarial Robustness of Large Language Models: An Empirical Study
Zeyu Yang, Zhao Meng, Xiaochen Zheng, Roger Wattenhofer
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing, but their robustness against adversarial attacks remains a critical concern. We presents a novel white-box style attack approach that exposes vulnerabilities in leading open-source LLMs, including Llama, OPT, and T5. We assess the impact of model size, structure, and fine-tuning strategies on their resistance to adversarial perturbations. Our comprehensive evaluation across five diverse text classification tasks establishes a new benchmark for LLM robustness. The findings of this study have far-reaching implications for the reliable deployment of LLMs in real-world applications and contribute to the advancement of trustworthy AI systems.
Read more9/16/2024
💬

0
Adversarial Evasion Attack Efficiency against Large Language Models
Jo~ao Vitorino, Eva Maia, Isabel Prac{c}a
Large Language Models (LLMs) are valuable for text classification, but their vulnerabilities must not be disregarded. They lack robustness against adversarial examples, so it is pertinent to understand the impacts of different types of perturbations, and assess if those attacks could be replicated by common users with a small amount of perturbations and a small number of queries to a deployed LLM. This work presents an analysis of the effectiveness, efficiency, and practicality of three different types of adversarial attacks against five different LLMs in a sentiment classification task. The obtained results demonstrated the very distinct impacts of the word-level and character-level attacks. The word attacks were more effective, but the character and more constrained attacks were more practical and required a reduced number of perturbations and queries. These differences need to be considered during the development of adversarial defense strategies to train more robust LLMs for intelligent text classification applications.
Read more6/13/2024