Large Language Models for UAVs: Current State and Pathways to the Future

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the current state and future potential of using large language models (LLMs) for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
- The authors discuss how LLMs can enhance UAV capabilities in areas like spectral sensing, autonomous decision-making, and other key functions.
- The paper outlines challenges and research directions for integrating LLMs with UAVs to unlock new possibilities in this rapidly evolving field.
Plain English Explanation
The paper examines how advanced AI language models can be used to improve the abilities of drones or UAVs. Large language models are powerful AI systems that can understand and generate human-like text. The researchers explore how these language models could enhance key UAV capabilities, such as spectral sensing to detect environmental conditions, and autonomous decision-making to help drones navigate and operate more independently.
The paper provides an overview of the current state of this technology and outlines promising directions for future research and development. For example, the authors discuss how language models could enable UAVs to better interpret and respond to complex situations, similar to how humans use language to understand and make decisions. Integrating advanced AI like this into drones has the potential to unlock new applications and capabilities that could benefit fields from disaster response to environmental monitoring.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by highlighting the growing importance of UAVs across various domains, from military and civilian applications to scientific research. However, the authors note that current UAV systems often lack the cognitive capabilities to handle complex, dynamic environments autonomously.
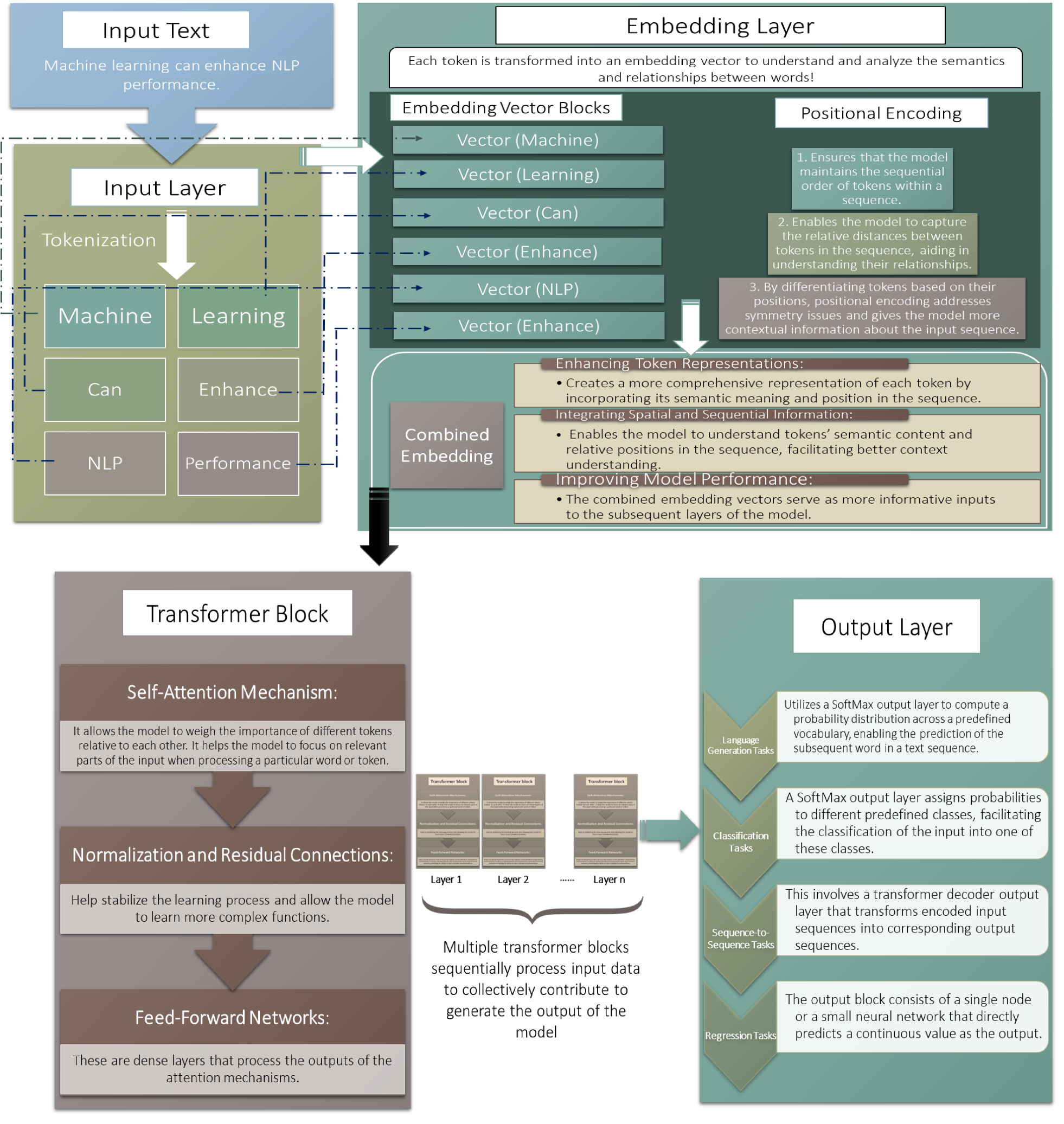
To address this, the researchers explore the potential of leveraging large language models to enhance UAV autonomy and decision-making. The authors discuss how LLMs, trained on vast amounts of text data, can develop rich contextual understanding and reasoning abilities that could be highly valuable for UAV operations.
The paper then delves into specific use cases where LLMs could benefit UAVs, such as spectral sensing to detect environmental conditions, autonomous navigation in cluttered or uncertain environments, and collaborative decision-making among swarms of UAVs. The authors also discuss the potential for LLMs to enhance UAV-human interaction and multisensory perception.
Throughout the paper, the researchers outline key challenges and research directions for integrating LLMs into UAV systems, such as addressing computational and energy constraints, ensuring safety and reliability, and developing appropriate training and deployment strategies.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the potential benefits and challenges of using large language models for UAV applications. The authors make a compelling case for how LLMs could significantly enhance UAV capabilities, particularly in areas like autonomous decision-making and interpretation of complex environments.
However, the paper also acknowledges several important limitations and areas for further research. For example, the authors highlight the need to address computational and energy constraints, as LLMs can be resource-intensive to deploy on small UAV platforms. Additionally, the paper emphasizes the importance of ensuring the safety and reliability of LLM-powered UAV systems, as failures or unexpected behaviors could have serious consequences.
Further research is also needed to develop appropriate training strategies and deployment architectures to seamlessly integrate LLMs with UAV hardware and software. The authors also note the potential for biases and other issues inherent in large language models to manifest in UAV applications, which would require careful consideration and mitigation.
Overall, the paper provides a well-rounded and thoughtful exploration of the current state and future potential of LLMs for UAVs. The authors strike a balance between enthusiasm for the technology and recognition of the challenges that need to be addressed, encouraging readers to think critically about the feasibility and implications of this emerging field.
Conclusion
This paper offers a comprehensive look at the current state and future potential of using large language models (LLMs) to enhance the capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The researchers make a compelling case for how LLMs could unlock new possibilities in areas like spectral sensing, autonomous decision-making, and human-UAV interaction.
By outlining key use cases, challenges, and research directions, the paper provides a roadmap for further developing and integrating advanced AI language models with UAV systems. As the authors note, realizing the full potential of this technology will require addressing a range of technical, safety, and reliability concerns.
Overall, this paper serves as a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and industry professionals working at the intersection of AI and autonomous systems. By exploring the synergies between LLMs and UAVs, the authors shed light on an exciting frontier in the evolution of intelligent, adaptable, and context-aware aerial vehicles.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Large Language Models for UAVs: Current State and Pathways to the Future
Shumaila Javaid, Nasir Saeed, Bin He
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have emerged as a transformative technology across diverse sectors, offering adaptable solutions to complex challenges in both military and civilian domains. Their expanding capabilities present a platform for further advancement by integrating cutting-edge computational tools like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. These advancements have significantly impacted various facets of human life, fostering an era of unparalleled efficiency and convenience. Large Language Models (LLMs), a key component of AI, exhibit remarkable learning and adaptation capabilities within deployed environments, demonstrating an evolving form of intelligence with the potential to approach human-level proficiency. This work explores the significant potential of integrating UAVs and LLMs to propel the development of autonomous systems. We comprehensively review LLM architectures, evaluating their suitability for UAV integration. Additionally, we summarize the state-of-the-art LLM-based UAV architectures and identify novel opportunities for LLM embedding within UAV frameworks. Notably, we focus on leveraging LLMs to refine data analysis and decision-making processes, specifically for enhanced spectral sensing and sharing in UAV applications. Furthermore, we investigate how LLM integration expands the scope of existing UAV applications, enabling autonomous data processing, improved decision-making, and faster response times in emergency scenarios like disaster response and network restoration. Finally, we highlight crucial areas for future research that are critical for facilitating the effective integration of LLMs and UAVs.
Read more5/6/2024


0
Large Language Models for Human-like Autonomous Driving: A Survey
Yun Li, Kai Katsumata, Ehsan Javanmardi, Manabu Tsukada
Large Language Models (LLMs), AI models trained on massive text corpora with remarkable language understanding and generation capabilities, are transforming the field of Autonomous Driving (AD). As AD systems evolve from rule-based and optimization-based methods to learning-based techniques like deep reinforcement learning, they are now poised to embrace a third and more advanced category: knowledge-based AD empowered by LLMs. This shift promises to bring AD closer to human-like AD. However, integrating LLMs into AD systems poses challenges in real-time inference, safety assurance, and deployment costs. This survey provides a comprehensive and critical review of recent progress in leveraging LLMs for AD, focusing on their applications in modular AD pipelines and end-to-end AD systems. We highlight key advancements, identify pressing challenges, and propose promising research directions to bridge the gap between LLMs and AD, thereby facilitating the development of more human-like AD systems. The survey first introduces LLMs' key features and common training schemes, then delves into their applications in modular AD pipelines and end-to-end AD, respectively, followed by discussions on open challenges and future directions. Through this in-depth analysis, we aim to provide insights and inspiration for researchers and practitioners working at the intersection of AI and autonomous vehicles, ultimately contributing to safer, smarter, and more human-centric AD technologies.
Read more7/30/2024

0
Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models: A Review
Saikat Barua
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming artificial intelligence, enabling autonomous agents to perform diverse tasks across various domains. These agents, proficient in human-like text comprehension and generation, have the potential to revolutionize sectors from customer service to healthcare. However, they face challenges such as multimodality, human value alignment, hallucinations, and evaluation. Techniques like prompting, reasoning, tool utilization, and in-context learning are being explored to enhance their capabilities. Evaluation platforms like AgentBench, WebArena, and ToolLLM provide robust methods for assessing these agents in complex scenarios. These advancements are leading to the development of more resilient and capable autonomous agents, anticipated to become integral in our digital lives, assisting in tasks from email responses to disease diagnosis. The future of AI, with LLMs at the forefront, is promising.
Read more4/9/2024
💬

0
A Survey on Large Language Model based Autonomous Agents
Lei Wang, Chen Ma, Xueyang Feng, Zeyu Zhang, Hao Yang, Jingsen Zhang, Zhiyuan Chen, Jiakai Tang, Xu Chen, Yankai Lin, Wayne Xin Zhao, Zhewei Wei, Ji-Rong Wen
Autonomous agents have long been a prominent research focus in both academic and industry communities. Previous research in this field often focuses on training agents with limited knowledge within isolated environments, which diverges significantly from human learning processes, and thus makes the agents hard to achieve human-like decisions. Recently, through the acquisition of vast amounts of web knowledge, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in achieving human-level intelligence. This has sparked an upsurge in studies investigating LLM-based autonomous agents. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey of these studies, delivering a systematic review of the field of LLM-based autonomous agents from a holistic perspective. More specifically, we first discuss the construction of LLM-based autonomous agents, for which we propose a unified framework that encompasses a majority of the previous work. Then, we present a comprehensive overview of the diverse applications of LLM-based autonomous agents in the fields of social science, natural science, and engineering. Finally, we delve into the evaluation strategies commonly used for LLM-based autonomous agents. Based on the previous studies, we also present several challenges and future directions in this field. To keep track of this field and continuously update our survey, we maintain a repository of relevant references at https://github.com/Paitesanshi/LLM-Agent-Survey.
Read more4/5/2024