A Legal Risk Taxonomy for Generative Artificial Intelligence
2404.09479

0
0
⚙️
Abstract
For the first time, this paper presents a taxonomy of legal risks associated with generative AI (GenAI) by breaking down complex legal concepts to provide a common understanding of potential legal challenges for developing and deploying GenAI models. The methodology is based on (1) examining the legal claims that have been filed in existing lawsuits and (2) evaluating the reasonably foreseeable legal claims that may be filed in future lawsuits. First, we identified 29 lawsuits against prominent GenAI entities and tallied the claims of each lawsuit. From there, we identified seven claims that are cited at least four times across these lawsuits as the most likely claims for future GenAI lawsuits. For each of these seven claims, we describe the elements of the claim (what the plaintiff must prove to prevail) and provide an example of how it may apply to GenAI. Next, we identified 30 other potential claims that we consider to be more speculative, because they have been included in fewer than four lawsuits or have yet to be filed. We further separated those 30 claims into 19 that are most likely to be made in relation to pre-deployment of GenAI models and 11 that are more likely to be made in connection with post-deployment of GenAI models since the legal risks will vary between entities that create versus deploy them. For each of these claims, we describe the elements of the claim and the potential remedies that plaintiffs may seek to help entities determine their legal risks in developing or deploying GenAI. Lastly, we close the paper by noting the novelty of GenAI technology and propose some applications for the paper's taxonomy in driving further research.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a legal risk taxonomy for generative artificial intelligence (AI) models, identifying the most common legal claims and risks associated with these technologies.
- The authors examine the current state of litigation involving generative AI and analyze the key legal risks, including copyright, trademark, defamation, privacy, and more.
- The goal is to provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and mitigating the legal challenges posed by generative AI systems.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at the various legal risks and potential lawsuits that can arise from the use of generative AI systems. Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content like text, images, or audio, often by learning from large datasets.
As these technologies become more advanced and widespread, they are starting to raise legal concerns. The authors of this paper have identified the most common legal claims that have been made against generative AI so far, including issues around copyright, trademark, defamation, privacy, and more.
By outlining this "legal risk taxonomy," the goal is to help companies and developers of generative AI systems understand the legal landscape and take steps to mitigate these risks. This can involve things like improving transparency, implementing content moderation, and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by establishing the scope of the legal risks associated with generative AI models, noting that these technologies have the potential to infringe on a wide range of intellectual property rights and personal interests.
The authors then dive into an analysis of the most litigated claims involving generative AI so far. This includes copyright infringement, where AI-generated content is accused of copying or reproducing existing works without permission. There have also been trademark-related lawsuits, where generative AI is used to create content that allegedly infringes on established brand identities.
Additionally, the paper examines the legal risks around defamation, where AI-generated content could be seen as damaging someone's reputation, as well as privacy and data protection concerns, as these models may generate personal information or content without consent.
The paper also covers other potential legal issues, such as the use of generative AI for harassment or discrimination, and the challenges around contractual liability when these systems are used in commercial products and services.
Critical Analysis
While the paper provides a comprehensive taxonomy of the legal risks associated with generative AI, it acknowledges that the legal landscape is still evolving, and there are many unresolved questions and uncertainties. The authors note that courts and policymakers are still grappling with how to apply existing laws and regulations to these rapidly-advancing technologies.
One potential limitation of the research is that it is based on an analysis of existing litigation, which may not fully capture the range of legal issues that could arise in the future as generative AI becomes more sophisticated and integrated into our lives. As the field of AI ethics continues to evolve, new legal challenges may emerge that are not yet visible in current case law.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into potential statutory and policy-based approaches to regulating generative AI, which could significantly shape the legal landscape going forward. Further research in this area could provide valuable insights for policymakers and lawmakers.
Conclusion
This paper offers a valuable legal risk taxonomy for generative AI, providing a comprehensive overview of the key legal claims and challenges that have emerged so far. By understanding these risks, companies and developers can take proactive steps to ensure the responsible development and deployment of generative AI systems.
As these technologies continue to advance and become more prevalent, it will be crucial for the legal system to keep pace and adapt in order to protect individual rights and interests. The insights from this research can help guide that process and contribute to the ongoing dialogue around the governance of generative AI.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
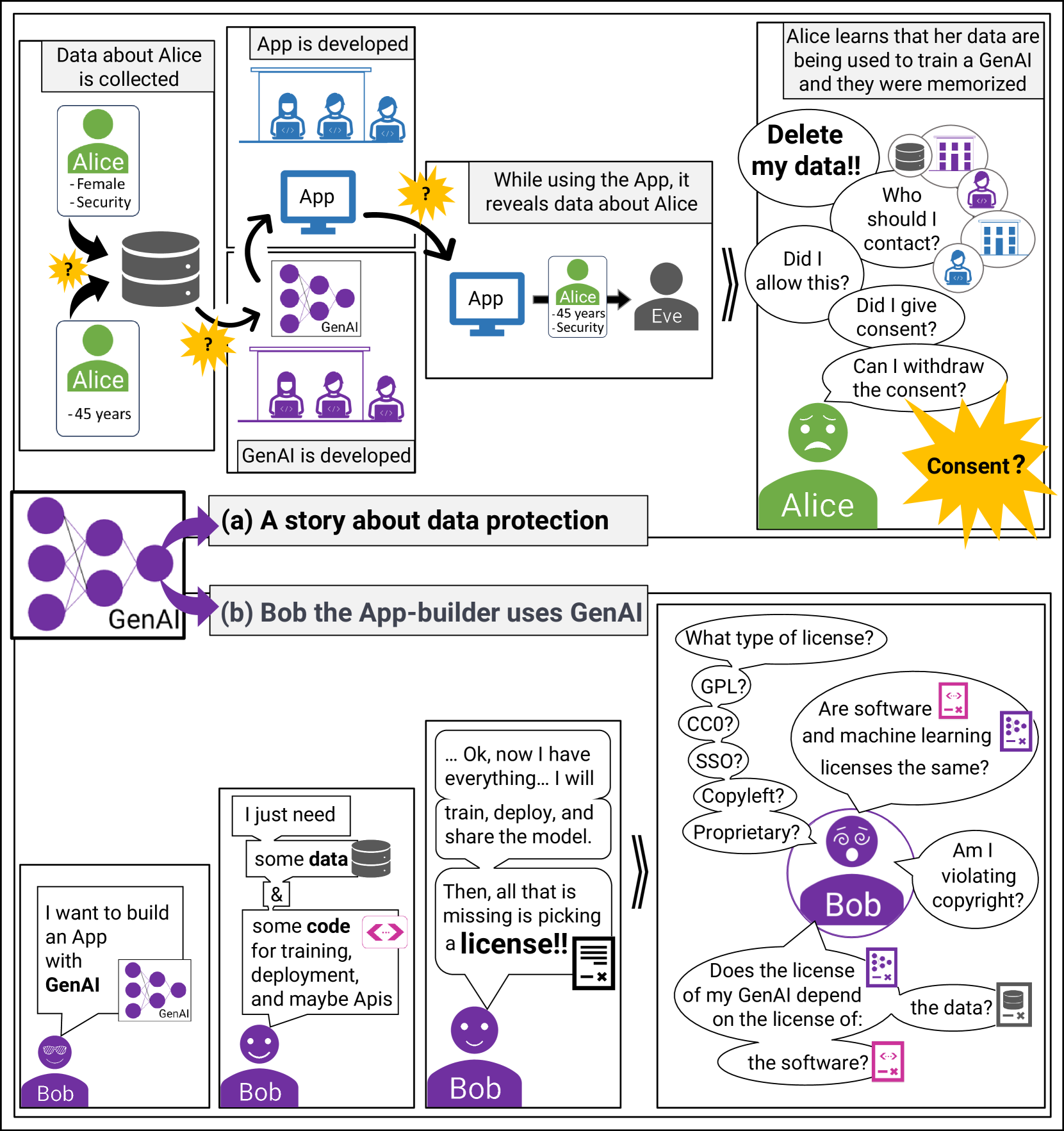
Legal Aspects for Software Developers Interested in Generative AI Applications
Steffen Herbold, Brian Valerius, Anamaria Mojica-Hanke, Isabella Lex, Joel Mittel

0
0
Recent successes in Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) have led to new technologies capable of generating high-quality code, natural language, and images. The next step is to integrate GenAI technology into products, a task typically conducted by software developers. Such product development always comes with a certain risk of liability. Within this article, we want to shed light on the current state of two such risks: data protection and copyright. Both aspects are crucial for GenAI. This technology deals with data for both model training and generated output. We summarize key aspects regarding our current knowledge that every software developer involved in product development using GenAI should be aware of to avoid critical mistakes that may expose them to liability claims.
4/26/2024

Generative AI Misuse: A Taxonomy of Tactics and Insights from Real-World Data
Nahema Marchal, Rachel Xu, Rasmi Elasmar, Iason Gabriel, Beth Goldberg, William Isaac

0
0
Generative, multimodal artificial intelligence (GenAI) offers transformative potential across industries, but its misuse poses significant risks. Prior research has shed light on the potential of advanced AI systems to be exploited for malicious purposes. However, we still lack a concrete understanding of how GenAI models are specifically exploited or abused in practice, including the tactics employed to inflict harm. In this paper, we present a taxonomy of GenAI misuse tactics, informed by existing academic literature and a qualitative analysis of approximately 200 observed incidents of misuse reported between January 2023 and March 2024. Through this analysis, we illuminate key and novel patterns in misuse during this time period, including potential motivations, strategies, and how attackers leverage and abuse system capabilities across modalities (e.g. image, text, audio, video) in the wild.
6/24/2024
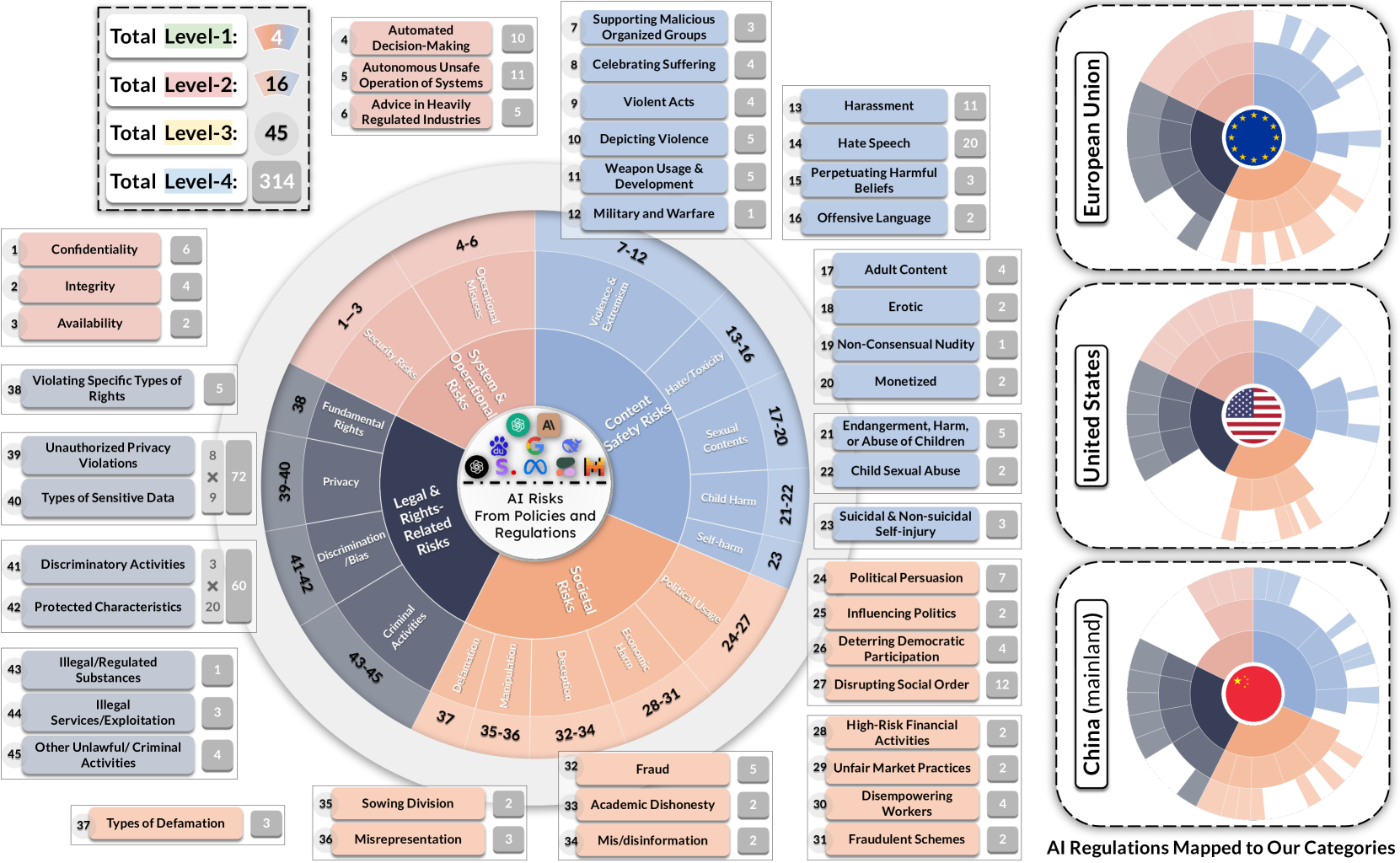
AI Risk Categorization Decoded (AIR 2024): From Government Regulations to Corporate Policies
Yi Zeng, Kevin Klyman, Andy Zhou, Yu Yang, Minzhou Pan, Ruoxi Jia, Dawn Song, Percy Liang, Bo Li

0
0
We present a comprehensive AI risk taxonomy derived from eight government policies from the European Union, United States, and China and 16 company policies worldwide, making a significant step towards establishing a unified language for generative AI safety evaluation. We identify 314 unique risk categories organized into a four-tiered taxonomy. At the highest level, this taxonomy encompasses System & Operational Risks, Content Safety Risks, Societal Risks, and Legal & Rights Risks. The taxonomy establishes connections between various descriptions and approaches to risk, highlighting the overlaps and discrepancies between public and private sector conceptions of risk. By providing this unified framework, we aim to advance AI safety through information sharing across sectors and the promotion of best practices in risk mitigation for generative AI models and systems.
6/27/2024
🤖
Generative AI Models: Opportunities and Risks for Industry and Authorities
Tobias Alt, Andrea Ibisch, Clemens Meiser, Anna Wilhelm, Raphael Zimmer, Christian Berghoff, Christoph Droste, Jens Karschau, Friederike Laus, Rainer Plaga, Carola Plesch, Britta Sennewald, Thomas Thaeren, Kristina Unverricht, Steffen Waurick

0
0
Generative AI models are capable of performing a wide range of tasks that traditionally require creativity and human understanding. They learn patterns from existing data during training and can subsequently generate new content such as texts, images, and music that follow these patterns. Due to their versatility and generally high-quality results, they, on the one hand, represent an opportunity for digitalization. On the other hand, the use of generative AI models introduces novel IT security risks that need to be considered for a comprehensive analysis of the threat landscape in relation to IT security. In response to this risk potential, companies or authorities using them should conduct an individual risk analysis before integrating generative AI into their workflows. The same applies to developers and operators, as many risks in the context of generative AI have to be taken into account at the time of development or can only be influenced by the operating company. Based on this, existing security measures can be adjusted, and additional measures can be taken.
6/10/2024