Lung-CADex: Fully automatic Zero-Shot Detection and Classification of Lung Nodules in Thoracic CT Images

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
• This paper discusses the use of BibTeX, a widely adopted bibliography management system, in the context of academic writing and publishing. • BibTeX is a software tool that helps researchers organize and format their bibliographic references, making it easier to create and manage citations within their documents. • The paper covers the key features and capabilities of BibTeX, as well as its integration with various text editors and document preparation systems.
Plain English Explanation
BibTeX is a tool that makes it easier for researchers to keep track of the books, articles, and other sources they use in their work. When you're writing a research paper, you often need to include a list of all the references you used, and BibTeX helps you create and manage that list.
Here's how it works: you create a BibTeX file that contains all the details about the sources you've used, like the author's name, the title of the work, the publication date, and so on. Then, when you're writing your paper, you can easily insert citations to those sources using special BibTeX commands. BibTeX will automatically format the citations and the reference list at the end of your paper, saving you a lot of time and effort.
BibTeX is especially useful for researchers who work on complex projects with lots of references, or who need to use a specific citation style (like APA or MLA). By using BibTeX, they can focus on the content of their work without getting bogged down in the nitty-gritty of citation formatting.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of BibTeX, a widely used bibliography management system. BibTeX is a software tool that helps researchers organize and format their bibliographic references, making it easier to create and manage citations within their documents.
The paper discusses the key features and capabilities of BibTeX, including its ability to store bibliographic information in a structured format, its integration with various text editors and document preparation systems (such as LaTeX), and its support for a wide range of citation styles.
The paper also covers the process of creating and managing BibTeX databases, which involve defining different types of bibliographic entries (e.g., journal articles, books, conference proceedings) and specifying the relevant metadata for each entry. The paper explains how BibTeX users can then reference these entries within their documents using special citation commands, and how BibTeX automatically generates the formatted reference list at the end of the document.
Additionally, the paper discusses the advantages of using BibTeX, such as its ability to ensure consistency in citation formatting, its support for collaborative work, and its integration with other tools and workflows commonly used in academic research.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-structured overview of BibTeX, highlighting its key features and benefits for academic researchers. However, the paper does not delve into some potential limitations or challenges associated with the use of BibTeX.
For example, the paper does not discuss the difficulty of maintaining and updating large BibTeX databases, particularly when dealing with a large number of sources or when collaborating with other researchers. The paper also does not address the potential learning curve for researchers unfamiliar with BibTeX, or the challenges of integrating BibTeX with certain document preparation systems or citation management tools.
Furthermore, the paper does not explore any emerging alternatives or complementary tools that may be used in conjunction with BibTeX, such as web-based citation managers or reference management software. Discussing these developments and their implications for the future of bibliography management could have provided a more comprehensive and forward-looking perspective.
Conclusion
The paper provides a detailed and informative overview of BibTeX, a widely adopted bibliography management system used by academic researchers. BibTeX offers a powerful and efficient way to organize, format, and manage bibliographic references, helping researchers focus on the content of their work rather than the intricacies of citation formatting.
While the paper does not address all potential limitations or challenges associated with BibTeX, it successfully highlights the key features and benefits of the system, making it a valuable resource for both novice and experienced researchers looking to improve their bibliography management practices.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
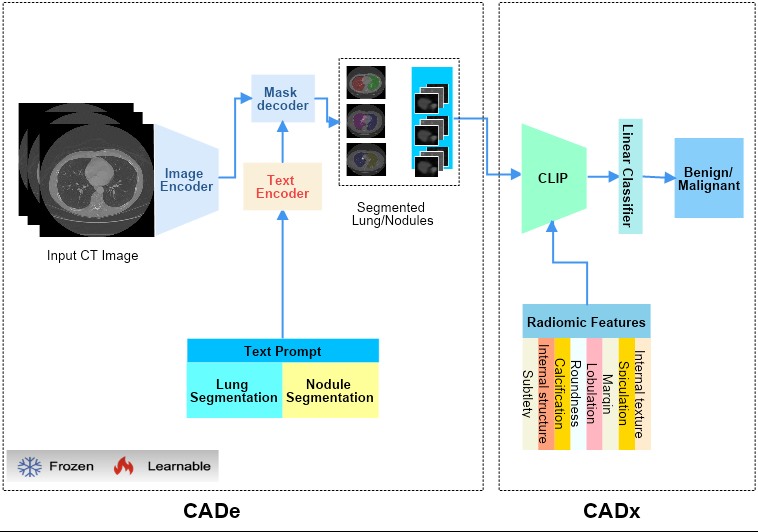
Lung-CADex: Fully automatic Zero-Shot Detection and Classification of Lung Nodules in Thoracic CT Images
Furqan Shaukat, Syed Muhammad Anwar, Abhijeet Parida, Van Khanh Lam, Marius George Linguraru, Mubarak Shah
Lung cancer has been one of the major threats to human life for decades. Computer-aided diagnosis can help with early lung nodul detection and facilitate subsequent nodule characterization. Large Visual Language models (VLMs) have been found effective for multiple downstream medical tasks that rely on both imaging and text data. However, lesion level detection and subsequent diagnosis using VLMs have not been explored yet. We propose CADe, for segmenting lung nodules in a zero-shot manner using a variant of the Segment Anything Model called MedSAM. CADe trains on a prompt suite on input computed tomography (CT) scans by using the CLIP text encoder through prefix tuning. We also propose, CADx, a method for the nodule characterization as benign/malignant by making a gallery of radiomic features and aligning image-feature pairs through contrastive learning. Training and validation of CADe and CADx have been done using one of the largest publicly available datasets, called LIDC. To check the generalization ability of the model, it is also evaluated on a challenging dataset, LUNGx. Our experimental results show that the proposed methods achieve a sensitivity of 0.86 compared to 0.76 that of other fully supervised methods.The source code, datasets and pre-processed data can be accessed using the link:
Read more7/4/2024

0
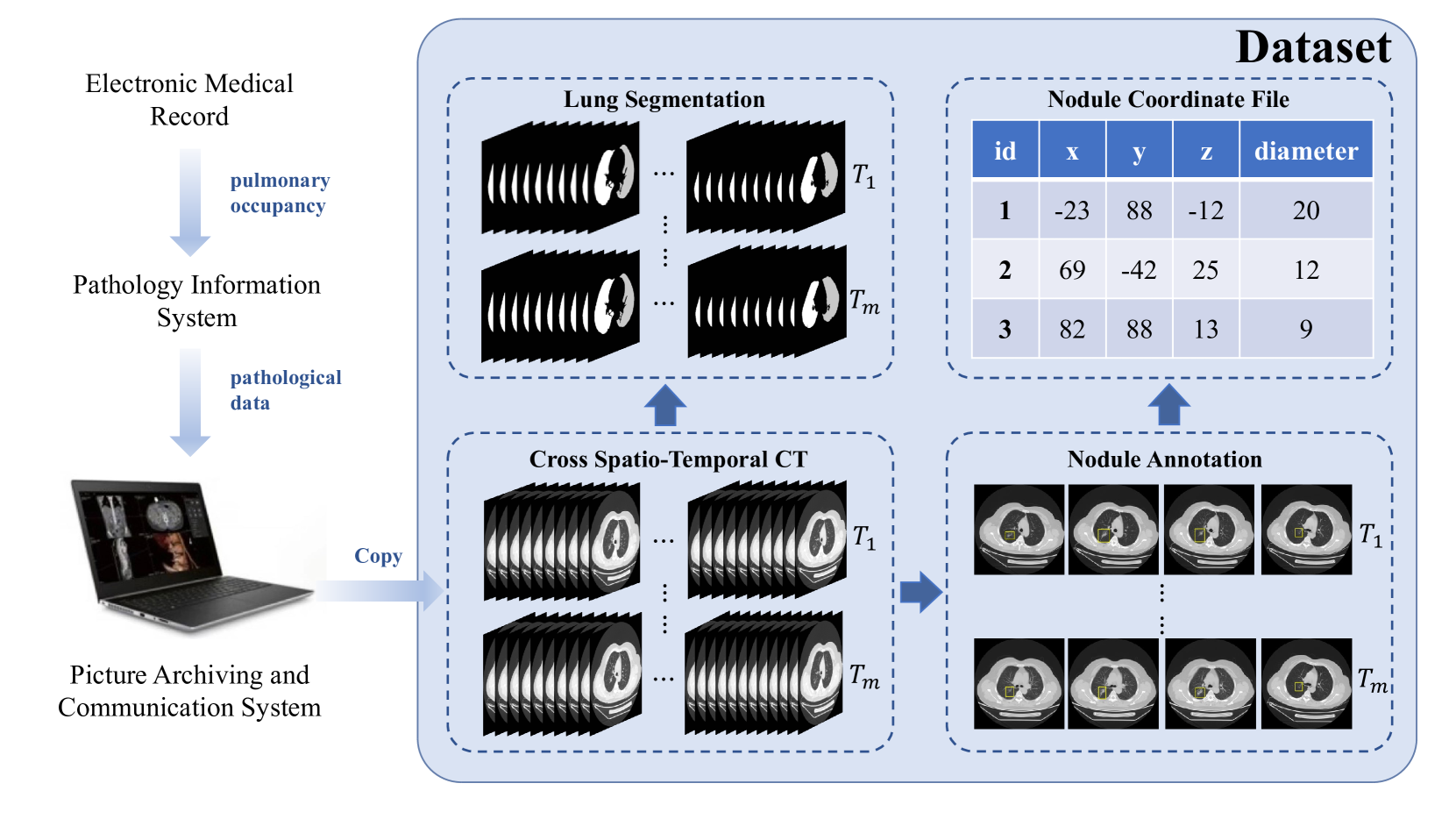
A Cross Spatio-Temporal Pathology-based Lung Nodule Dataset
Muwei Jian, Haoran Zhang, Mingju Shao, Hongyu Chen, Huihui Huang, Yanjie Zhong, Changlei Zhang, Bin Wang, Penghui Gao
Recently, intelligent analysis of lung nodules with the assistant of computer aided detection (CAD) techniques can improve the accuracy rate of lung cancer diagnosis. However, existing CAD systems and pulmonary datasets mainly focus on Computed Tomography (CT) images from one single period, while ignoring the cross spatio-temporal features associated with the progression of nodules contained in imaging data from various captured periods of lung cancer. If the evolution patterns of nodules across various periods in the patients' CT sequences can be explored, it will play a crucial role in guiding the precise screening identification of lung cancer. Therefore, a cross spatio-temporal lung nodule dataset with pathological information for nodule identification and diagnosis is constructed, which contains 328 CT sequences and 362 annotated nodules from 109 patients. This comprehensive database is intended to drive research in the field of CAD towards more practical and robust methods, and also contribute to the further exploration of precision medicine related field. To ensure patient confidentiality, we have removed sensitive information from the dataset.
Read more6/27/2024
➖

0
A Lung Nodule Dataset with Histopathology-based Cancer Type Annotation
Muwei Jian, Hongyu Chen, Zaiyong Zhang, Nan Yang, Haorang Zhang, Lifu Ma, Wenjing Xu, Huixiang Zhi
Recently, Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) systems have emerged as indispensable tools in clinical diagnostic workflows, significantly alleviating the burden on radiologists. Nevertheless, despite their integration into clinical settings, CAD systems encounter limitations. Specifically, while CAD systems can achieve high performance in the detection of lung nodules, they face challenges in accurately predicting multiple cancer types. This limitation can be attributed to the scarcity of publicly available datasets annotated with expert-level cancer type information. This research aims to bridge this gap by providing publicly accessible datasets and reliable tools for medical diagnosis, facilitating a finer categorization of different types of lung diseases so as to offer precise treatment recommendations. To achieve this objective, we curated a diverse dataset of lung Computed Tomography (CT) images, comprising 330 annotated nodules (nodules are labeled as bounding boxes) from 95 distinct patients. The quality of the dataset was evaluated using a variety of classical classification and detection models, and these promising results demonstrate that the dataset has a feasible application and further facilitate intelligent auxiliary diagnosis.
Read more6/27/2024
🤿

0
Application of Computer Deep Learning Model in Diagnosis of Pulmonary Nodules
Yutian Yang (University of California, Davis), Hongjie Qiu (University of Washington), Yulu Gong (Northern Arizona University), Xiaoyi Liu (Arizona State University), Yang Lin (University of Pennsylvania), Muqing Li (University of California San Diego)
The 3D simulation model of the lung was established by using the reconstruction method. A computer aided pulmonary nodule detection model was constructed. The process iterates over the images to refine the lung nodule recognition model based on neural networks. It is integrated with 3D virtual modeling technology to improve the interactivity of the system, so as to achieve intelligent recognition of lung nodules. A 3D RCNN (Region-based Convolutional Neural Network) was utilized for feature extraction and nodule identification. The LUNA16 large sample database was used as the research dataset. FROC (Free-response Receiver Operating Characteristic) analysis was applied to evaluate the model, calculating sensitivity at various false positive rates to derive the average FROC. Compared with conventional diagnostic methods, the recognition rate was significantly improved. This technique facilitates the detection of pulmonary abnormalities at an initial phase, which holds immense value for the prompt diagnosis of lung malignancies.
Read more6/21/2024