More Questions than Answers? Lessons from Integrating Explainable AI into a Cyber-AI Tool

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
More Questions than Answers? Lessons from Integrating Explainable AI into a Cyber-AI Tool
Ashley Suh, Harry Li, Caitlin Kenney, Kenneth Alperin, Steven R. Gomez
We share observations and challenges from an ongoing effort to implement Explainable AI (XAI) in a domain-specific workflow for cybersecurity analysts. Specifically, we briefly describe a preliminary case study on the use of XAI for source code classification, where accurate assessment and timeliness are paramount. We find that the outputs of state-of-the-art saliency explanation techniques (e.g., SHAP or LIME) are lost in translation when interpreted by people with little AI expertise, despite these techniques being marketed for non-technical users. Moreover, we find that popular XAI techniques offer fewer insights for real-time human-AI workflows when they are post hoc and too localized in their explanations. Instead, we observe that cyber analysts need higher-level, easy-to-digest explanations that can offer as little disruption as possible to their workflows. We outline unaddressed gaps in practical and effective XAI, then touch on how emerging technologies like Large Language Models (LLMs) could mitigate these existing obstacles.
Read more8/12/2024


0
The future of human-centric eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) is not post-hoc explanations
Vinitra Swamy, Jibril Frej, Tanja Kaser
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) plays a crucial role in enabling human understanding and trust in deep learning systems. As models get larger, more ubiquitous, and pervasive in aspects of daily life, explainability is necessary to minimize adverse effects of model mistakes. Unfortunately, current approaches in human-centric XAI (e.g. predictive tasks in healthcare, education, or personalized ads) tend to rely on a single post-hoc explainer, whereas recent work has identified systematic disagreement between post-hoc explainers when applied to the same instances of underlying black-box models. In this paper, we therefore present a call for action to address the limitations of current state-of-the-art explainers. We propose a shift from post-hoc explainability to designing interpretable neural network architectures. We identify five needs of human-centric XAI (real-time, accurate, actionable, human-interpretable, and consistent) and propose two schemes for interpretable-by-design neural network workflows (adaptive routing with InterpretCC and temporal diagnostics with I2MD). We postulate that the future of human-centric XAI is neither in explaining black-boxes nor in reverting to traditional, interpretable models, but in neural networks that are intrinsically interpretable.
Read more5/29/2024

0
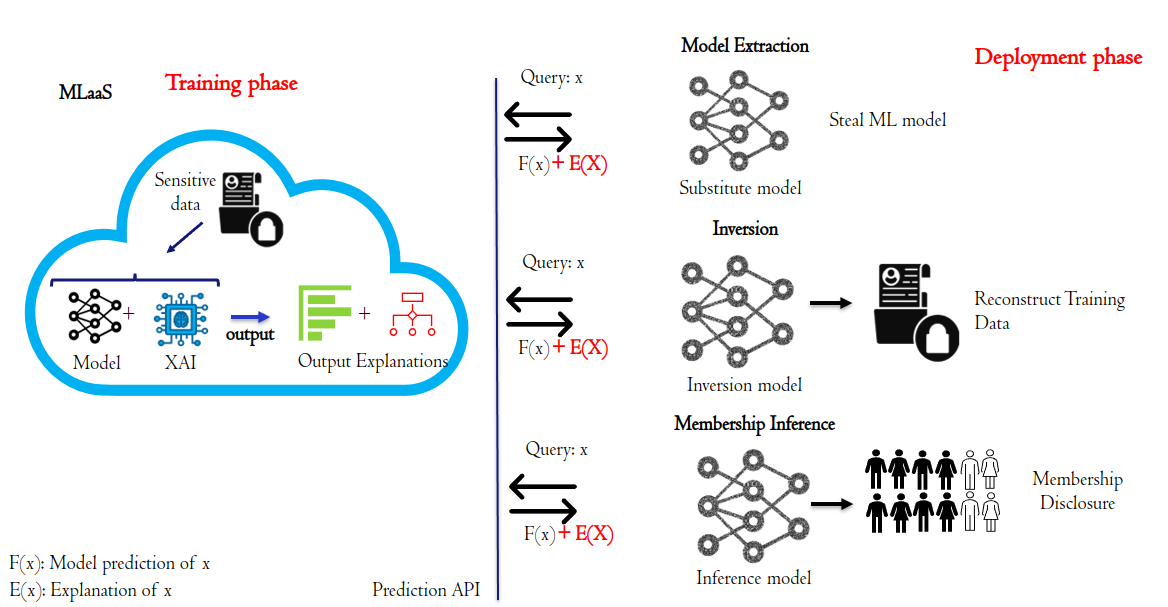
Privacy Implications of Explainable AI in Data-Driven Systems
Fatima Ezzeddine
Machine learning (ML) models, demonstrably powerful, suffer from a lack of interpretability. The absence of transparency, often referred to as the black box nature of ML models, undermines trust and urges the need for efforts to enhance their explainability. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques address this challenge by providing frameworks and methods to explain the internal decision-making processes of these complex models. Techniques like Counterfactual Explanations (CF) and Feature Importance play a crucial role in achieving this goal. Furthermore, high-quality and diverse data remains the foundational element for robust and trustworthy ML applications. In many applications, the data used to train ML and XAI explainers contain sensitive information. In this context, numerous privacy-preserving techniques can be employed to safeguard sensitive information in the data, such as differential privacy. Subsequently, a conflict between XAI and privacy solutions emerges due to their opposing goals. Since XAI techniques provide reasoning for the model behavior, they reveal information relative to ML models, such as their decision boundaries, the values of features, or the gradients of deep learning models when explanations are exposed to a third entity. Attackers can initiate privacy breaching attacks using these explanations, to perform model extraction, inference, and membership attacks. This dilemma underscores the challenge of finding the right equilibrium between understanding ML decision-making and safeguarding privacy.
Read more6/26/2024


0
Explainable Artificial Intelligence: A Survey of Needs, Techniques, Applications, and Future Direction
Melkamu Mersha, Khang Lam, Joseph Wood, Ali AlShami, Jugal Kalita
Artificial intelligence models encounter significant challenges due to their black-box nature, particularly in safety-critical domains such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) addresses these challenges by providing explanations for how these models make decisions and predictions, ensuring transparency, accountability, and fairness. Existing studies have examined the fundamental concepts of XAI, its general principles, and the scope of XAI techniques. However, there remains a gap in the literature as there are no comprehensive reviews that delve into the detailed mathematical representations, design methodologies of XAI models, and other associated aspects. This paper provides a comprehensive literature review encompassing common terminologies and definitions, the need for XAI, beneficiaries of XAI, a taxonomy of XAI methods, and the application of XAI methods in different application areas. The survey is aimed at XAI researchers, XAI practitioners, AI model developers, and XAI beneficiaries who are interested in enhancing the trustworthiness, transparency, accountability, and fairness of their AI models.
Read more9/4/2024