Multi-Robot System Architecture design in SysML and BPMN

0
🏅
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Multi-Robot Systems (MRS) are complex systems with many software and hardware components.
- The main problem addressed is the complexity of designing MRS.
- The proposed solution uses a modular modeling and simulation approach based on formal system engineering methods.
- This decomposition and reduction of MRS design complexity is achieved through the use of two Architecture Description Languages (ADLs): Systems Modeling Language (SysML) and Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN).
- The simulation is implemented in the Java Agent Development (JADE) middleware.
Plain English Explanation
Designing complex Multi-Robot Systems (MRS) can be a challenging task due to the large number of software and hardware components involved. The researchers propose a solution that breaks down the design process into more manageable pieces.
They use two formal modeling languages, SysML and BPMN, to create detailed blueprints of the MRS. This allows them to design the system in an abstract, technology-agnostic way, making it easier to transfer the design to different programming languages or platforms.
To test the proposed MRS design, the researchers simulate it in a multi-agent environment using the JADE middleware. This simulation helps them analyze and verify the performance of the MRS model before actually building it.
By using this modular modeling and simulation approach, the researchers aim to reduce the overall complexity of designing MRS, making it easier for engineers to create these sophisticated robotic systems.
Technical Explanation
The researchers address the design complexity of Multi-Robot Systems (MRS) by proposing a modular modeling and simulation technique based on formal system engineering methods.
To model the MRS, they use two Architecture Description Languages (ADLs): Systems Modeling Language (SysML) and Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). These abstract design languages allow the researchers to create system blueprints that are technology-agnostic, enabling the design to be easily transferred between different programming languages or platforms.
To simulate the MRS, the researchers implement the system in a multi-agent environment using the Java Agent Development (JADE) middleware. The simulation results can then be used to analyze and verify the proposed MRS model through performance evaluation.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to addressing the design complexity of Multi-Robot Systems (MRS). By using formal modeling languages and simulation, the researchers are able to decompose the problem and create a more modular, technology-agnostic design.
However, the paper does not provide much detail on the actual implementation or evaluation of the proposed solution. It would be helpful to see more information on the specific modeling and simulation techniques used, as well as the results of the performance analysis.
Additionally, the paper does not address potential limitations or areas for further research. It would be useful to understand the scope and boundaries of the proposed approach, as well as any challenges or tradeoffs that may arise in real-world deployment of MRS.
Overall, the paper presents an interesting and potentially valuable technique for managing the complexity of MRS design, but more empirical evidence and critical analysis would strengthen the claims and implications.
Conclusion
This paper introduces a modular modeling and simulation approach to address the design complexity of Multi-Robot Systems (MRS). By using formal Architecture Description Languages (ADLs) like SysML and BPMN, the researchers are able to create technology-agnostic system blueprints. These blueprints are then simulated in a multi-agent environment using the JADE middleware to analyze and verify the proposed MRS model.
This innovative approach has the potential to significantly reduce the complexity of designing MRS, making it easier for engineers to develop these sophisticated robotic systems. While the paper lacks some details on the specific implementation and evaluation, it presents an interesting and valuable contribution to the field of multi-robot systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🏅

0
Multi-Robot System Architecture design in SysML and BPMN
Ahmed R. Sadik (Honda Research Institute Europe, Offenbach am Main, Germany), Christian Goerick (Honda Research Institute Europe, Offenbach am Main, Germany)
Multi-Robot System (MRS) is a complex system that contains many different software and hardware components. This main problem addressed in this article is the MRS design complexity. The proposed solution provides a modular modeling and simulation technique that is based on formal system engineering method, therefore the MRS design complexity is decomposed and reduced. Modeling the MRS has been achieved via two formal Architecture Description Languages (ADLs), which are Systems Modeling Language (SysML) and Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN), to design the system blueprints. By using those abstract design ADLs, the implementation of the project becomes technology agnostic. This allows to transfer the design concept from on programming language to another. During the simulation phase, a multi-agent environment is used to simulate the MRS blueprints. The simulation has been implemented in Java Agent Development (JADE) middleware. Therefore, its results can be used to analysis and verify the proposed MRS model in form of performance evaluation matrix.
Read more7/29/2024


0
State-of-the-art in Robot Learning for Multi-Robot Collaboration: A Comprehensive Survey
Bin Wu, C Steve Suh
With the continuous breakthroughs in core technology, the dawn of large-scale integration of robotic systems into daily human life is on the horizon. Multi-robot systems (MRS) built on this foundation are undergoing drastic evolution. The fusion of artificial intelligence technology with robot hardware is seeing broad application possibilities for MRS. This article surveys the state-of-the-art of robot learning in the context of Multi-Robot Cooperation (MRC) of recent. Commonly adopted robot learning methods (or frameworks) that are inspired by humans and animals are reviewed and their advantages and disadvantages are discussed along with the associated technical challenges. The potential trends of robot learning and MRS integration exploiting the merging of these methods with real-world applications is also discussed at length. Specifically statistical methods are used to quantitatively corroborate the ideas elaborated in the article.
Read more8/23/2024

0
Hierarchically Decentralized Heterogeneous Multi-Robot Task Allocation System
Sujeet Kashid, Ashwin D. Kumat
With plans to send humans to the Moon and further, the supply of resources like oxygen, water, fuel, etc., can be satiated by performing In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU), where resources from the extra-terrestrial body are extracted to be utilized. These ISRU missions can be carried out by a Multi-Robot System (MRS). In this research, a high-level auction- based Multi-Robot Task Allocation (MRTA) system is developed for coordinating tasks amongst multiple robots with distinct capabilities. A hierarchical decentralized coordination architecture is implemented in this research to allocate the tasks amongst the robots for achieving intentional cooperation in the Multi-Robot System (MRS). 3 different policies are formulated that govern how robots should act in the multiple auction situations of the auction-based task allocation system proposed in this research, and their performance is evaluated in a 2D simulation called pyrobosim using ROS2. The decentralized coordination architecture and the auction-based MRTA make the MRS highly scalable, reliable, flexible, and robust.
Read more5/7/2024
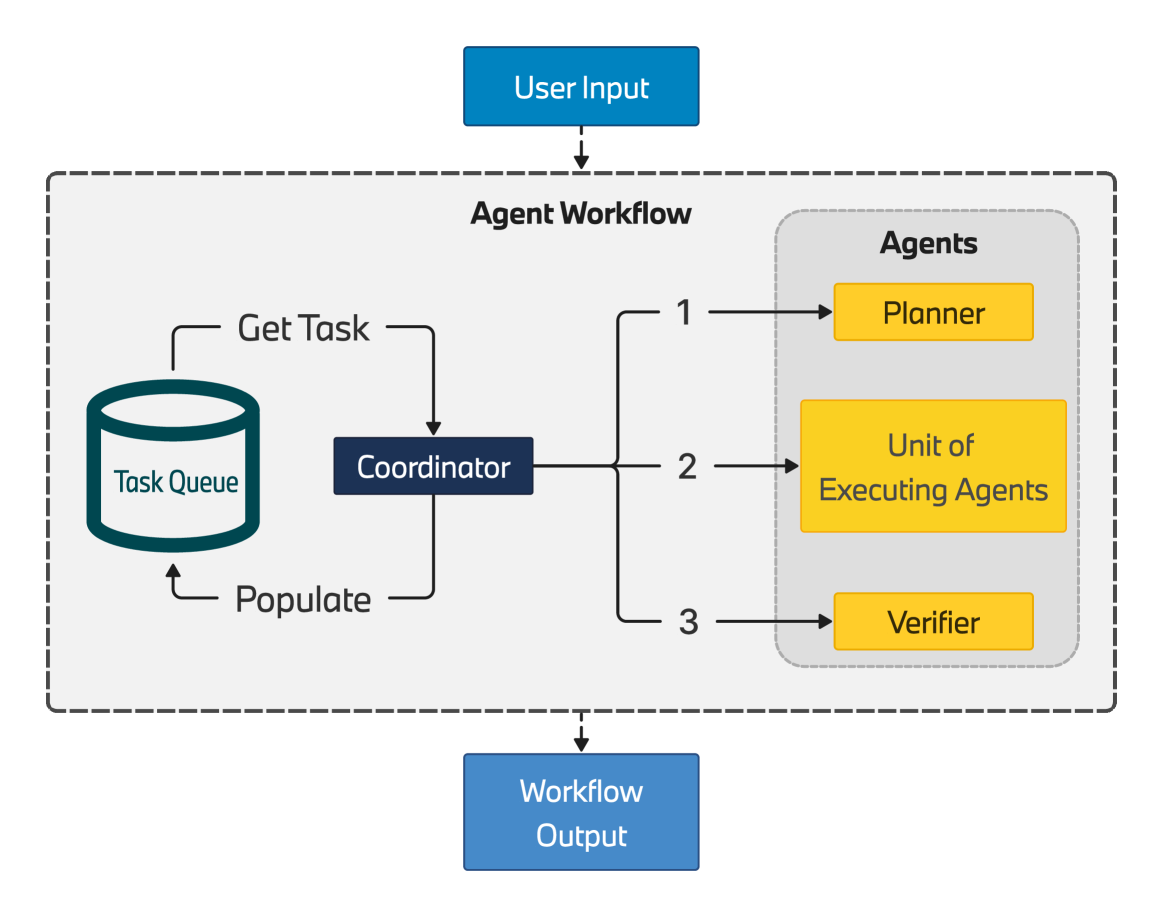

0
BMW Agents -- A Framework For Task Automation Through Multi-agent Collaboration
Noel Crawford, Edward B. Duffy, Iman Evazzade, Torsten Foehr, Gregory Robbins, Debbrata Kumar Saha, Jiya Varma, Marcin Ziolkowski
Autonomous agents driven by Large Language Models (LLMs) offer enormous potential for automation. Early proof of this technology can be found in various demonstrations of agents solving complex tasks, interacting with external systems to augment their knowledge, and triggering actions. In particular, workflows involving multiple agents solving complex tasks in a collaborative fashion exemplify their capacity to operate in less strict and less well-defined environments. Thus, a multi-agent approach has great potential for serving as a backbone in many industrial applications, ranging from complex knowledge retrieval systems to next generation robotic process automation. Given the reasoning abilities within the current generation of LLMs, complex processes require a multi-step approach that includes a plan of well-defined and modular tasks. Depending on the level of complexity, these tasks can be executed either by a single agent or a group of agents. In this work, we focus on designing a flexible agent engineering framework with careful attention to planning and execution, capable of handling complex use case applications across various domains. The proposed framework provides reliability in industrial applications and presents techniques to ensure a scalable, flexible, and collaborative workflow for multiple autonomous agents working together towards solving tasks.
Read more7/2/2024