Neural Implicit Morphing of Face Images

0
🧠
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Face morphing is a problem in computer graphics with many artistic and forensic applications.
- It is challenging due to variations in pose, lighting, gender, and ethnicity.
- The task involves warping to align features and blending for a seamless transition between warped images.
- The authors propose using coordinate-based neural networks to represent these warpings and blendings.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a technique called "face morphing," which is the process of smoothly transitioning between two different facial images. This can be useful for artistic applications as well as forensic applications, such as identifying suspects.
The challenge with face morphing is that the two faces can vary in many ways, like their pose, lighting, gender, and ethnicity. To address this, the authors suggest using a special type of neural network called a "coordinate-based neural network" to handle the warping (aligning the facial features) and blending (smoothly transitioning between the two images).
The key advantage of this approach is that it allows for a continuous, time-dependent warping/blending process, rather than just a single, static result. This means the transition between the two faces can be shown as a smooth animation.
Technical Explanation
The authors propose using coordinate-based neural networks to represent the warping and blending operations required for face morphing. During training, they combine energy functionals used in classical approaches without the need for discretizations, taking advantage of the smoothness and flexibility of the neural network representation.
Their method is time-dependent, allowing for a continuous warping/blending of the input images. Importantly, the neural network stores both the direct and inverse transformations required for the warping, eliminating the need for explicitly inverting them.
In their experiments, the authors show that their method produces results that are competitive with both classical and generative models in terms of image quality and the ability to evade face-morphing detectors. Aesthetically, the resulting images present a seamless blending of diverse faces, which is a novel contribution compared to previous work.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel and interesting approach to the challenge of face morphing, leveraging the power of coordinate-based neural networks. However, the authors do not deeply explore the limitations or potential issues with their method.
For example, the paper does not address the potential for bias or artifacts in the generated images, which could be a concern, especially for forensic applications. Additionally, the authors do not discuss the computational complexity or real-time performance of their approach, which could be important factors for certain use cases.
Readers may also want to know more about the specific neural network architecture and training process used, as well as how the method compares to other state-of-the-art 3D facial animation techniques in terms of quality and flexibility.
Conclusion
The proposed coordinate-based neural network approach to face morphing is a promising and novel contribution to the field of computer graphics. The ability to represent continuous, time-dependent warping and blending of faces could have significant implications for both artistic and forensic applications.
While the paper demonstrates the technical feasibility of this approach, further research is needed to address potential issues around bias, artifacts, and performance. Overall, this work represents an exciting step forward in the quest to create high-quality, controllable facial animations that can seamlessly blend diverse facial features.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🧠

0
Neural Implicit Morphing of Face Images
Guilherme Schardong, Tiago Novello, Hallison Paz, Iurii Medvedev, Vin'icius da Silva, Luiz Velho, Nuno Gonc{c}alves
Face morphing is a problem in computer graphics with numerous artistic and forensic applications. It is challenging due to variations in pose, lighting, gender, and ethnicity. This task consists of a warping for feature alignment and a blending for a seamless transition between the warped images. We propose to leverage coord-based neural networks to represent such warpings and blendings of face images. During training, we exploit the smoothness and flexibility of such networks by combining energy functionals employed in classical approaches without discretizations. Additionally, our method is time-dependent, allowing a continuous warping/blending of the images. During morphing inference, we need both direct and inverse transformations of the time-dependent warping. The first (second) is responsible for warping the target (source) image into the source (target) image. Our neural warping stores those maps in a single network dismissing the need for inverting them. The results of our experiments indicate that our method is competitive with both classical and generative models under the lens of image quality and face-morphing detectors. Aesthetically, the resulting images present a seamless blending of diverse faces not yet usual in the literature.
Read more6/17/2024
🛠️

0
Leveraging Diffusion For Strong and High Quality Face Morphing Attacks
Zander W. Blasingame, Chen Liu
Face morphing attacks seek to deceive a Face Recognition (FR) system by presenting a morphed image consisting of the biometric qualities from two different identities with the aim of triggering a false acceptance with one of the two identities, thereby presenting a significant threat to biometric systems. The success of a morphing attack is dependent on the ability of the morphed image to represent the biometric characteristics of both identities that were used to create the image. We present a novel morphing attack that uses a Diffusion-based architecture to improve the visual fidelity of the image and the ability of the morphing attack to represent characteristics from both identities. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed attack by evaluating its visual fidelity via the Frechet Inception Distance (FID). Also, extensive experiments are conducted to measure the vulnerability of FR systems to the proposed attack. The ability of a morphing attack detector to detect the proposed attack is measured and compared against two state-of-the-art GAN-based morphing attacks along with two Landmark-based attacks. Additionally, a novel metric to measure the relative strength between different morphing attacks is introduced and evaluated.
Read more4/11/2024


0
Face Swap via Diffusion Model
Feifei Wang
This technical report presents a diffusion model based framework for face swapping between two portrait images. The basic framework consists of three components, i.e., IP-Adapter, ControlNet, and Stable Diffusion's inpainting pipeline, for face feature encoding, multi-conditional generation, and face inpainting respectively. Besides, I introduce facial guidance optimization and CodeFormer based blending to further improve the generation quality. Specifically, we engage a recent light-weighted customization method (i.e., DreamBooth-LoRA), to guarantee the identity consistency by 1) using a rare identifier sks to represent the source identity, and 2) injecting the image features of source portrait into each cross-attention layer like the text features. Then I resort to the strong inpainting ability of Stable Diffusion, and utilize canny image and face detection annotation of the target portrait as the conditions, to guide ContorlNet's generation and align source portrait with the target portrait. To further correct face alignment, we add the facial guidance loss to optimize the text embedding during the sample generation. The code is available at: https://github.com/somuchtome/Faceswap
Read more5/30/2024

0
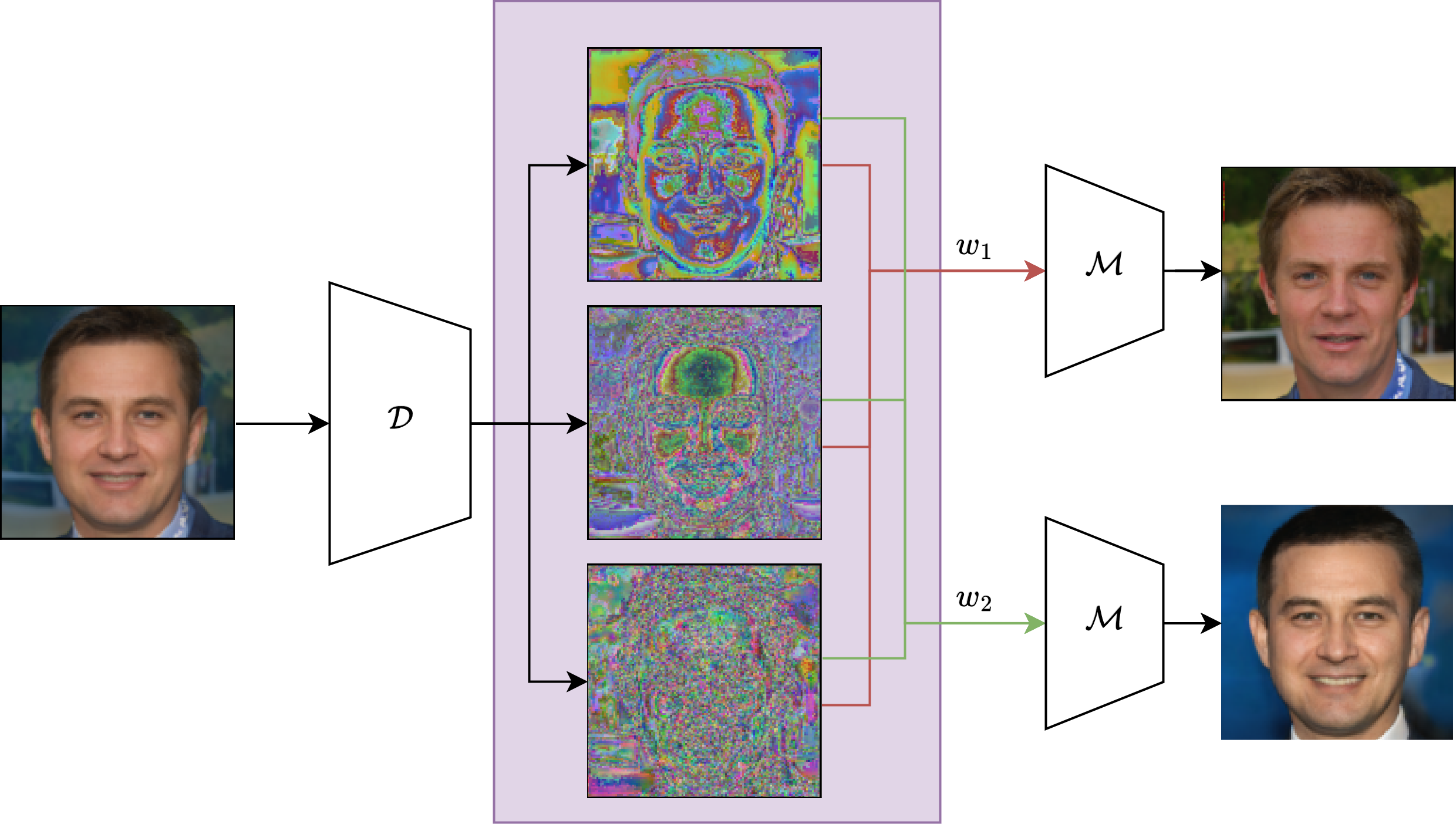
Facial Demorphing via Identity Preserving Image Decomposition
Nitish Shukla, Arun Ross
A face morph is created by combining the face images usually pertaining to two distinct identities. The goal is to generate an image that can be matched with two identities thereby undermining the security of a face recognition system. To deal with this problem, several morph attack detection techniques have been developed. But these methods do not extract any information about the underlying bonafides used to create them. Demorphing addresses this limitation. However, current demorphing techniques are mostly reference-based, i.e, they need an image of one of the identities to recover the other. In this work, we treat demorphing as an ill-posed decomposition problem. We propose a novel method that is reference-free and recovers the bonafides with high accuracy. Our method decomposes the morph into several identity-preserving feature components. A merger network then weighs and combines these components to recover the bonafides. Our method is observed to reconstruct high-quality bonafides in terms of definition and fidelity. Experiments on the CASIA-WebFace, SMDD and AMSL datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Read more8/21/2024