Optimizing Vehicular Users Association in Urban Mobile Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This research paper focuses on optimizing the association between vehicular users and mobile network infrastructure in urban environments.
- The key objectives are to improve handover management and network performance for highly mobile vehicular users.
- The approach involves developing models and algorithms to intelligently associate vehicles with the most suitable access points based on various factors.
Plain English Explanation
The paper tackles the challenge of efficiently connecting vehicles to mobile network access points in crowded urban areas. As vehicles constantly move around, the network needs to handover their connections from one access point to another to maintain connectivity.
The researchers develop sophisticated models and algorithms to optimize this user association process. Their techniques consider factors like signal strength, vehicle mobility patterns, and network congestion to intelligently match vehicles with the best access points. This helps ensure reliable, high-quality connectivity for vehicular users as they navigate the city.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework for optimizing the association of vehicular users with mobile network access points in dense urban environments. The key contributions include:
-
Mobility-aware User Association Model: The researchers develop a model that considers the unique mobility patterns of vehicular users to predict their future locations and optimize their association with access points.
-
Handover Cost Minimization: The approach aims to minimize the overhead and service disruptions caused by frequent handovers as vehicles move between coverage areas.
-
Joint Optimization of User Association and Resource Allocation: The framework jointly optimizes the user-access point association and the allocation of network resources like spectrum and transmit power.
-
Efficient Optimization Algorithm: The authors devise a low-complexity algorithm based on the Lagrangian dual decomposition method to solve the overall optimization problem.
Extensive simulations demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed techniques in improving key performance metrics like throughput, handover rate, and service continuity for vehicular users.
Critical Analysis
The research presents a well-designed and innovative solution for the challenging problem of vehicular user association in dense urban mobile networks. The consideration of user mobility patterns and the joint optimization of association and resource allocation are notable strengths.
However, the paper does not address some practical limitations, such as the availability and reliability of location data for predicting vehicle movements, or the computational overhead of the optimization algorithm in real-time deployments. Additionally, the simulations are conducted in idealized scenarios, and further validation in real-world urban environments would be beneficial.
Overall, the research provides a solid foundation for improving handover management and network performance for vehicular users, but additional work may be needed to address the practical challenges of deploying such techniques in complex urban settings.
Conclusion
This paper presents an innovative framework for optimizing the association of vehicular users with mobile network access points in dense urban environments. By considering user mobility patterns and jointly optimizing the association and resource allocation, the proposed techniques can improve key performance metrics like throughput, handover rate, and service continuity.
The research contributes valuable insights and techniques that could ultimately enhance the quality of mobile network services for highly mobile users in crowded urban areas, supporting the growing demand for reliable connectivity in smart cities and autonomous transportation systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Optimizing Vehicular Users Association in Urban Mobile Networks
Geymerson S. Ramos, Razvan Stanica, Rian G. S. Pinheiro, Andre L. L. Aquino
This study aims to optimize vehicular user association to base stations in a mobile network. We propose an efficient heuristic solution that considers the base station average handover frequency, the channel quality indicator, and bandwidth capacity. We evaluate this solution using real-world base station locations from S~ao Paulo, Brazil, and the SUMO mobility simulator. We compare our approach against a state of the art solution which uses route prediction, maintaining or surpassing the provided quality of service with the same number of handover operations. Additionally, the proposed solution reduces the execution time by more than 80% compared to an exact method, while achieving optimal solutions.
Read more9/10/2024

0
Mobile Networks on the Move: Optimizing Moving Base Stations Dynamics in Urban Scenarios
Laura Finarelli, Falko Dressler, Marco Marsan Ajmone, Gianluca Rizzo
Base station densification is one of the key approaches for delivering high capacity in radio access networks. However, current static deployments are often impractical and financially unsustainable, as they increase both capital and operational expenditures of the network. An alternative paradigm is the moving base stations (MBSs) approach, by which part of base stations are installed on vehicles. However, to the best of our knowledge, it is still unclear if and up to which point MBSs allow decreasing the number of static base stations (BSs) deployed in urban settings. In this work, we start tackling this issue by proposing a modeling approach for a first-order evaluation of potential infrastructure savings enabled by the MBSs paradigm. Starting from a set of stochastic geometry results, and a traffic demand profile over time, we formulate an optimization problem for the derivation of the optimal combination of moving and static BSs which minimizes the overall amount of BSs deployed, while guaranteeing a target mean QoS for users. Initial results on a two-district scenario with measurement-based network traffic profiles suggest that substantial infrastructure savings are achievable. We show that these results are robust against different values of user density.
Read more4/30/2024

0
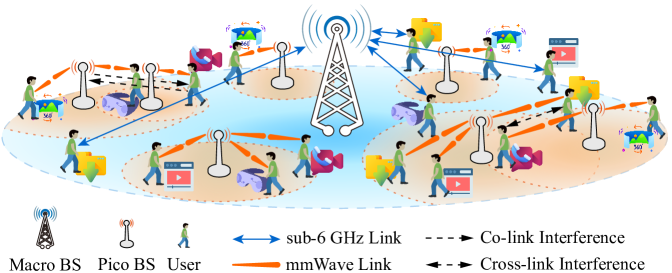
User Association and Channel Allocation in 5G Mobile Asymmetric Multi-band Heterogeneous Networks
Miao Dai, Gang Sun, Hongfang Yu, Sheng Wang, Dusit Niyato
With the proliferation of mobile terminals and the continuous upgrading of services, 4G LTE networks are showing signs of weakness. To enhance the capacity of wireless networks, millimeter waves are introduced to drive the evolution of networks towards multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks. The distinct propagation characteristics of mmWaves and microwaves, as well as the vastly different hardware configurations of heterogeneous base stations, make traditional access strategies no longer effective. Therefore, to narrowing the gap between theory and practice, we investigate the access strategy in multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks, taking into account the characteristics of mobile users, asynchronous switching between uplink and downlink of pico base stations, asymmetric service requirements, and user communication continuity. We formulate the problem as integer nonlinear programming and prove its intractability. Thereby, we decouple it into three subproblems: user association, switch point selection, and subchannel allocation, and design an algorithm based on optimal matching and spectral clustering to solve it efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in terms of overall data rate, effective data rate, and number of satisfied users.
Read more5/30/2024

0
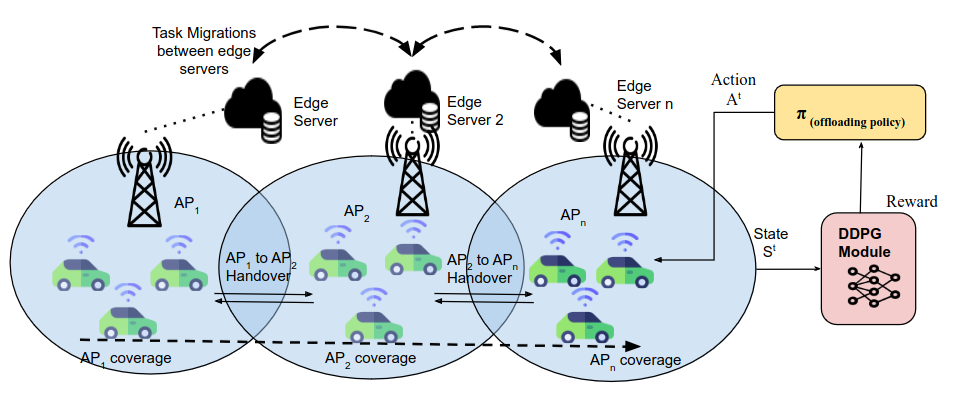
Communication-Aware Consistent Edge Selection for Mobile Users and Autonomous Vehicles
Nazish Tahir, Ramviyas Parasuraman, Haijian Sun
Offloading time-sensitive, computationally intensive tasks-such as advanced learning algorithms for autonomous driving-from vehicles to nearby edge servers, vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) systems, or other collaborating vehicles via vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication enhances service efficiency. However, whence traversing the path to the destination, the vehicle's mobility necessitates frequent handovers among the access points (APs) to maintain continuous and uninterrupted wireless connections to maintain the network's Quality of Service (QoS). These frequent handovers subsequently lead to task migrations among the edge servers associated with the respective APs. This paper addresses the joint problem of task migration and access-point handover by proposing a deep reinforcement learning framework based on the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm. A joint allocation method of communication and computation of APs is proposed to minimize computational load, service latency, and interruptions with the overarching goal of maximizing QoS. We implement and evaluate our proposed framework on simulated experiments to achieve smooth and seamless task switching among edge servers, ultimately reducing latency.
Read more8/9/2024