Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Network Instrument: Measuring PQC Adoption Rates and Identifying Migration Pathways

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a "Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Network Instrument" to measure PQC adoption rates and identify migration pathways.
- The instrument aims to help organizations and individuals understand the current state of PQC adoption and plan their migration strategies.
- The paper describes the design and implementation of the PQC Network Instrument, as well as the insights it provides into PQC adoption trends.
Plain English Explanation
The paper introduces a tool called the "Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Network Instrument" that helps track the adoption of PQC technologies. PQC refers to new types of cryptographic algorithms designed to be secure against attacks from powerful quantum computers.
The PQC Network Instrument is designed to:
- Measure PQC Adoption Rates: The tool collects data on how quickly organizations and individuals are adopting PQC technologies, such as the specific PQC algorithms they are using and the rate at which they are transitioning.
- Identify Migration Pathways: The instrument also provides insights into the different approaches organizations are taking to migrate their systems and data from traditional cryptography to PQC. This can help others plan their own migration strategies.
By using this tool, the researchers hope to give the broader community a better understanding of the current state of PQC adoption. This information can then be used to guide decisions about PQC implementation and help ensure a smooth transition to these new cryptographic standards.
Technical Explanation
The PQC Network Instrument is designed as a distributed system that collects data from various sources to track PQC adoption. It consists of the following key components:
- Data Collection Agents: These are software agents deployed on systems and networks to gather information about the cryptographic algorithms and protocols being used.
- Data Aggregation Server: This central server receives the data collected by the agents and combines it to provide a holistic view of PQC adoption.
- Visualization and Reporting Tools: The instrument includes interactive dashboards and reports that allow users to analyze the PQC adoption trends and migration pathways.
The researchers used this instrument to conduct a large-scale study of PQC adoption across different sectors and geographic regions. The results provide insights into the current state of PQC deployment, the most widely adopted PQC algorithms, and the various migration strategies being employed.
Critical Analysis
The PQC Network Instrument represents a valuable tool for tracking the adoption of these important cryptographic technologies. However, the paper does acknowledge some limitations of the instrument, such as the potential for incomplete or biased data collection due to the voluntary nature of the agent deployments.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific challenges or considerations organizations may face when migrating to PQC. Further research could explore these implementation details and provide more guidance for organizations embarking on the PQC transition.
Overall, the PQC Network Instrument is a promising step towards better understanding the adoption of post-quantum cryptography and helping the community navigate this important shift in cryptographic standards.
Conclusion
The PQC Network Instrument presented in this paper provides a valuable tool for measuring PQC adoption rates and identifying migration pathways. By collecting and analyzing data from a wide range of sources, the instrument offers insights into the current state of PQC deployment and the various strategies organizations are using to transition to these new cryptographic algorithms.
This information can help guide the broader community's efforts to ensure a smooth and secure migration to post-quantum cryptography, which is crucial as quantum computing advances and poses a threat to traditional encryption methods. The PQC Network Instrument represents an important step towards understanding and facilitating the widespread adoption of these essential cryptographic technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Network Instrument: Measuring PQC Adoption Rates and Identifying Migration Pathways
Jakub Sowa, Bach Hoang, Advaith Yeluru, Steven Qie, Anita Nikolich, Ravishankar Iyer, Phuong Cao
The problem of adopting quantum-resistant cryptographic network protocols or post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is critically important to democratizing quantum computing. The problem is urgent because practical quantum computers will break classical encryption in the next few decades. Past encrypted data has already been collected and can be decrypted in the near future. The main challenges of adopting post-quantum cryptography lie in algorithmic complexity and hardware/software/network implementation. The grand question of how existing cyberinfrastructure will support post-quantum cryptography remains unanswered. This paper describes: i) the design of a novel Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) network instrument placed at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and a part of the FABRIC testbed; ii) the latest results on PQC adoption rate across a wide spectrum of network protocols (Secure Shell -- SSH, Transport Layer Security -- TLS, etc.); iii) the current state of PQC implementation in key scientific applications (e.g., OpenSSH or SciTokens); iv) the challenges of being quantum-resistant; and v) discussion of potential novel attacks. This is the first large-scale measurement of PQC adoption at national-scale supercomputing centers and FABRIC testbeds. Our results show that only OpenSSH and Google Chrome have successfully implemented PQC and achieved an initial adoption rate of 0.029% (6,044 out of 20,556,816) for OpenSSH connections at NCSA coming from major Internet Service Providers or Autonomous Systems (ASes) such as OARNET, GTT, Google Fiber Webpass (U.S.) and Uppsala Lans Landsting (Sweden), with an overall increasing adoption rate year-over-year for 2023-2024. Our analyses identify pathways to migrate current applications to be quantum-resistant.
Read more8/2/2024

0
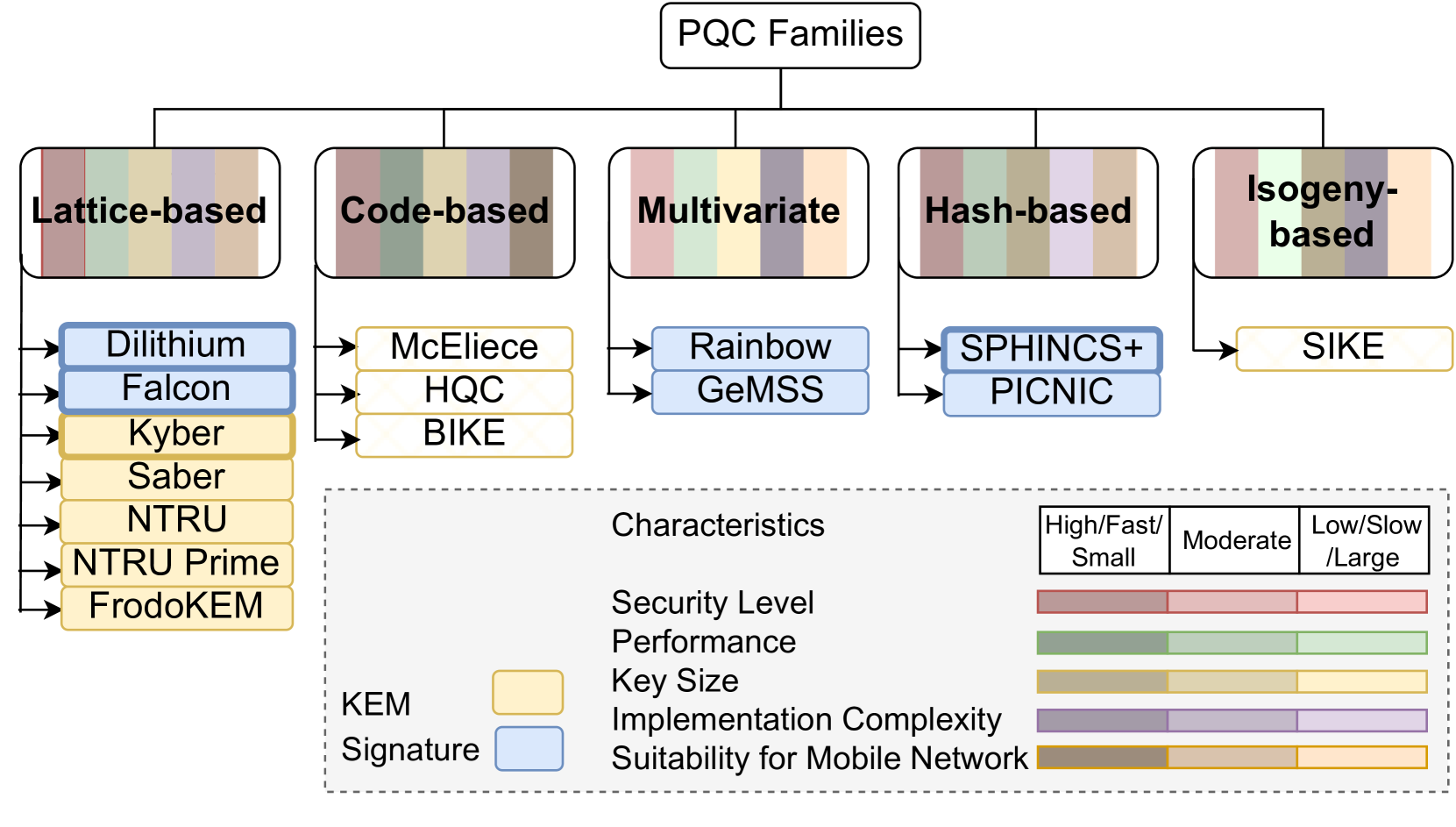
Exploring Post Quantum Cryptography with Quantum Key Distribution for Sustainable Mobile Network Architecture Design
Sanzida Hoque, Abdullah Aydeger, Engin Zeydan
The proliferation of mobile networks and their increasing importance to modern life, combined with the emerging threat of quantum computing, present new challenges and opportunities for cybersecurity. This paper addresses the complexity of protecting these critical infrastructures against future quantum attacks while considering operational sustainability. We begin with an overview of the current landscape, identify the main vulnerabilities in mobile networks, and evaluate existing security solutions with new post-quantum cryptography (PQC) methods. We then present a quantum-secure architecture with PQC and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) tailored explicitly for sustainable mobile networks and illustrate its applicability with several use cases that emphasize the need for advanced protection measures in this new era. In addition, a comprehensive analysis of PQC algorithm families is presented, focusing on their suitability for integration in mobile environments, with particular attention to the trade-offs between energy consumption and security improvements. Finally, recommendations for strengthening mobile networks against quantum threats are provided through a detailed examination of current challenges and opportunities.
Read more4/17/2024
🔮

0
Applications of Post-quantum Cryptography
Emils Bagirovs, Grigory Provodin, Tuomo Sipola, Jari Hautamaki
With the constantly advancing capabilities of quantum computers, conventional cryptographic systems relying on complex math problems may encounter unforeseen vulnerabilities. Unlike regular computers, which are often deemed cost-ineffective in cryptographic attacks, quantum computers have a significant advantage in calculation speed. This distinction potentially makes currently used algorithms less secure or even completely vulnerable, compelling the exploration of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) as the most reasonable solution to quantum threats. This review aims to provide current information on applications, benefits, and challenges associated with the PQC. The review employs a systematic scoping review with the scope restricted to the years 2022 and 2023; only articles that were published in scientific journals were used in this paper. The review examined the articles on the applications of quantum computing in various spheres. However, the scope of this paper was restricted to the domain of the PQC because most of the analyzed articles featured this field. Subsequently, the paper is analyzing various PQC algorithms, including lattice-based, hash-based, code-based, multivariate polynomial, and isogeny-based cryptography. Each algorithm is being judged based on its potential applications, robustness, and challenges. All the analyzed algorithms are promising for the post-quantum era in such applications as digital signatures, communication channels, and IoT. Moreover, some of the algorithms are already implemented in the spheres of banking transactions, communication, and intellectual property. Meanwhile, despite their potential, these algorithms face serious challenges since they lack standardization, require vast amounts of storage and computation power, and might have unknown vulnerabilities that can be discovered only with years of cryptanalysis.
Read more6/26/2024


0
Post-Quantum Secure UE-to-UE Communications
Sanzida Hoque, Abdullah Aydeger, Engin Zeydan
The rapid development of quantum computing poses a significant threat to the security of current cryptographic systems, including those used in User Equipment (UE) for mobile communications. Conventional cryptographic algorithms such as Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) and Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) are vulnerable to quantum computing attacks, which could jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data transmitted by UEs. This demo paper proposes the integration of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) in TLS for UE Communication to mitigate the risks of quantum attacks. We present our setup and explain each of the components used. We also provide the entire workflow of the demo for other researchers to replicate the same setup. By addressing the implementation of PQC within a 5G network to secure UE-to-UE communication, this research aims to pave the way for developing quantum-resistant mobile devices and securing the future of wireless communications.
Read more8/22/2024