Probabilistic Fault-Tolerant Robust Traffic Grooming in OTN-over-DWDM Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a probabilistic fault-tolerant robust traffic grooming solution for Optical Transport Network (OTN) over Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) networks.
- The authors aim to address the challenges of traffic grooming, infrastructure placement, and fault-tolerance in these types of networks.
- The proposed approach uses robust optimization techniques to account for uncertainties and provide resilience against potential failures.
Plain English Explanation
Optical Transport Networks (OTN) and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) are technologies used to transmit large amounts of data over fiber optic cables. In these networks, traffic grooming is the process of combining smaller data streams into larger ones to use network resources more efficiently.
This paper presents a new way to manage traffic grooming in OTN-over-DWDM networks that is more resilient to potential problems or failures. The researchers use a technique called "robust optimization" to account for uncertainties in the network, such as unexpected changes in traffic patterns or unexpected equipment failures.
By using this robust approach, the network can still function effectively even if some parts of the infrastructure fail or if the traffic demands change. This helps make the network more reliable and able to withstand disruptions.
Technical Explanation
The authors formulate the traffic grooming problem as a robust optimization model that considers probabilistic demands and potential network failures. They develop a two-stage stochastic programming approach, where the first stage decides the infrastructure placement and the second stage optimizes the traffic grooming.
Key aspects of the technical approach include:
- Modeling uncertainties in traffic demands using probability distributions
- Incorporating potential equipment failures and their likelihood
- Optimizing the placement of network infrastructure like transponders and multiplexers
- Determining the optimal grooming of traffic flows to minimize cost and maximize resilience
The authors evaluate their approach through simulations on realistic network topologies and traffic patterns. They compare the robust solution to a deterministic baseline and demonstrate significant improvements in cost, traffic prediction accuracy, and fault-tolerance.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and rigorous technical solution to the problem of fault-tolerant traffic grooming in OTN-over-DWDM networks. The use of robust optimization techniques to handle uncertainties is a key strength of the approach.
However, the complexity of the mathematical modeling and optimization algorithms may limit the practical deployability of the solution, especially in large-scale networks. Additionally, the paper does not address the computational complexity and scalability of the proposed methods.
Further research could explore more efficient algorithms or heuristics to improve the practicality of the solution. Validating the approach on real-world network data and assessing its performance under diverse failure scenarios would also strengthen the insights provided by this work.
Conclusion
This paper presents an innovative probabilistic fault-tolerant approach to traffic grooming in OTN-over-DWDM networks. By incorporating uncertainties in traffic demands and potential equipment failures, the proposed robust optimization solution can provide a more resilient and cost-effective network infrastructure.
The technical contributions of this work have the potential to enhance the reliability and efficiency of communication networks, which is crucial as the demand for high-bandwidth, low-latency services continues to grow. Further refinements and real-world validations could pave the way for practical deployments of this fault-tolerant traffic grooming approach.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Probabilistic Fault-Tolerant Robust Traffic Grooming in OTN-over-DWDM Networks
Dimitrios Michael Manias, Joe Naoum-Sawaya, Abbas Javadtalab, Abdallah Shami
The development of next-generation networks is revolutionizing network operators' management and orchestration practices worldwide. The critical services supported by these networks require increasingly stringent performance requirements, especially when considering the aspect of network reliability. This increase in reliability, coupled with the mass generation and consumption of information stemming from the increasing complexity of the network and the integration of artificial intelligence agents, affects transport networks, which will be required to allow the feasibility of such services to materialize. To this end, traditional recovery schemes are inadequate to ensure the resilience requirements of next-generation critical services given the increasingly dynamic nature of the network. The work presented in this paper proposes a probabilistic and fault-tolerant robust traffic grooming model for OTN-over-DWDM networks. The model's parameterization gives network operators the ability to control the level of protection and reliability required to meet their quality of service and service level agreement guarantees. The results demonstrate that the robust solution can ensure fault tolerance even in the face of demand uncertainty without service disruptions and the need for reactive network maintenance.
Read more5/24/2024


0
DRL-Assisted Dynamic QoT-Aware Service Provisioning in Multi-Band Elastic Optical Networks
Yiran Teng, Carlos Natalino, Farhad Arpanaei, Alfonso S'anchez-Maci'an, Paolo Monti, Shuangyi Yan, Dimitra Simeonidou
We propose a DRL-assisted approach for service provisioning in multi-band elastic optical networks. Our simulation environment uses an accurate QoT estimator based on the GN/EGN model. Results show that the proposed approach reduces request blocking by 50% compared with heuristics from the literature.
Read more8/7/2024
🛠️

0
Optimization of Energy Consumption in Delay-Tolerant Networks
Junran Wang, Milena Radenkovic
Delay tolerant network is a network architecture and protocol suite specifically designed to handle challenging communications environments, such as deep space communications, disaster response, and remote area communications. Although DTN [1]can provide efficient and reliable data transmission in environments with high latency, unstable connections, and high bit error rates, its energy consumption optimization problem is still a challenge, especially in scenarios with limited resources.To solve this problem, this study combines the Epidemic[2] and MaxProp[3] routing protocols with Machine Learning Models to optimize the energy consumption of DTNs. Hundreds of simulations were conducted in the ONE simulator, and an external real-world dataset from San Francisco taxi mobility traces [54] was imported. Random Forest[4] and Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM)[5] models were employed for data analysis. Through optimization involving Hyperparameter Tuning and Feature Selection, the Random Forest model achieved an R-squared value of 0.53, while the GBM model achieved an R-squared value of 0.65.
Read more6/7/2024
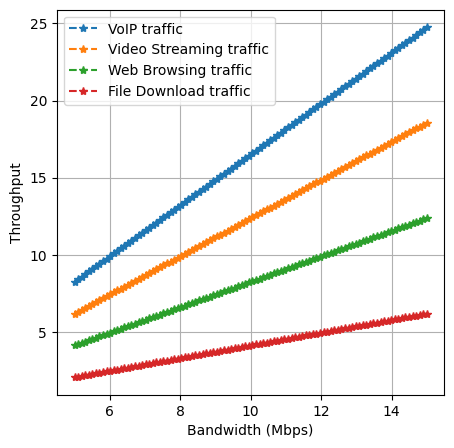

0
Maximization of Communication Network Throughput using Dynamic Traffic Allocation Scheme
Md. Arquam, Suchi Kumari
Optimizing network throughput in real-world dynamic systems is critical, especially for diverse and delay-sensitive multimedia data types such as VoIP and video streaming. Traditional routing protocols, which rely on static metrics and single shortest-path algorithms, were unable in managing this complex information. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that enhances resource utilization while maintaining Quality of Service (QoS). Our dynamic traffic allocation model prioritizes different data types based on their delay sensitivity and allocates traffic by considering factors such as bandwidth, latency, and network failures. This approach is shown to significantly improve network throughput compared to static load balancing, especially for multimedia applications. Simulation results confirm the effectiveness of this dynamic method in maximizing network throughput and maintaining QoS across various data types.
Read more9/10/2024