Psychoacoustic Challenges Of Speech Enhancement On VoIP Platforms

0
🗣️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores the psychoacoustic challenges of speech enhancement on Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) platforms
- Examines how VoIP characteristics can impact the perception and quality of enhanced speech
- Proposes an experimental design to evaluate speech enhancement algorithms in VoIP settings
Plain English Explanation
This paper investigates the psychoacoustic challenges that arise when trying to enhance speech quality on VoIP platforms. VoIP technology, which enables voice communication over the internet, can introduce various distortions and artifacts that can affect how the enhanced speech is perceived by listeners.
The researchers designed an experiment to understand how different VoIP factors, such as codec selection, packet loss, and background noise, can influence the psychoacoustic experience of users. By evaluating speech enhancement algorithms in these realistic VoIP conditions, the team aimed to identify the key challenges and provide insights for improving the user experience of speech enhancement on VoIP platforms.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes the dataset and experimental design used to assess the psychoacoustic impact of speech enhancement in VoIP settings. The researchers collected a dataset of speech samples that were processed through various VoIP conditions, such as different codec settings, packet loss rates, and background noise levels.
To evaluate the speech enhancement algorithms, the team used subjective listening tests where participants rated the quality and intelligibility of the processed speech samples. The researchers analyzed the results to understand how the VoIP factors influenced the perceptual experience of the enhanced speech.
The findings from this study provide valuable insights into the psychoacoustic challenges that must be addressed when developing speech enhancement systems for VoIP platforms. The researchers highlight the importance of considering the unique characteristics of VoIP environments to ensure that speech enhancement algorithms deliver a satisfactory user experience.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-designed experiment to investigate the psychoacoustic challenges of speech enhancement in VoIP settings. However, the researchers acknowledge that the study is limited to a specific set of VoIP conditions and may not capture the full range of real-world scenarios. Additionally, the subjective listening tests relied on human participants, which can introduce potential biases and individual differences in perception.
To further strengthen the research, the authors could consider exploring more diverse VoIP conditions, such as different network bandwidth profiles or device types. Additionally, incorporating objective speech quality metrics could provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the enhanced speech performance.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the importance of understanding the psychoacoustic factors that influence the perception of speech enhancement on VoIP platforms. By designing an experiment to evaluate the impact of VoIP characteristics on the user experience, the researchers have provided valuable insights for developers and researchers working on improving speech enhancement in VoIP environments. These findings can help drive the development of more effective and user-friendly speech enhancement solutions for VoIP applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🗣️

0
Psychoacoustic Challenges Of Speech Enhancement On VoIP Platforms
Joseph Konan, Shikhar Agnihotri, Ojas Bhargave, Shuo Han, Yunyang Zeng, Ankit Shah, Bhiksha Raj
Within the ambit of VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) telecommunications, the complexities introduced by acoustic transformations merit rigorous analysis. This research, rooted in the exploration of proprietary sender-side denoising effects, meticulously evaluates platforms such as Google Meets and Zoom. The study draws upon the Deep Noise Suppression (DNS) 2020 dataset, ensuring a structured examination tailored to various denoising settings and receiver interfaces. A methodological novelty is introduced via Blinder-Oaxaca decomposition, traditionally an econometric tool, repurposed herein to analyze acoustic-phonetic perturbations within VoIP systems. To further ground the implications of these transformations, psychoacoustic metrics, specifically PESQ and STOI, were used to explain of perceptual quality and intelligibility. Cumulatively, the insights garnered underscore the intricate landscape of VoIP-influenced acoustic dynamics. In addition to the primary findings, a multitude of metrics are reported, extending the research purview. Moreover, out-of-domain benchmarking for both time and time-frequency domain speech enhancement models is included, thereby enhancing the depth and applicability of this inquiry.
Read more8/2/2024


0
Effective Noise-aware Data Simulation for Domain-adaptive Speech Enhancement Leveraging Dynamic Stochastic Perturbation
Chien-Chun Wang, Li-Wei Chen, Hung-Shin Lee, Berlin Chen, Hsin-Min Wang
Cross-domain speech enhancement (SE) is often faced with severe challenges due to the scarcity of noise and background information in an unseen target domain, leading to a mismatch between training and test conditions. This study puts forward a novel data simulation method to address this issue, leveraging noise-extractive techniques and generative adversarial networks (GANs) with only limited target noisy speech data. Notably, our method employs a noise encoder to extract noise embeddings from target-domain data. These embeddings aptly guide the generator to synthesize utterances acoustically fitted to the target domain while authentically preserving the phonetic content of the input clean speech. Furthermore, we introduce the notion of dynamic stochastic perturbation, which can inject controlled perturbations into the noise embeddings during inference, thereby enabling the model to generalize well to unseen noise conditions. Experiments on the VoiceBank-DEMAND benchmark dataset demonstrate that our domain-adaptive SE method outperforms an existing strong baseline based on data simulation.
Read more9/4/2024
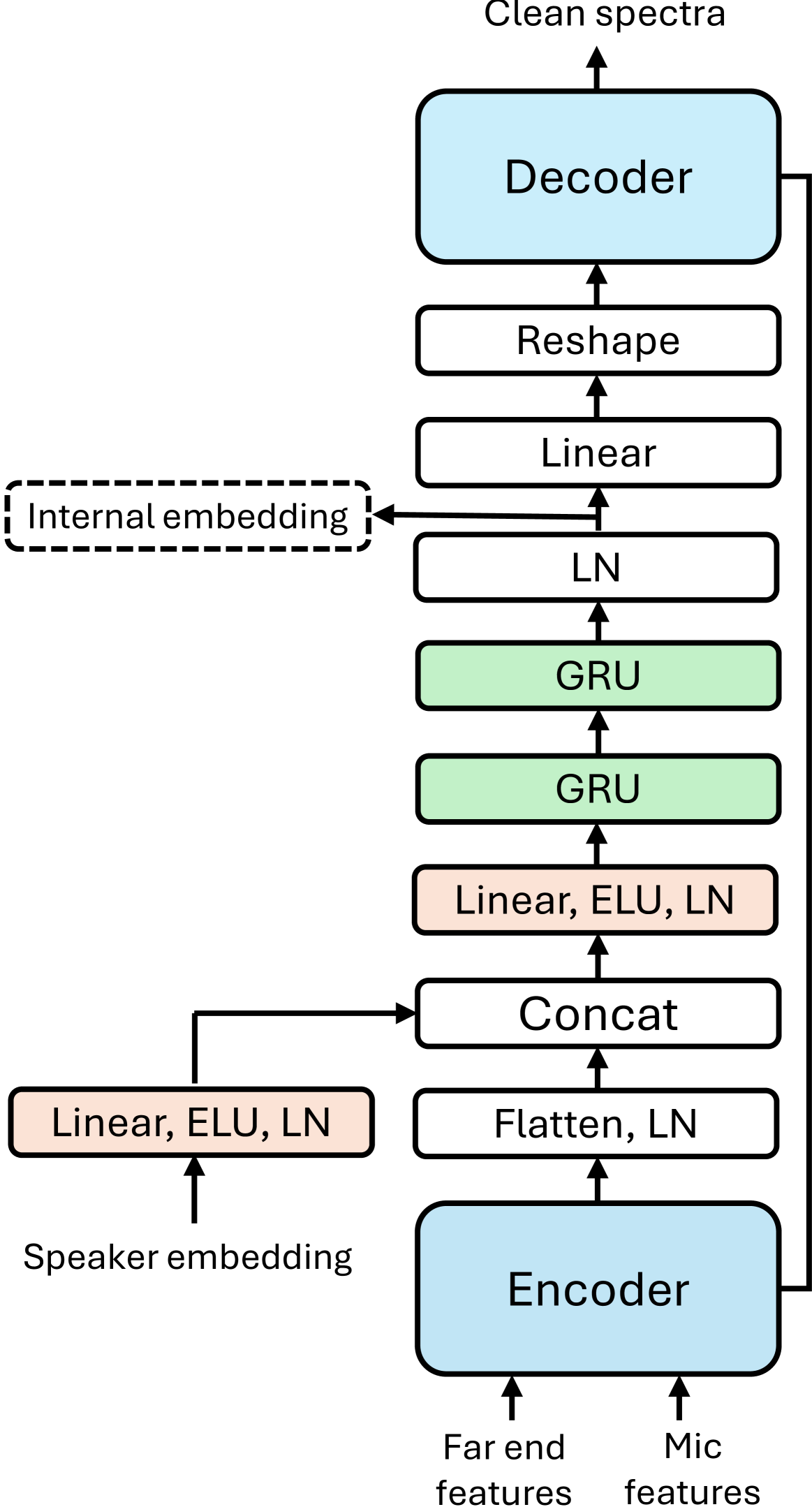

0
Personalized Speech Enhancement Without a Separate Speaker Embedding Model
Tanel Parnamaa, Ando Saabas
Personalized speech enhancement (PSE) models can improve the audio quality of teleconferencing systems by adapting to the characteristics of a speaker's voice. However, most existing methods require a separate speaker embedding model to extract a vector representation of the speaker from enrollment audio, which adds complexity to the training and deployment process. We propose to use the internal representation of the PSE model itself as the speaker embedding, thereby avoiding the need for a separate model. We show that our approach performs equally well or better than the standard method of using a pre-trained speaker embedding model on noise suppression and echo cancellation tasks. Moreover, our approach surpasses the ICASSP 2023 Deep Noise Suppression Challenge winner by 0.15 in Mean Opinion Score.
Read more6/17/2024
💬

0
An Investigation of Noise Robustness for Flow-Matching-Based Zero-Shot TTS
Xiaofei Wang, Sefik Emre Eskimez, Manthan Thakker, Hemin Yang, Zirun Zhu, Min Tang, Yufei Xia, Jinzhu Li, Sheng Zhao, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda
Recently, zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems, capable of synthesizing any speaker's voice from a short audio prompt, have made rapid advancements. However, the quality of the generated speech significantly deteriorates when the audio prompt contains noise, and limited research has been conducted to address this issue. In this paper, we explored various strategies to enhance the quality of audio generated from noisy audio prompts within the context of flow-matching-based zero-shot TTS. Our investigation includes comprehensive training strategies: unsupervised pre-training with masked speech denoising, multi-speaker detection and DNSMOS-based data filtering on the pre-training data, and fine-tuning with random noise mixing. The results of our experiments demonstrate significant improvements in intelligibility, speaker similarity, and overall audio quality compared to the approach of applying speech enhancement to the audio prompt.
Read more6/11/2024