Psychological Profiling in Cybersecurity: A Look at LLMs and Psycholinguistic Features
2406.18783

0
0
🏅
Abstract
The increasing sophistication of cyber threats necessitates innovative approaches to cybersecurity. In this paper, we explore the potential of psychological profiling techniques, particularly focusing on the utilization of Large Language Models (LLMs) and psycholinguistic features. We investigate the intersection of psychology and cybersecurity, discussing how LLMs can be employed to analyze textual data for identifying psychological traits of threat actors. We explore the incorporation of psycholinguistic features, such as linguistic patterns and emotional cues, into cybersecurity frameworks. Our research underscores the importance of integrating psychological perspectives into cybersecurity practices to bolster defense mechanisms against evolving threats.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) and psycholinguistic features for psychological profiling in the field of cybersecurity.
- The researchers investigate how LLMs and linguistic analysis can be leveraged to identify and understand the psychological traits and behavioral patterns of cyber threat actors.
- The paper provides insights into the potential applications and limitations of this approach, as well as future research directions in this emerging area.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses how researchers are using advanced language models and techniques to better understand the psychological profiles of people involved in cybercrime and cyberattacks. By analyzing the linguistic patterns and psychological characteristics reflected in the language used by cyber threat actors, the researchers aim to develop more effective strategies for detecting, mitigating, and preventing cyber threats.
The core idea is that the way people communicate, both in terms of the words they use and the underlying psychological traits they reveal, can provide valuable insights into their motivations, decision-making processes, and potential future actions. By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and psycholinguistic features, the researchers hope to gain a better understanding of the mindset and behaviors of cyber criminals, hackers, and other threat actors.
This research builds on previous work exploring the intersection of LLMs and cybersecurity as well as the use of generative AI and LLMs in the cybersecurity domain. By combining linguistic analysis and psychological profiling, the researchers aim to develop more robust and nuanced approaches to understanding and addressing cybercrime.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by outlining the importance of psychological profiling in the field of cybersecurity, as understanding the mindset and behavioral patterns of cyber threat actors can inform more effective prevention and response strategies.
The researchers then describe their approach, which involves leveraging LLMs and psycholinguistic features to analyze the language used by cyber threat actors. Specifically, they use LLMs to extract contextual information and linguistic patterns from textual data associated with cyber incidents, such as hacker forums, online discussions, and ransom notes.
By analyzing the psycholinguistic features of this language, the researchers aim to identify underlying psychological traits and behavioral tendencies that may be indicative of certain types of cyber threats. This includes factors such as personality, emotional states, cognitive biases, and decision-making processes.
The paper presents the results of several case studies and experiments that demonstrate the potential of this approach. For example, the researchers show how LLM-based linguistic analysis can be used to differentiate between various types of cyber threat actors, such as hacktivists, state-sponsored actors, and financially motivated criminals.
The researchers also discuss the limitations and challenges of this approach, such as the difficulty of obtaining reliable and representative data, the potential for bias and inaccuracies in the linguistic analysis, and the need for further validation and cross-disciplinary collaboration to refine the techniques.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising and timely approach to leveraging advanced language models and psycholinguistic analysis for enhancing cybersecurity. By focusing on the psychological and behavioral aspects of cyber threat actors, the researchers are addressing an important gap in the field, which has traditionally been dominated by technical and data-driven approaches.
One strength of the paper is its recognition of the limitations and potential pitfalls of this approach. The researchers acknowledge the challenges of obtaining reliable data, the risk of biases and inaccuracies in the linguistic analysis, and the need for further validation and collaboration with experts in psychology, criminology, and other relevant fields.
However, the paper could have delved deeper into the ethical considerations and potential misuse of this technology. While the researchers mention the need for responsible development and deployment, they could have provided a more nuanced discussion of the privacy implications, the risk of profiling and discrimination, and the potential for this technology to be abused by malicious actors or authoritarian regimes.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the broader societal implications of this research, such as its potential impact on privacy, civil liberties, and the criminal justice system. By addressing these broader concerns, the researchers could have strengthened the overall critical analysis and demonstrated a more holistic understanding of the implications of their work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this paper presents a novel and promising approach to using LLMs and psycholinguistic analysis for psychological profiling in the field of cybersecurity. The researchers have demonstrated the potential of this technique to enhance our understanding of cyber threat actors and inform more effective prevention and response strategies.
However, the paper also highlights the need for continued research, cross-disciplinary collaboration, and a careful consideration of the ethical and societal implications of this technology. As the field of cybersecurity continues to evolve, the integration of psychological and behavioral insights will likely play an increasingly important role in addressing the complex and ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
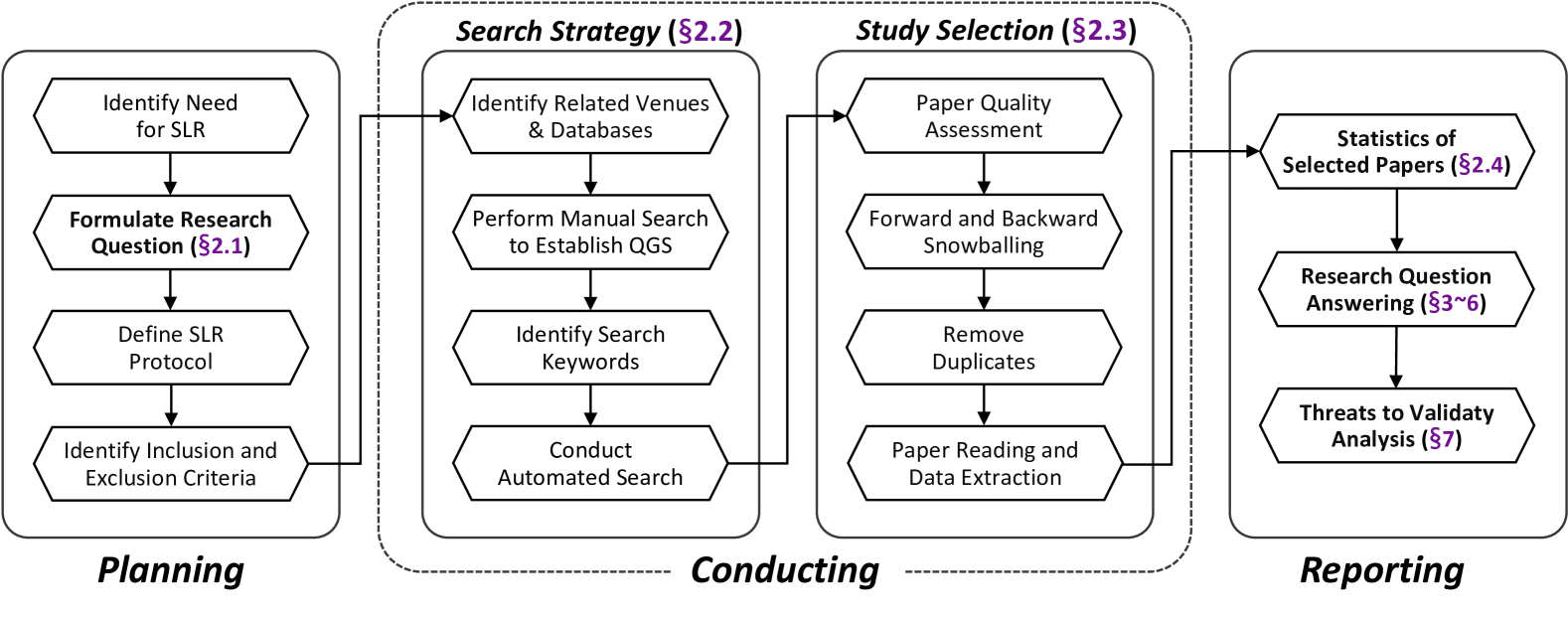
Large Language Models for Cyber Security: A Systematic Literature Review
HanXiang Xu, ShenAo Wang, NingKe Li, KaiLong Wang, YanJie Zhao, Kai Chen, Ting Yu, Yang Liu, HaoYu Wang

0
0
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities for leveraging artificial intelligence in various domains, including cybersecurity. As the volume and sophistication of cyber threats continue to grow, there is an increasing need for intelligent systems that can automatically detect vulnerabilities, analyze malware, and respond to attacks. In this survey, we conduct a comprehensive review of the literature on the application of LLMs in cybersecurity (LLM4Security). By comprehensively collecting over 30K relevant papers and systematically analyzing 127 papers from top security and software engineering venues, we aim to provide a holistic view of how LLMs are being used to solve diverse problems across the cybersecurity domain. Through our analysis, we identify several key findings. First, we observe that LLMs are being applied to a wide range of cybersecurity tasks, including vulnerability detection, malware analysis, network intrusion detection, and phishing detection. Second, we find that the datasets used for training and evaluating LLMs in these tasks are often limited in size and diversity, highlighting the need for more comprehensive and representative datasets. Third, we identify several promising techniques for adapting LLMs to specific cybersecurity domains, such as fine-tuning, transfer learning, and domain-specific pre-training. Finally, we discuss the main challenges and opportunities for future research in LLM4Security, including the need for more interpretable and explainable models, the importance of addressing data privacy and security concerns, and the potential for leveraging LLMs for proactive defense and threat hunting. Overall, our survey provides a comprehensive overview of the current state-of-the-art in LLM4Security and identifies several promising directions for future research.
5/10/2024
🔎
When LLMs Meet Cybersecurity: A Systematic Literature Review
Jie Zhang, Haoyu Bu, Hui Wen, Yu Chen, Lun Li, Hongsong Zhu

0
0
The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have opened new avenues across various fields, including cybersecurity, which faces an ever-evolving threat landscape and need for innovative technologies. Despite initial explorations into the application of LLMs in cybersecurity, there is a lack of a comprehensive overview of this research area. This paper bridge this gap by providing a systematic literature review, encompassing an analysis of over 180 works, spanning across 25 LLMs and more than 10 downstream scenarios. Our comprehensive overview addresses three critical research questions: the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, LLMs' applications in various cybersecurity tasks, and the existing challenges and further research in this area. This study aims to shed light on the extensive potential of LLMs in enhancing cybersecurity practices, and serve as a valuable resource for applying LLMs in this doamin. We also maintain and regularly updated list of practical guides on LLMs for cybersecurity at https://github.com/tmylla/Awesome-LLM4Cybersecurity.
5/7/2024
🤖
Generative AI and Large Language Models for Cyber Security: All Insights You Need
Mohamed Amine Ferrag, Fatima Alwahedi, Ammar Battah, Bilel Cherif, Abdechakour Mechri, Norbert Tihanyi

0
0
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the future of cybersecurity through Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs). We explore LLM applications across various domains, including hardware design security, intrusion detection, software engineering, design verification, cyber threat intelligence, malware detection, and phishing detection. We present an overview of LLM evolution and its current state, focusing on advancements in models such as GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Mixtral-8x7B, BERT, Falcon2, and LLaMA. Our analysis extends to LLM vulnerabilities, such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, data poisoning, DDoS attacks, and adversarial instructions. We delve into mitigation strategies to protect these models, providing a comprehensive look at potential attack scenarios and prevention techniques. Furthermore, we evaluate the performance of 42 LLM models in cybersecurity knowledge and hardware security, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. We thoroughly evaluate cybersecurity datasets for LLM training and testing, covering the lifecycle from data creation to usage and identifying gaps for future research. In addition, we review new strategies for leveraging LLMs, including techniques like Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ), Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF), Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), Quantized Low-Rank Adapters (QLoRA), and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). These insights aim to enhance real-time cybersecurity defenses and improve the sophistication of LLM applications in threat detection and response. Our paper provides a foundational understanding and strategic direction for integrating LLMs into future cybersecurity frameworks, emphasizing innovation and robust model deployment to safeguard against evolving cyber threats.
5/22/2024

LLM Questionnaire Completion for Automatic Psychiatric Assessment
Gony Rosenman, Lior Wolf, Talma Hendler

0
0
We employ a Large Language Model (LLM) to convert unstructured psychological interviews into structured questionnaires spanning various psychiatric and personality domains. The LLM is prompted to answer these questionnaires by impersonating the interviewee. The obtained answers are coded as features, which are used to predict standardized psychiatric measures of depression (PHQ-8) and PTSD (PCL-C), using a Random Forest regressor. Our approach is shown to enhance diagnostic accuracy compared to multiple baselines. It thus establishes a novel framework for interpreting unstructured psychological interviews, bridging the gap between narrative-driven and data-driven approaches for mental health assessment.
6/12/2024