Two-Way Aerial Secure Communications via Distributed Collaborative Beamforming under Eavesdropper Collusion
2404.07444

0
0
Abstract
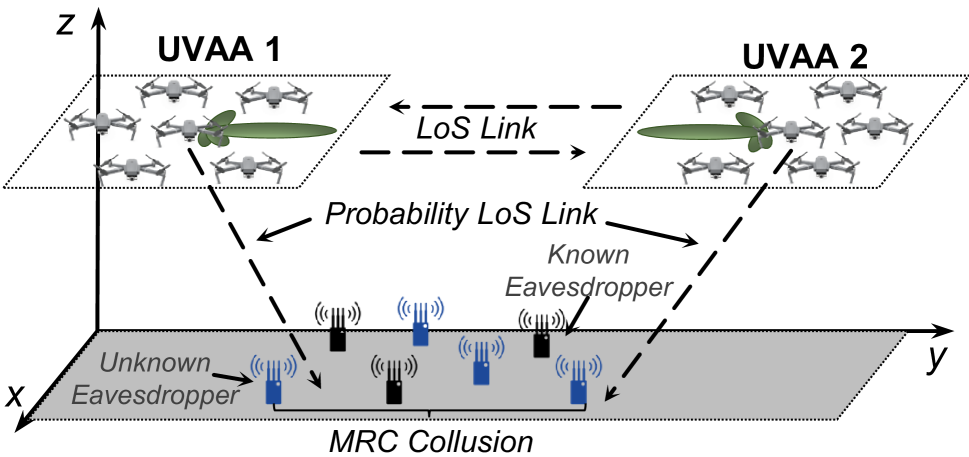
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)-enabled aerial communication provides a flexible, reliable, and cost-effective solution for a range of wireless applications. However, due to the high line-of-sight (LoS) probability, aerial communications between UAVs are vulnerable to eavesdropping attacks, particularly when multiple eavesdroppers collude. In this work, we aim to introduce distributed collaborative beamforming (DCB) into UAV swarms and handle the eavesdropper collusion by controlling the corresponding signal distributions. Specifically, we consider a two-way DCB-enabled aerial communication between two UAV swarms and construct these swarms as two UAV virtual antenna arrays. Then, we minimize the two-way known secrecy capacity and the maximum sidelobe level to avoid information leakage from the known and unknown eavesdroppers, respectively. Simultaneously, we also minimize the energy consumption of UAVs for constructing virtual antenna arrays. Due to the conflicting relationships between secure performance and energy efficiency, we consider these objectives as a multi-objective optimization problem. Following this, we propose an enhanced multi-objective swarm intelligence algorithm via the characterized properties of the problem. Simulation results show that our proposed algorithm can obtain a set of informative solutions and outperform other state-of-the-art baseline algorithms. Experimental tests demonstrate that our method can be deployed in limited computing power platforms of UAVs and is beneficial for saving computational resources.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores secure aerial communications using distributed collaborative beamforming techniques to prevent eavesdropping by colluding attackers
- Proposes a multi-objective optimization approach to balance security, energy efficiency, and communication throughput
- Leverages virtual antenna arrays formed by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to enable robust two-way communications
Plain English Explanation
This research paper focuses on enhancing the security of aerial communications, particularly in scenarios where there is a risk of eavesdropping by multiple coordinated attackers. The key idea is to use a technique called distributed collaborative beamforming to create secure wireless links between UAVs and ground stations.
By coordinating the transmissions from multiple UAVs, the researchers can form a virtual antenna array that can directionally focus the communication signals and minimize the information leakage to potential eavesdroppers. This helps to secure the skies and ensure reliable real-time telemetry for critical applications.
The proposed approach also considers other important factors, such as energy efficiency and overall communication throughput, using a multi-objective optimization framework. This allows the system to find a balance between these competing goals and provide a more holistic solution for secure aerial communications.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a novel framework for two-way aerial secure communications using distributed collaborative beamforming under the threat of eavesdropper collusion. The key technical components include:
-
Distributed Collaborative Beamforming: The UAVs in the network coordinate their transmissions to form a virtual antenna array, enabling directional communication and minimizing information leakage to potential eavesdroppers.
-
Eavesdropper Collusion: The researchers consider a realistic scenario where multiple eavesdroppers can collude to jointly intercept the communication, posing a significant security challenge.
-
Multi-Objective Optimization: The system aims to simultaneously optimize for security (minimizing information leakage), energy efficiency, and communication throughput, using a multi-objective optimization approach.
-
System Architecture: The proposed framework leverages the capabilities of UAVs to establish secure two-way communications between ground stations, with the UAVs forming the virtual antenna array and carrying out the distributed collaborative beamforming.
The researchers develop analytical models to characterize the trade-offs between the various performance metrics and propose efficient algorithms to solve the multi-objective optimization problem. Through simulations and performance analysis, they demonstrate the effectiveness of their approach in enhancing the security of aerial communications while maintaining desirable energy and throughput characteristics.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed and comprehensive framework for secure aerial communications, addressing the important challenge of eavesdropper collusion. However, some potential limitations and areas for further research include:
-
Practical Considerations: The paper focuses on the theoretical aspects and performance analysis, but the implementation and deployment of the proposed system in real-world scenarios may face additional challenges, such as synchronization, coordination, and hardware constraints.
-
Eavesdropper Capabilities: The paper assumes a specific eavesdropping model, but in practice, the capabilities and tactics of adversaries may be more sophisticated, requiring further investigation.
-
Adaptability and Resilience: The system's ability to adapt to dynamic environments, such as changing eavesdropper locations or channel conditions, and its overall resilience to various types of attacks could be explored in more depth.
-
User Privacy and Data Confidentiality: While the paper focuses on securing the communication channel, the broader implications of user privacy and data confidentiality in aerial communications systems should also be considered.
-
Scalability and Computational Complexity: As the network size and number of UAVs increases, the computational complexity and scalability of the proposed optimization algorithms should be further analyzed.
Overall, the research presented in this paper provides a valuable contribution to the field of secure aerial communications and offers a promising approach to address the challenges of eavesdropper collusion. Continued research and development in this area can lead to more robust and reliable solutions for critical applications that rely on secure aerial communications.
Conclusion
This research paper introduces a novel framework for two-way aerial secure communications using distributed collaborative beamforming techniques to mitigate the threat of eavesdropper collusion. By leveraging the capabilities of UAVs to form virtual antenna arrays, the proposed system can directionally focus the communication signals and minimize information leakage to potential adversaries.
The key innovation of this work lies in the multi-objective optimization approach, which simultaneously considers security, energy efficiency, and communication throughput, allowing the system to find a balanced solution that meets the diverse requirements of aerial communication systems. The analytical models and algorithms developed in this paper demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach and provide a solid foundation for further research and development in this important field.
As the use of UAVs and aerial communications continues to grow, the need for robust and secure solutions becomes increasingly critical. This research contributes to the ongoing effort to secure the skies and ensure reliable real-time telemetry for a wide range of applications, from military operations to commercial drone deliveries and emergency response scenarios. The insights and techniques presented in this paper can serve as a foundation for further advancements in the field of secure aerial communications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

UAV-enabled Collaborative Beamforming via Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning
Saichao Liu, Geng Sun, Jiahui Li, Shuang Liang, Qingqing Wu, Pengfei Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
In this paper, we investigate an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-assistant air-to-ground communication system, where multiple UAVs form a UAV-enabled virtual antenna array (UVAA) to communicate with remote base stations by utilizing collaborative beamforming. To improve the work efficiency of the UVAA, we formulate a UAV-enabled collaborative beamforming multi-objective optimization problem (UCBMOP) to simultaneously maximize the transmission rate of the UVAA and minimize the energy consumption of all UAVs by optimizing the positions and excitation current weights of all UAVs. This problem is challenging because these two optimization objectives conflict with each other, and they are non-concave to the optimization variables. Moreover, the system is dynamic, and the cooperation among UAVs is complex, making traditional methods take much time to compute the optimization solution for a single task. In addition, as the task changes, the previously obtained solution will become obsolete and invalid. To handle these issues, we leverage the multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MADRL) to address the UCBMOP. Specifically, we use the heterogeneous-agent trust region policy optimization (HATRPO) as the basic framework, and then propose an improved HATRPO algorithm, namely HATRPO-UCB, where three techniques are introduced to enhance the performance. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can learn a better strategy compared with other methods. Moreover, extensive experiments also demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed techniques.
4/12/2024

Collaborative Ground-Space Communications via Evolutionary Multi-objective Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jiahui Li, Geng Sun, Qingqing Wu, Dusit Niyato, Jiawen Kang, Abbas Jamalipour, Victor C. M. Leung

0
0
In this paper, we propose a distributed collaborative beamforming (DCB)-based uplink communication paradigm for enabling ground-space direct communications. Specifically, DCB treats the terminals that are unable to establish efficient direct connections with the low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites as distributed antennas, forming a virtual antenna array to enhance the terminal-to-satellite uplink achievable rates and durations. However, such systems need multiple trade-off policies that variously balance the terminal-satellite uplink achievable rate, energy consumption of terminals, and satellite switching frequency to satisfy the scenario requirement changes. Thus, we perform a multi-objective optimization analysis and formulate a long-term optimization problem. To address availability in different terminal cluster scales, we reformulate this problem into an action space-reduced and universal multi-objective Markov decision process. Then, we propose an evolutionary multi-objective deep reinforcement learning algorithm to obtain the desirable policies, in which the low-value actions are masked to speed up the training process. As such, the applicability of a one-time trained model can cover more changing terminal-satellite uplink scenarios. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outmatches various baselines, and draw some useful insights. Specifically, it is found that DCB enables terminals that cannot reach the uplink achievable threshold to achieve efficient direct uplink transmission, which thus reveals that DCB is an effective solution for enabling direct ground-space communications. Moreover, it reveals that the proposed algorithm achieves multiple policies favoring different objectives and achieving near-optimal uplink achievable rates with low switching frequency.
4/12/2024
👀
Towards Secure and Reliable Heterogeneous Real-time Telemetry Communication in Autonomous UAV Swarms
Pavlo Mykytyn, Marcin Brzozowski, Zoya Dyka, Peter Langendorfer

0
0
In the era of cutting-edge autonomous systems, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are becoming an essential part of the solutions for numerous complex challenges. This paper evaluates UAV peer-to-peer telemetry communication, highlighting its security vulnerabilities and explores a transition to a het-erogeneous multi-hop mesh all-to-all communication architecture to increase inter-swarm connectivity and reliability. Additionally, we suggest a symmetric key agreement and data encryption mechanism implementation for inter - swarm communication, to ensure data integrity and confidentiality without compromising performance.
4/12/2024

Multi-UAV Multi-RIS QoS-Aware Aerial Communication Systems using DRL and PSO
Marwan Dhuheir, Aiman Erbad, Ala Al-Fuqaha, Mohsen Guizani

0
0
Recently, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have attracted the attention of researchers in academia and industry for providing wireless services to ground users in diverse scenarios like festivals, large sporting events, natural and man-made disasters due to their advantages in terms of versatility and maneuverability. However, the limited resources of UAVs (e.g., energy budget and different service requirements) can pose challenges for adopting UAVs for such applications. Our system model considers a UAV swarm that navigates an area, providing wireless communication to ground users with RIS support to improve the coverage of the UAVs. In this work, we introduce an optimization model with the aim of maximizing the throughput and UAVs coverage through optimal path planning of UAVs and multi-RIS phase configurations. The formulated optimization is challenging to solve using standard linear programming techniques, limiting its applicability in real-time decision-making. Therefore, we introduce a two-step solution using deep reinforcement learning and particle swarm optimization. We conduct extensive simulations and compare our approach to two competitive solutions presented in the recent literature. Our simulation results demonstrate that our adopted approach is 20 % better than the brute-force approach and 30% better than the baseline solution in terms of QoS.
6/26/2024