Recent Advances in End-to-End Simultaneous Speech Translation
2406.00497

0
0
🗣️
Abstract
Simultaneous speech translation (SimulST) is a demanding task that involves generating translations in real-time while continuously processing speech input. This paper offers a comprehensive overview of the recent developments in SimulST research, focusing on four major challenges. Firstly, the complexities associated with processing lengthy and continuous speech streams pose significant hurdles. Secondly, satisfying real-time requirements presents inherent difficulties due to the need for immediate translation output. Thirdly, striking a balance between translation quality and latency constraints remains a critical challenge. Finally, the scarcity of annotated data adds another layer of complexity to the task. Through our exploration of these challenges and the proposed solutions, we aim to provide valuable insights into the current landscape of SimulST research and suggest promising directions for future exploration.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores recent advancements in end-to-end simultaneous speech translation, which aims to translate spoken language in real-time with minimal latency.
- The authors discuss various segmentation strategies that can be used to chunk the input audio and generate partial translations, a key challenge in simultaneous translation.
- They also review recent progress in related areas like Simultron, SeamlessExpressiveLM, and Simultaneous Interpretation Corpus, which provide additional context and opportunities for advancement.
Plain English Explanation
Simultaneous speech translation is the process of translating spoken language in real-time, as someone is talking, rather than waiting until they finish. This allows for more natural, interactive conversations between speakers of different languages. However, it presents technical challenges, as the translation system needs to decide when to start translating partial fragments of the input speech rather than waiting for the full sentence.
The researchers in this paper explore different strategies for "segmenting" the input audio - that is, breaking it up into smaller chunks that can be translated independently. By developing effective segmentation methods, the translation system can provide rapid, incremental output without sacrificing accuracy.
The paper also references related advancements, like Simultron, which enables simultaneous speech-to-speech translation on a device, and SeamlessExpressiveLM, which models expressive speech characteristics. These complementary innovations could further enhance the end-to-end simultaneous translation experience.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by providing an overview of end-to-end simultaneous speech translation, which aims to translate spoken language in real-time with low latency. A key challenge is developing effective "segmentation strategies" - methods for chunking the input audio into smaller fragments that can be translated independently and incrementally.
The authors review several segmentation approaches, including:
- Fixed-delay: Waiting a fixed amount of time before starting translation
- Adaptive: Dynamically adjusting the delay based on the input speech
- Prefix-to-prefix: Translating each prefix of the input as it is received
- Prefix-to-full: Translating the full sentence once a prefix has been received
The paper also discusses complementary advances in related areas, such as Simultron, a system for simultaneous speech-to-speech translation on a device, and SeamlessExpressiveLM, which models expressive speech characteristics to improve translation quality. Additionally, the Simultaneous Interpretation Corpus is highlighted as a valuable resource for training and evaluating simultaneous translation models.
The TransVIP and CrossVoice systems are also mentioned as examples of recent advances in speech-to-speech translation that could complement the end-to-end simultaneous translation techniques discussed in the paper.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the key challenges and recent advancements in end-to-end simultaneous speech translation. The authors thoroughly examine various segmentation strategies and discuss their tradeoffs, which is a crucial aspect of this problem.
While the paper covers a lot of ground, it would be helpful to see more concrete experimental results and comparisons between the different segmentation approaches. Additionally, the paper could delve deeper into the limitations of the current techniques, such as potential issues with accuracy, latency, or robustness to noise or speaker variability.
It would also be interesting to see the authors' thoughts on the broader societal implications of such simultaneous translation technologies, particularly in terms of their potential to enhance cross-cultural communication and accessibility.
Conclusion
This paper offers a detailed review of the state-of-the-art in end-to-end simultaneous speech translation, with a focus on the critical challenge of developing effective segmentation strategies. By exploring various chunking approaches and related advancements in complementary areas, the authors provide a valuable summary of the current research landscape and the key issues that need to be addressed.
As simultaneous translation systems continue to improve, they have the potential to significantly enhance global communication, facilitate more natural interactions between speakers of different languages, and improve accessibility for those with language barriers. The insights and future directions outlined in this paper will undoubtedly help drive further progress in this important and rapidly evolving field.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

StreamSpeech: Simultaneous Speech-to-Speech Translation with Multi-task Learning
Shaolei Zhang, Qingkai Fang, Shoutao Guo, Zhengrui Ma, Min Zhang, Yang Feng

0
0
Simultaneous speech-to-speech translation (Simul-S2ST, a.k.a streaming speech translation) outputs target speech while receiving streaming speech inputs, which is critical for real-time communication. Beyond accomplishing translation between speech, Simul-S2ST requires a policy to control the model to generate corresponding target speech at the opportune moment within speech inputs, thereby posing a double challenge of translation and policy. In this paper, we propose StreamSpeech, a direct Simul-S2ST model that jointly learns translation and simultaneous policy in a unified framework of multi-task learning. Adhering to a multi-task learning approach, StreamSpeech can perform offline and simultaneous speech recognition, speech translation and speech synthesis via an All-in-One seamless model. Experiments on CVSS benchmark demonstrate that StreamSpeech achieves state-of-the-art performance in both offline S2ST and Simul-S2ST tasks. Besides, StreamSpeech is able to present high-quality intermediate results (i.e., ASR or translation results) during simultaneous translation process, offering a more comprehensive real-time communication experience.
6/6/2024
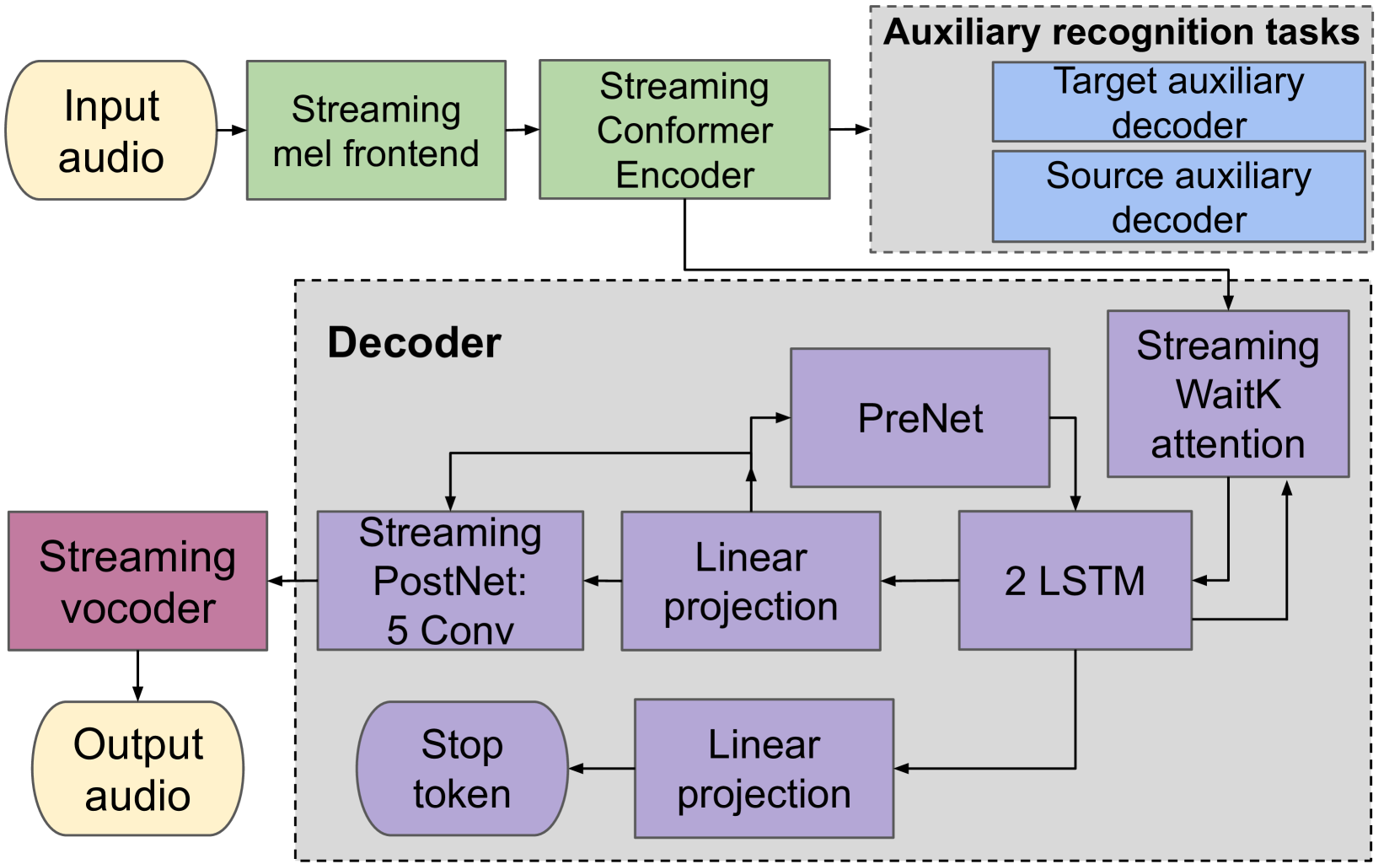
SimulTron: On-Device Simultaneous Speech to Speech Translation
Alex Agranovich, Eliya Nachmani, Oleg Rybakov, Yifan Ding, Ye Jia, Nadav Bar, Heiga Zen, Michelle Tadmor Ramanovich

0
0
Simultaneous speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) holds the promise of breaking down communication barriers and enabling fluid conversations across languages. However, achieving accurate, real-time translation through mobile devices remains a major challenge. We introduce SimulTron, a novel S2ST architecture designed to tackle this task. SimulTron is a lightweight direct S2ST model that uses the strengths of the Translatotron framework while incorporating key modifications for streaming operation, and an adjustable fixed delay. Our experiments show that SimulTron surpasses Translatotron 2 in offline evaluations. Furthermore, real-time evaluations reveal that SimulTron improves upon the performance achieved by Translatotron 1. Additionally, SimulTron achieves superior BLEU scores and latency compared to previous real-time S2ST method on the MuST-C dataset. Significantly, we have successfully deployed SimulTron on a Pixel 7 Pro device, show its potential for simultaneous S2ST on-device.
6/5/2024
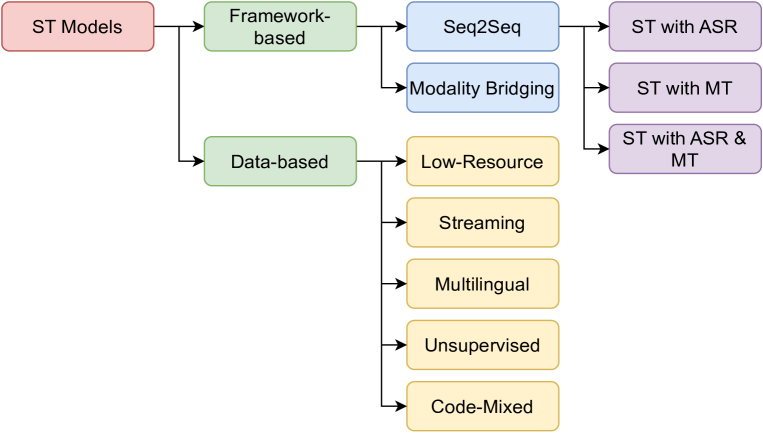
End-to-End Speech-to-Text Translation: A Survey
Nivedita Sethiya, Chandresh Kumar Maurya

0
0
Speech-to-text translation pertains to the task of converting speech signals in a language to text in another language. It finds its application in various domains, such as hands-free communication, dictation, video lecture transcription, and translation, to name a few. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), as well as Machine Translation(MT) models, play crucial roles in traditional ST translation, enabling the conversion of spoken language in its original form to written text and facilitating seamless cross-lingual communication. ASR recognizes spoken words, while MT translates the transcribed text into the target language. Such disintegrated models suffer from cascaded error propagation and high resource and training costs. As a result, researchers have been exploring end-to-end (E2E) models for ST translation. However, to our knowledge, there is no comprehensive review of existing works on E2E ST. The present survey, therefore, discusses the work in this direction. Our attempt has been to provide a comprehensive review of models employed, metrics, and datasets used for ST tasks, providing challenges and future research direction with new insights. We believe this review will be helpful to researchers working on various applications of ST models.
6/11/2024
📶
StreamAtt: Direct Streaming Speech-to-Text Translation with Attention-based Audio History Selection
Sara Papi, Marco Gaido, Matteo Negri, Luisa Bentivogli

0
0
Streaming speech-to-text translation (StreamST) is the task of automatically translating speech while incrementally receiving an audio stream. Unlike simultaneous ST (SimulST), which deals with pre-segmented speech, StreamST faces the challenges of handling continuous and unbounded audio streams. This requires additional decisions about what to retain of the previous history, which is impractical to keep entirely due to latency and computational constraints. Despite the real-world demand for real-time ST, research on streaming translation remains limited, with existing works solely focusing on SimulST. To fill this gap, we introduce StreamAtt, the first StreamST policy, and propose StreamLAAL, the first StreamST latency metric designed to be comparable with existing metrics for SimulST. Extensive experiments across all 8 languages of MuST-C v1.0 show the effectiveness of StreamAtt compared to a naive streaming baseline and the related state-of-the-art SimulST policy, providing a first step in StreamST research.
6/11/2024