Self-Augmented Preference Optimization: Off-Policy Paradigms for Language Model Alignment
2405.20830

0
0
Abstract
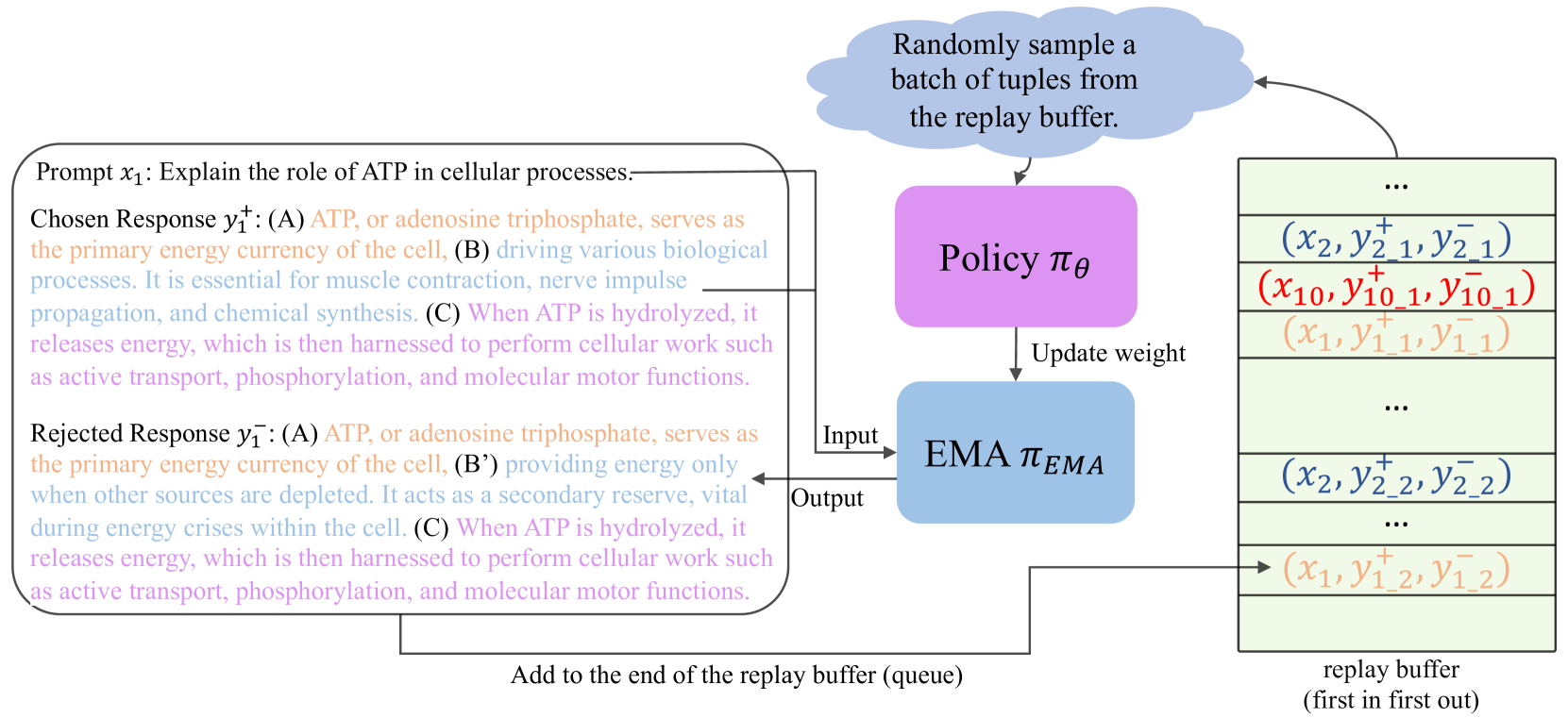
Traditional language model alignment methods, such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), are limited by their dependence on static, pre-collected paired preference data, which hampers their adaptability and practical applicability. To overcome this limitation, we introduce Self-Augmented Preference Optimization (SAPO), an effective and scalable training paradigm that does not require existing paired data. Building on the self-play concept, which autonomously generates negative responses, we further incorporate an off-policy learning pipeline to enhance data exploration and exploitation. Specifically, we employ an Exponential Moving Average (EMA) model in conjunction with a replay buffer to enable dynamic updates of response segments, effectively integrating real-time feedback with insights from historical data. Our comprehensive evaluations of the LLaMA3-8B and Mistral-7B models across benchmarks, including the Open LLM Leaderboard, IFEval, AlpacaEval 2.0, and MT-Bench, demonstrate that SAPO matches or surpasses established offline contrastive baselines, such as DPO and Odds Ratio Preference Optimization, and outperforms offline self-play methods like SPIN. Our code is available at https://github.com/yinyueqin/SAPO
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Self-Play Preference Optimization for Language Model Alignment
Yue Wu, Zhiqing Sun, Huizhuo Yuan, Kaixuan Ji, Yiming Yang, Quanquan Gu

0
0
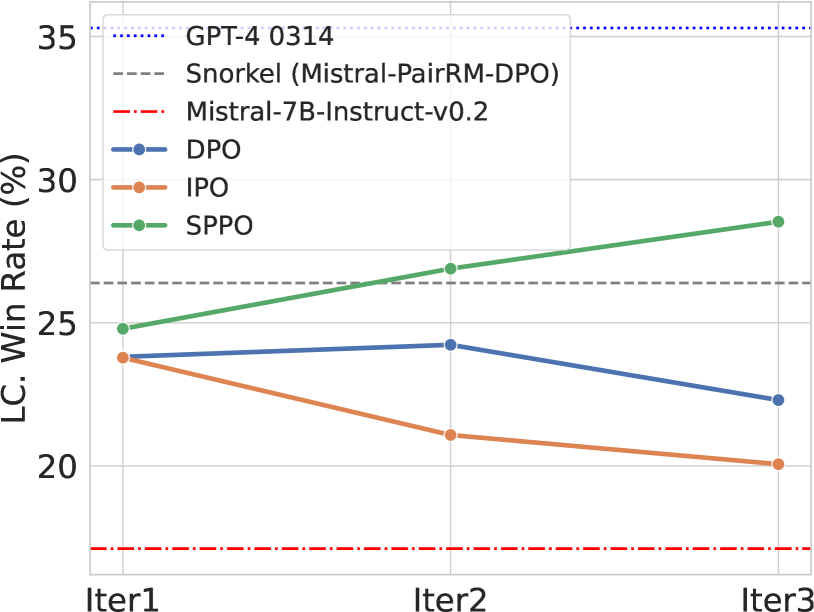
Traditional reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) approaches relying on parametric models like the Bradley-Terry model fall short in capturing the intransitivity and irrationality in human preferences. Recent advancements suggest that directly working with preference probabilities can yield a more accurate reflection of human preferences, enabling more flexible and accurate language model alignment. In this paper, we propose a self-play-based method for language model alignment, which treats the problem as a constant-sum two-player game aimed at identifying the Nash equilibrium policy. Our approach, dubbed Self-Play Preference Optimization (SPPO), approximates the Nash equilibrium through iterative policy updates and enjoys a theoretical convergence guarantee. Our method can effectively increase the log-likelihood of the chosen response and decrease that of the rejected response, which cannot be trivially achieved by symmetric pairwise loss such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Identity Preference Optimization (IPO). In our experiments, using only 60k prompts (without responses) from the UltraFeedback dataset and without any prompt augmentation, by leveraging a pre-trained preference model PairRM with only 0.4B parameters, SPPO can obtain a model from fine-tuning Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 that achieves the state-of-the-art length-controlled win-rate of 28.53% against GPT-4-Turbo on AlpacaEval 2.0. It also outperforms the (iterative) DPO and IPO on MT-Bench and the Open LLM Leaderboard. Starting from a stronger base model Llama-3-8B-Instruct, we are able to achieve a length-controlled win rate of 38.77%. Notably, the strong performance of SPPO is achieved without additional external supervision (e.g., responses, preferences, etc.) from GPT-4 or other stronger language models. Codes are available at https://github.com/uclaml/SPPO.
6/17/2024
MAPO: Advancing Multilingual Reasoning through Multilingual Alignment-as-Preference Optimization
Shuaijie She, Wei Zou, Shujian Huang, Wenhao Zhu, Xiang Liu, Xiang Geng, Jiajun Chen

0
0
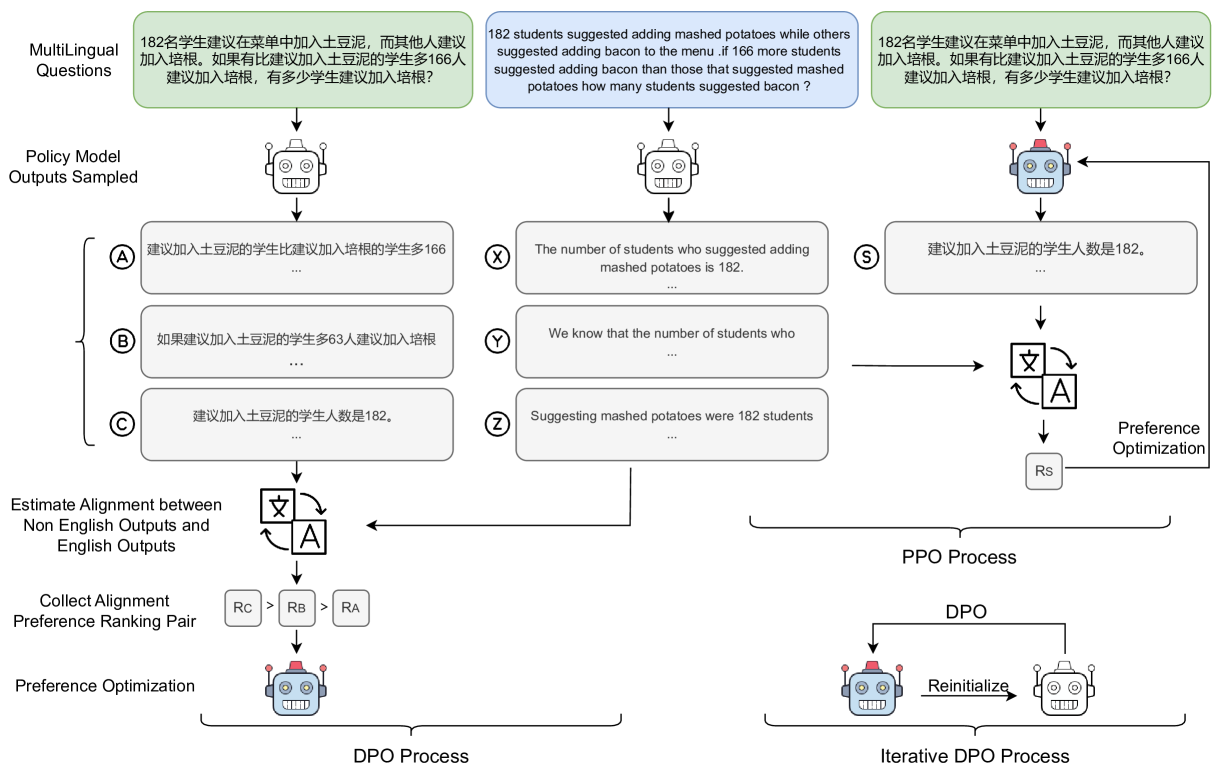
Though reasoning abilities are considered language-agnostic, existing LLMs exhibit inconsistent reasoning abilities across different languages, e.g., reasoning in the dominant language like English is superior to other languages due to the imbalance of multilingual training data. To enhance reasoning abilities in non-dominant languages, we propose a Multilingual-Alignment-as-Preference Optimization framework (MAPO), aiming to align the reasoning processes in other languages with the dominant language. Specifically, we harness an off-the-shelf translation model for the consistency between answers in non-dominant and dominant languages, which we adopt as the preference for optimization, e.g., Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) or Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). Experiments show that MAPO stably achieves significant improvements in the multilingual reasoning of various models on all three benchmarks (MSVAMP +16.2%, MGSM +6.1%, and MNumGLUESub +13.3%), with improved reasoning consistency across languages.
4/16/2024

BPO: Supercharging Online Preference Learning by Adhering to the Proximity of Behavior LLM
Wenda Xu, Jiachen Li, William Yang Wang, Lei Li

0
0
Direct alignment from preferences (DAP) has emerged as a promising paradigm for aligning large language models (LLMs) to human desiderata from pre-collected, offline preference datasets. While recent studies indicate that existing offline DAP methods can directly benefit from online training samples, we highlight the need to develop specific online DAP algorithms to fully harness the power of online training. Specifically, we identify that the learned LLM should adhere to the proximity of the behavior LLM, which collects the training samples. To this end, we propose online Preference Optimization in proximity to the Behavior LLM (BPO), emphasizing the importance of constructing a proper trust region for LLM alignment. We conduct extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness and applicability of our approach by integrating it with various DAP methods, resulting in significant performance improvements across a wide range of tasks when training with the same amount of preference data. Even when only introducing one additional data collection phase, our online BPO improves its offline DAP baseline from 72.0% to 80.2% on TL;DR and from 82.2% to 89.1% on Anthropic Helpfulness in terms of win rate against human reference text.
6/21/2024
Soft Preference Optimization: Aligning Language Models to Expert Distributions
Arsalan Sharifnassab, Sina Ghiassian, Saber Salehkaleybar, Surya Kanoria, Dale Schuurmans

0
0
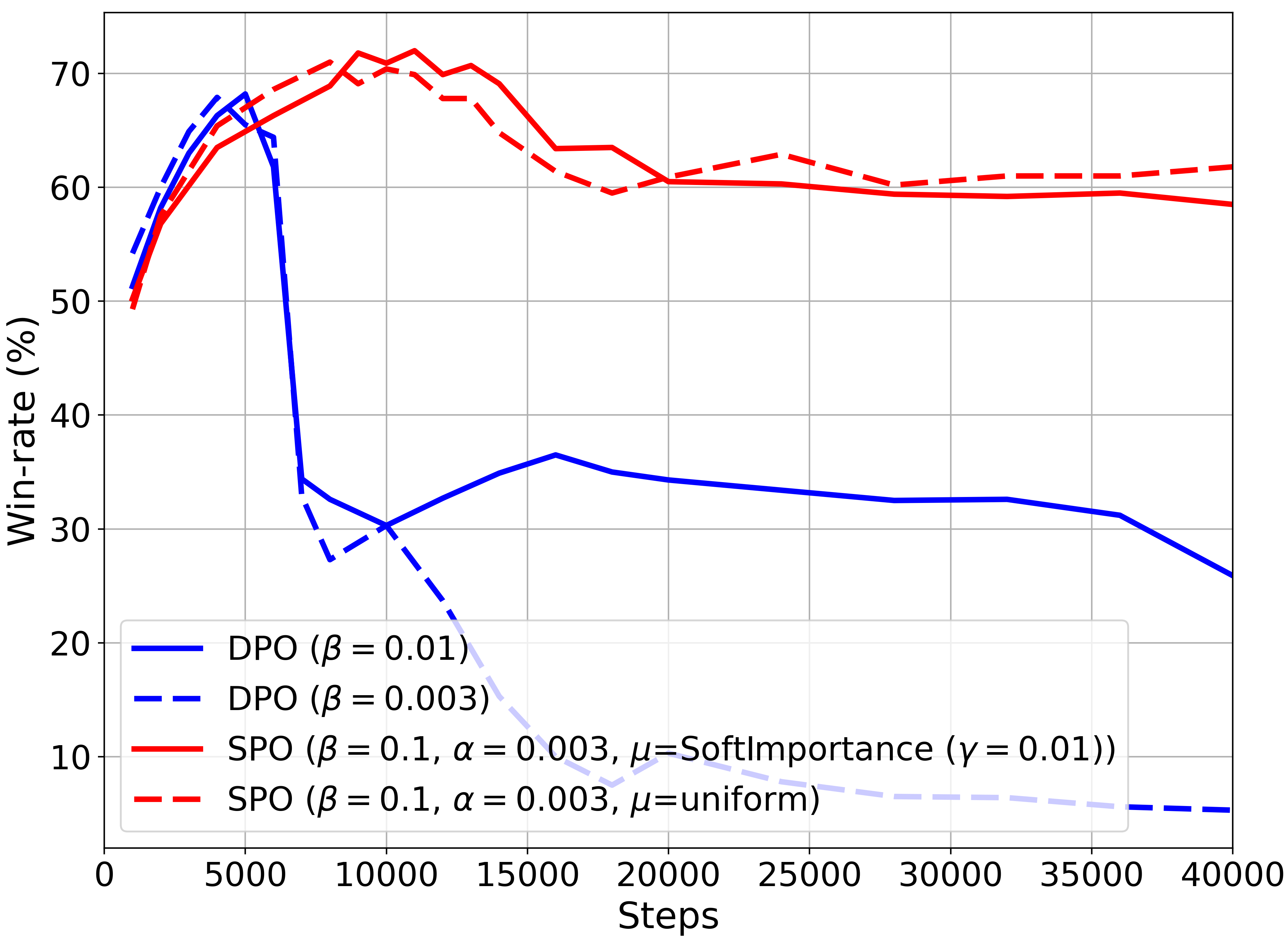
We propose Soft Preference Optimization (SPO), a method for aligning generative models, such as Large Language Models (LLMs), with human preferences, without the need for a reward model. SPO optimizes model outputs directly over a preference dataset through a natural loss function that integrates preference loss with a regularization term across the model's entire output distribution rather than limiting it to the preference dataset. Although SPO does not require the assumption of an existing underlying reward model, we demonstrate that, under the Bradley-Terry (BT) model assumption, it converges to a softmax of scaled rewards, with the distribution's softness adjustable via the softmax exponent, an algorithm parameter. We showcase SPO's methodology, its theoretical foundation, and its comparative advantages in simplicity, computational efficiency, and alignment precision.
5/29/2024