Similarity-aware Syncretic Latent Diffusion Model for Medical Image Translation with Representation Learning
2406.13977

0
0

Abstract
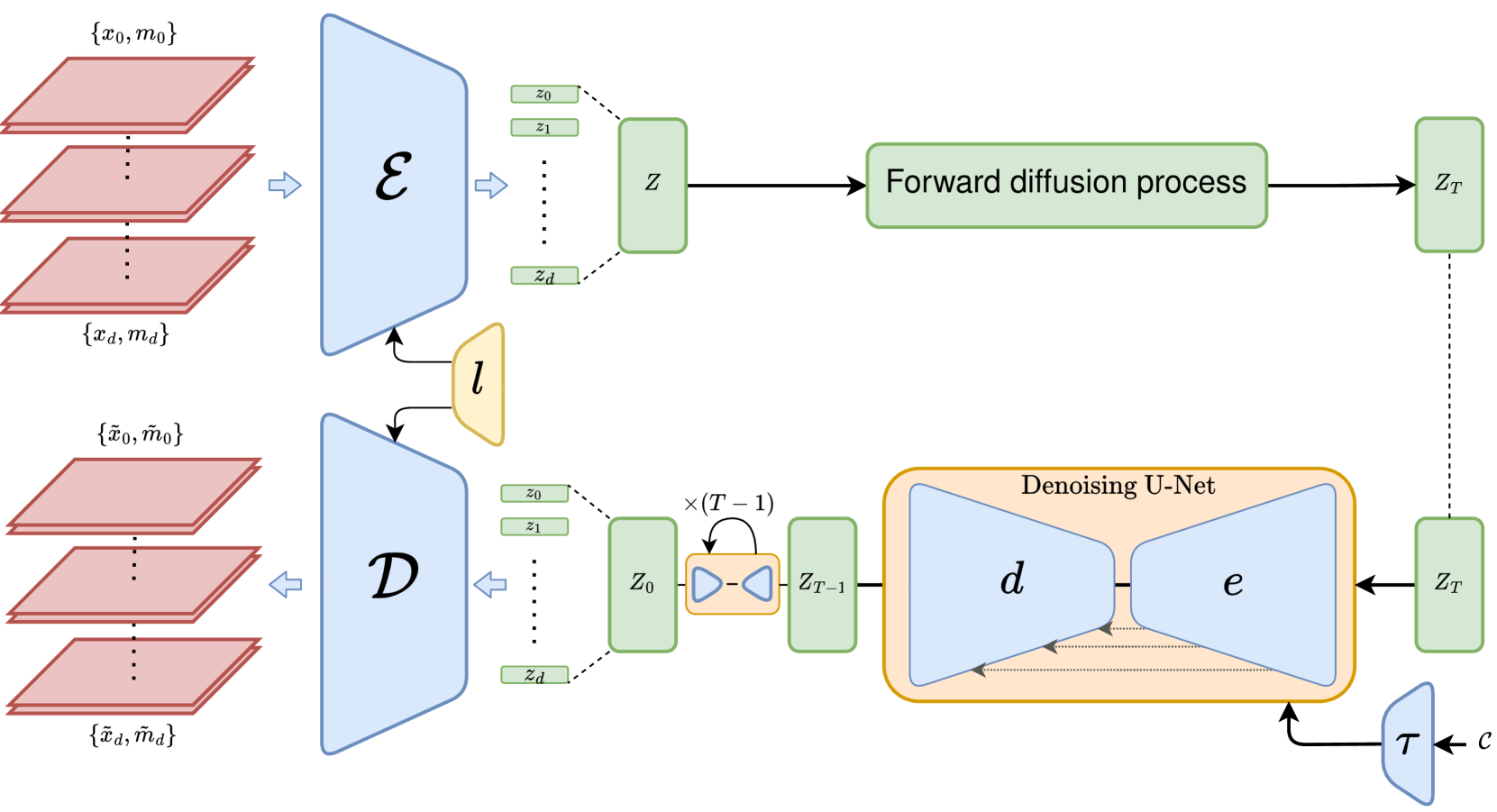
Non-contrast CT (NCCT) imaging may reduce image contrast and anatomical visibility, potentially increasing diagnostic uncertainty. In contrast, contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) facilitates the observation of regions of interest (ROI). Leading generative models, especially the conditional diffusion model, demonstrate remarkable capabilities in medical image modality transformation. Typical conditional diffusion models commonly generate images with guidance of segmentation labels for medical modal transformation. Limited access to authentic guidance and its low cardinality can pose challenges to the practical clinical application of conditional diffusion models. To achieve an equilibrium of generative quality and clinical practices, we propose a novel Syncretic generative model based on the latent diffusion model for medical image translation (S$^2$LDM), which can realize high-fidelity reconstruction without demand of additional condition during inference. S$^2$LDM enhances the similarity in distinct modal images via syncretic encoding and diffusing, promoting amalgamated information in the latent space and generating medical images with more details in contrast-enhanced regions. However, syncretic latent spaces in the frequency domain tend to favor lower frequencies, commonly locate in identical anatomic structures. Thus, S$^2$LDM applies adaptive similarity loss and dynamic similarity to guide the generation and supplements the shortfall in high-frequency details throughout the training process. Quantitative experiments confirm the effectiveness of our approach in medical image translation. Our code will release lately.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

MediSyn: Text-Guided Diffusion Models for Broad Medical 2D and 3D Image Synthesis
Joseph Cho, Cyril Zakka, Rohan Shad, Ross Wightman, Akshay Chaudhari, William Hiesinger

0
0
Diffusion models have recently gained significant traction due to their ability to generate high-fidelity and diverse images and videos conditioned on text prompts. In medicine, this application promises to address the critical challenge of data scarcity, a consequence of barriers in data sharing, stringent patient privacy regulations, and disparities in patient population and demographics. By generating realistic and varying medical 2D and 3D images, these models offer a rich, privacy-respecting resource for algorithmic training and research. To this end, we introduce MediSyn, a pair of instruction-tuned text-guided latent diffusion models with the ability to generate high-fidelity and diverse medical 2D and 3D images across specialties and modalities. Through established metrics, we show significant improvement in broad medical image and video synthesis guided by text prompts.
5/17/2024
3D MRI Synthesis with Slice-Based Latent Diffusion Models: Improving Tumor Segmentation Tasks in Data-Scarce Regimes
Aghiles Kebaili, J'er^ome Lapuyade-Lahorgue, Pierre Vera, Su Ruan

0
0
Despite the increasing use of deep learning in medical image segmentation, the limited availability of annotated training data remains a major challenge due to the time-consuming data acquisition and privacy regulations. In the context of segmentation tasks, providing both medical images and their corresponding target masks is essential. However, conventional data augmentation approaches mainly focus on image synthesis. In this study, we propose a novel slice-based latent diffusion architecture designed to address the complexities of volumetric data generation in a slice-by-slice fashion. This approach extends the joint distribution modeling of medical images and their associated masks, allowing a simultaneous generation of both under data-scarce regimes. Our approach mitigates the computational complexity and memory expensiveness typically associated with diffusion models. Furthermore, our architecture can be conditioned by tumor characteristics, including size, shape, and relative position, thereby providing a diverse range of tumor variations. Experiments on a segmentation task using the BRATS2022 confirm the effectiveness of the synthesized volumes and masks for data augmentation.
6/11/2024
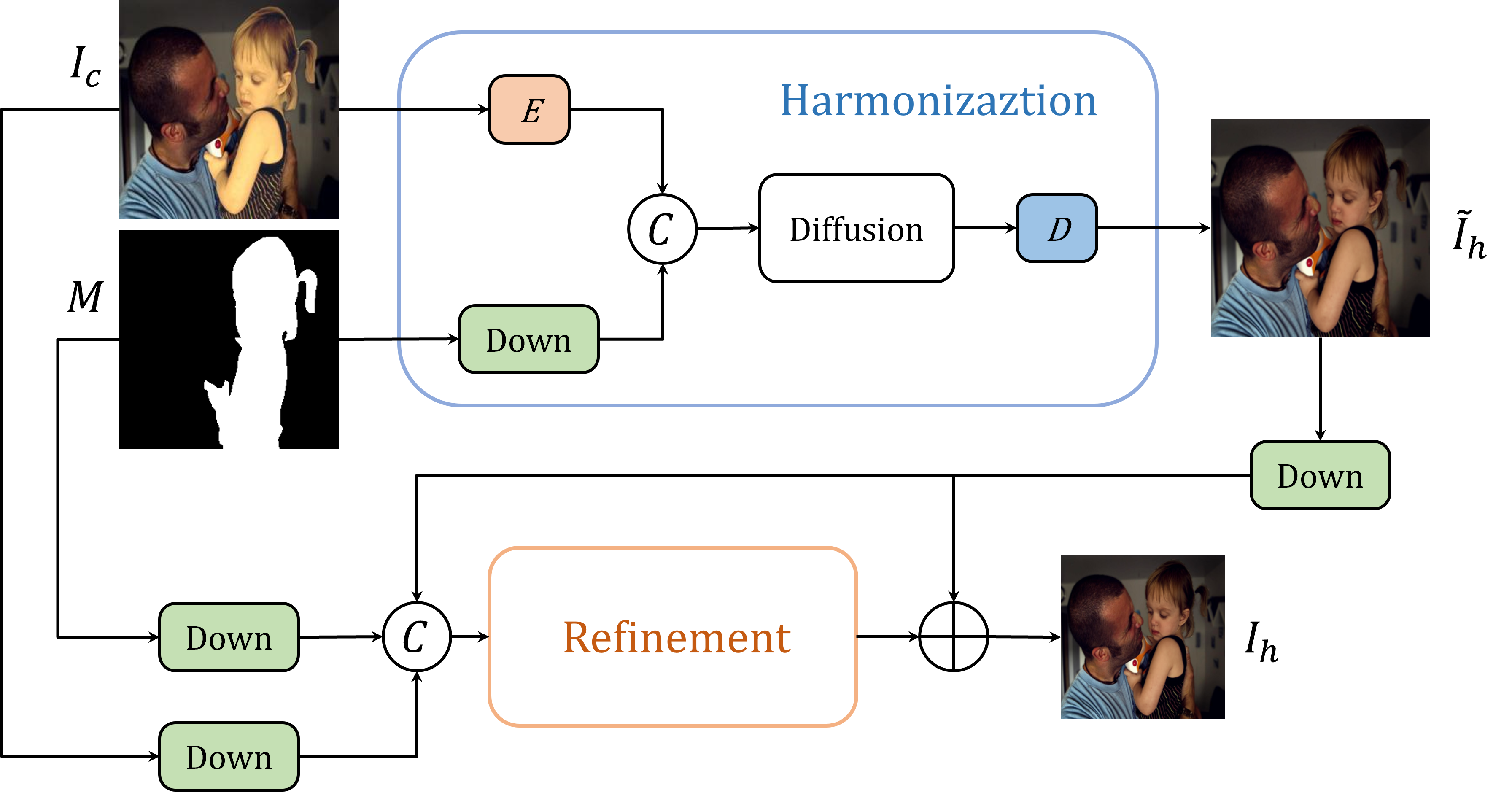
DiffHarmony: Latent Diffusion Model Meets Image Harmonization
Pengfei Zhou, Fangxiang Feng, Xiaojie Wang

0
0
Image harmonization, which involves adjusting the foreground of a composite image to attain a unified visual consistency with the background, can be conceptualized as an image-to-image translation task. Diffusion models have recently promoted the rapid development of image-to-image translation tasks . However, training diffusion models from scratch is computationally intensive. Fine-tuning pre-trained latent diffusion models entails dealing with the reconstruction error induced by the image compression autoencoder, making it unsuitable for image generation tasks that involve pixel-level evaluation metrics. To deal with these issues, in this paper, we first adapt a pre-trained latent diffusion model to the image harmonization task to generate the harmonious but potentially blurry initial images. Then we implement two strategies: utilizing higher-resolution images during inference and incorporating an additional refinement stage, to further enhance the clarity of the initially harmonized images. Extensive experiments on iHarmony4 datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method. The code and model will be made publicly available at https://github.com/nicecv/DiffHarmony .
4/10/2024

Towards Learning Contrast Kinetics with Multi-Condition Latent Diffusion Models
Richard Osuala, Daniel Lang, Preeti Verma, Smriti Joshi, Apostolia Tsirikoglou, Grzegorz Skorupko, Kaisar Kushibar, Lidia Garrucho, Walter H. L. Pinaya, Oliver Diaz, Julia Schnabel, Karim Lekadir

0
0
Contrast agents in dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging allow to localize tumors and observe their contrast kinetics, which is essential for cancer characterization and respective treatment decision-making. However, contrast agent administration is not only associated with adverse health risks, but also restricted for patients during pregnancy, and for those with kidney malfunction, or other adverse reactions. With contrast uptake as key biomarker for lesion malignancy, cancer recurrence risk, and treatment response, it becomes pivotal to reduce the dependency on intravenous contrast agent administration. To this end, we propose a multi-conditional latent diffusion model capable of acquisition time-conditioned image synthesis of DCE-MRI temporal sequences. To evaluate medical image synthesis, we additionally propose and validate the Fr'echet radiomics distance as an image quality measure based on biomarker variability between synthetic and real imaging data. Our results demonstrate our method's ability to generate realistic multi-sequence fat-saturated breast DCE-MRI and uncover the emerging potential of deep learning based contrast kinetics simulation. We publicly share our accessible codebase at https://github.com/RichardObi/ccnet and provide a user-friendly library for Fr'echet radiomics distance calculation at https://pypi.org/project/frd-score.
5/2/2024