Simulating Policy Impacts: Developing a Generative Scenario Writing Method to Evaluate the Perceived Effects of Regulation
2405.09679

0
0
Abstract
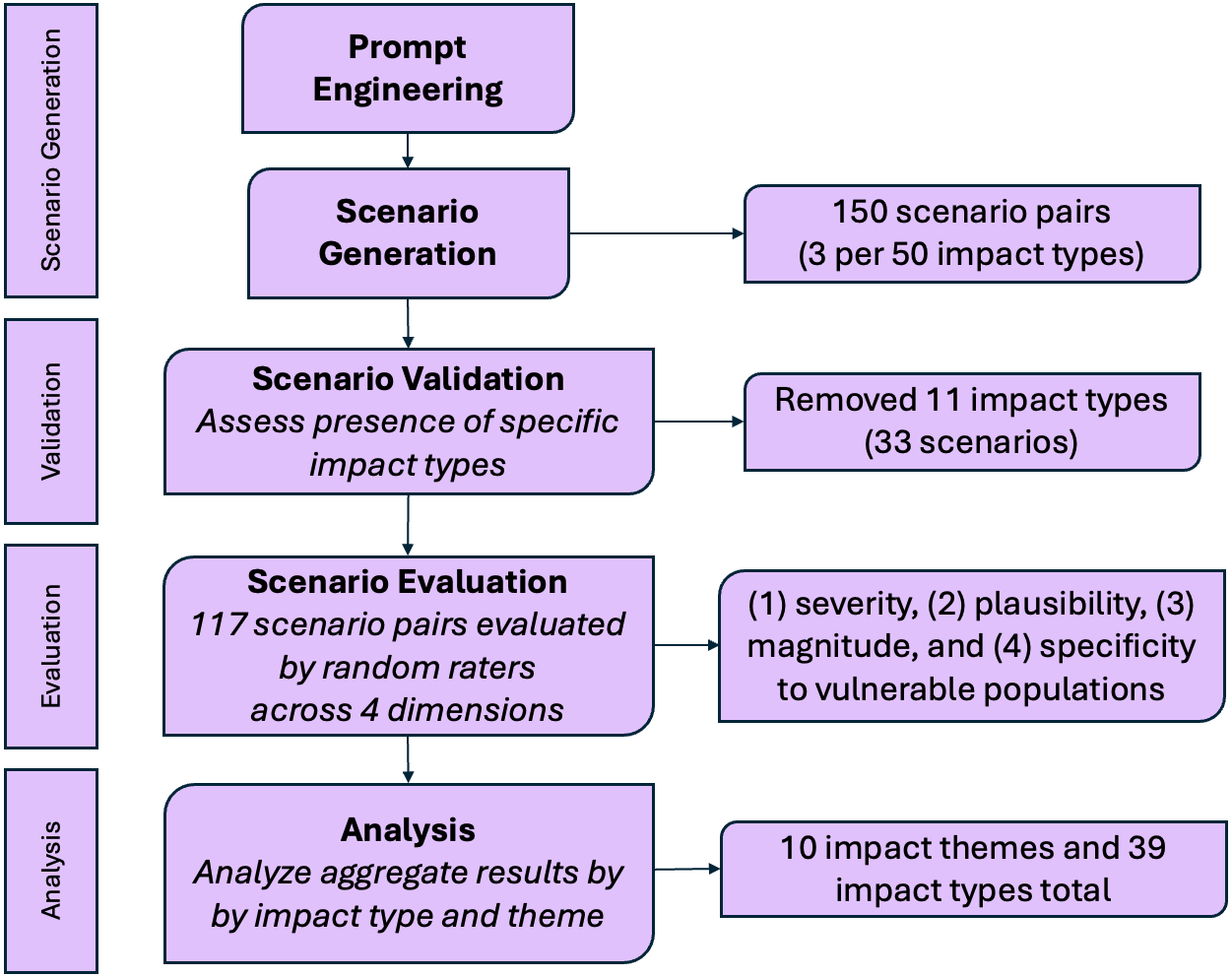
The rapid advancement of AI technologies yields numerous future impacts on individuals and society. Policy-makers are therefore tasked to react quickly and establish policies that mitigate those impacts. However, anticipating the effectiveness of policies is a difficult task, as some impacts might only be observable in the future and respective policies might not be applicable to the future development of AI. In this work we develop a method for using large language models (LLMs) to evaluate the efficacy of a given piece of policy at mitigating specified negative impacts. We do so by using GPT-4 to generate scenarios both pre- and post-introduction of policy and translating these vivid stories into metrics based on human perceptions of impacts. We leverage an already established taxonomy of impacts of generative AI in the media environment to generate a set of scenario pairs both mitigated and non-mitigated by the transparency legislation of Article 50 of the EU AI Act. We then run a user study (n=234) to evaluate these scenarios across four risk-assessment dimensions: severity, plausibility, magnitude, and specificity to vulnerable populations. We find that this transparency legislation is perceived to be effective at mitigating harms in areas such as labor and well-being, but largely ineffective in areas such as social cohesion and security. Through this case study on generative AI harms we demonstrate the efficacy of our method as a tool to iterate on the effectiveness of policy on mitigating various negative impacts. We expect this method to be useful to researchers or other stakeholders who want to brainstorm the potential utility of different pieces of policy or other mitigation strategies.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a novel "generative scenario writing method" to evaluate the perceived effects of policy regulations.
- The method involves simulating policy impacts by having participants write fictional narratives about how a new regulation might affect their lives and communities.
- The goal is to provide policymakers with a better understanding of how regulations could be interpreted and experienced by the public.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers developed a new way to study how people might react to new rules or laws. Instead of just asking people what they think, the researchers had them write stories about how a fictional new regulation could impact their lives and communities. This "generative scenario writing" approach allows the researchers to get a more nuanced, real-world understanding of how policies could be perceived and experienced by the public.
The key idea is that by having people create their own narratives, the researchers can uncover hidden assumptions, concerns, and interpretations that might not come up in a traditional survey or interview. This can help policymakers anticipate the actual effects of regulations, rather than relying only on top-down economic modeling or expert analysis.
For example, a link to "Psychosocial Impacts of Generative AI Harms" might explore how this method could reveal how new AI regulations could be seen through the lens of individual lives and communities. A link to "Impact of Generative Artificial Intelligence on Socioeconomic Inequalities: A Policy Perspective" might show how it could uncover differential impacts across diverse populations.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes a "generative scenario writing" method for evaluating the perceived effects of policy regulations. In this approach, participants are asked to write fictional narratives about how a new hypothetical regulation could impact their lives and communities.
The researchers recruited 120 participants and divided them into two groups. One group was asked to write scenarios about a new regulation restricting the use of facial recognition technology, while the other group wrote about a regulation banning the use of AI-generated text in social media. After writing the scenarios, participants answered survey questions about their perceptions of the regulations.
The narratives produced through this process were then analyzed using qualitative coding techniques to identify common themes, concerns, and interpretations. This allowed the researchers to gain insights into how the public might actually experience and react to the proposed policies, going beyond traditional top-down policy analysis.
The findings suggest that the generative scenario writing method can uncover nuanced public perspectives that may not emerge from other evaluation approaches. For example, participants expressed concerns about how facial recognition bans could impact public safety and security, or how AI text restrictions could affect free speech and creativity. A link to "The Frontier of AI Ethics: Anticipating and Evaluating Societal Impacts" might further contextualize this within the broader challenges of assessing the societal impacts of AI systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper makes a compelling case for the value of the generative scenario writing method in policy evaluation. By allowing participants to imagine and narrate the potential impacts of regulations, the researchers were able to surface a richer understanding of public perceptions than what might be obtained through traditional survey or interview techniques.
However, the study does have some limitations. The sample size, while reasonable for a qualitative study, is still relatively small, and the participants may not be representative of the broader population. Additionally, the fictional nature of the scenarios means that people's stated reactions may not fully align with how they would actually respond to real-world policy changes.
Further research could explore ways to validate the findings of the generative scenario writing method, such as by comparing the insights gained to actual behavioral data or longitudinal studies of policy implementation. A link to "The Evolution of Learning: Assessing the Transformative Impact of Generative AI" might suggest ways to extend this approach to the evaluation of generative AI systems and their societal impacts.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel "generative scenario writing" approach for evaluating the perceived effects of policy regulations. By having participants create fictional narratives about how new rules could impact their lives and communities, the researchers were able to uncover nuanced public perspectives that may not emerge from traditional top-down policy analysis.
The findings suggest that this method can provide valuable insights to policymakers, helping them anticipate how regulations might be interpreted and experienced by the public. As governments and organizations grapple with the challenges of regulating emerging technologies like AI, a link to "My Future, My Chatbot: A Scenario-Driven User" highlights the importance of developing innovative tools to understand and address the societal impacts of these transformative innovations.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🏅
Evaluating the Capabilities of LLMs for Supporting Anticipatory Impact Assessment
Mowafak Allaham, Nicholas Diakopoulos

0
0
Gaining insight into the potential negative impacts of emerging Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies in society is a challenge for implementing anticipatory governance approaches. One approach to produce such insight is to use Large Language Models (LLMs) to support and guide experts in the process of ideating and exploring the range of undesirable consequences of emerging technologies. However, performance evaluations of LLMs for such tasks are still needed, including examining the general quality of generated impacts but also the range of types of impacts produced and resulting biases. In this paper, we demonstrate the potential for generating high-quality and diverse impacts of AI in society by fine-tuning completion models (GPT-3 and Mistral-7B) on a diverse sample of articles from news media and comparing those outputs to the impacts generated by instruction-based (GPT-4 and Mistral-7B-Instruct) models. We examine the generated impacts for coherence, structure, relevance, and plausibility and find that the generated impacts using Mistral-7B, a small open-source model fine-tuned on impacts from the news media, tend to be qualitatively on par with impacts generated using a more capable and larger scale model such as GPT-4. Moreover, we find that impacts produced by instruction-based models had gaps in the production of certain categories of impacts in comparison to fine-tuned models. This research highlights a potential bias in the range of impacts generated by state-of-the-art LLMs and the potential of aligning smaller LLMs on news media as a scalable alternative to generate high quality and more diverse impacts in support of anticipatory governance approaches.
5/22/2024
🤖
The Psychosocial Impacts of Generative AI Harms
Faye-Marie Vassel, Evan Shieh, Cassidy R. Sugimoto, Thema Monroe-White

0
0
The rapid emergence of generative Language Models (LMs) has led to growing concern about the impacts that their unexamined adoption may have on the social well-being of diverse user groups. Meanwhile, LMs are increasingly being adopted in K-20 schools and one-on-one student settings with minimal investigation of potential harms associated with their deployment. Motivated in part by real-world/everyday use cases (e.g., an AI writing assistant) this paper explores the potential psychosocial harms of stories generated by five leading LMs in response to open-ended prompting. We extend findings of stereotyping harms analyzing a total of 150K 100-word stories related to student classroom interactions. Examining patterns in LM-generated character demographics and representational harms (i.e., erasure, subordination, and stereotyping) we highlight particularly egregious vignettes, illustrating the ways LM-generated outputs may influence the experiences of users with marginalized and minoritized identities, and emphasizing the need for a critical understanding of the psychosocial impacts of generative AI tools when deployed and utilized in diverse social contexts.
5/6/2024
🐍
The impact of generative artificial intelligence on socioeconomic inequalities and policy making
Valerio Capraro, Austin Lentsch, Daron Acemoglu, Selin Akgun, Aisel Akhmedova, Ennio Bilancini, Jean-Franc{c}ois Bonnefon, Pablo Bra~nas-Garza, Luigi Butera, Karen M. Douglas, Jim A. C. Everett, Gerd Gigerenzer, Christine Greenhow, Daniel A. Hashimoto, Julianne Holt-Lunstad, Jolanda Jetten, Simon Johnson, Chiara Longoni, Pete Lunn, Simone Natale, Iyad Rahwan, Neil Selwyn, Vivek Singh, Siddharth Suri, Jennifer Sutcliffe, Joe Tomlinson, Sander van der Linden, Paul A. M. Van Lange, Friederike Wall, Jay J. Van Bavel, Riccardo Viale

0
0
Generative artificial intelligence has the potential to both exacerbate and ameliorate existing socioeconomic inequalities. In this article, we provide a state-of-the-art interdisciplinary overview of the potential impacts of generative AI on (mis)information and three information-intensive domains: work, education, and healthcare. Our goal is to highlight how generative AI could worsen existing inequalities while illuminating how AI may help mitigate pervasive social problems. In the information domain, generative AI can democratize content creation and access, but may dramatically expand the production and proliferation of misinformation. In the workplace, it can boost productivity and create new jobs, but the benefits will likely be distributed unevenly. In education, it offers personalized learning, but may widen the digital divide. In healthcare, it might improve diagnostics and accessibility, but could deepen pre-existing inequalities. In each section we cover a specific topic, evaluate existing research, identify critical gaps, and recommend research directions, including explicit trade-offs that complicate the derivation of a priori hypotheses. We conclude with a section highlighting the role of policymaking to maximize generative AI's potential to reduce inequalities while mitigating its harmful effects. We discuss strengths and weaknesses of existing policy frameworks in the European Union, the United States, and the United Kingdom, observing that each fails to fully confront the socioeconomic challenges we have identified. We propose several concrete policies that could promote shared prosperity through the advancement of generative AI. This article emphasizes the need for interdisciplinary collaborations to understand and address the complex challenges of generative AI.
5/7/2024
🤖
Frontier AI Ethics: Anticipating and Evaluating the Societal Impacts of Generative Agents
Seth Lazar

0
0
Some have criticised Generative AI Systems for replicating the familiar pathologies of already widely-deployed AI systems. Other critics highlight how they foreshadow vastly more powerful future systems, which might threaten humanity's survival. The first group says there is nothing new here; the other looks through the present to a perhaps distant horizon. In this paper, I instead pay attention to what makes these particular systems distinctive: both their remarkable scientific achievement, and the most likely and consequential ways in which they will change society over the next five to ten years. In particular, I explore the potential societal impacts and normative questions raised by the looming prospect of 'Generative Agents', in which multimodal large language models (LLMs) form the executive centre of complex, tool-using AI systems that can take unsupervised sequences of actions towards some goal.
4/11/2024