Sky-GVIO: an enhanced GNSS/INS/Vision navigation with FCN-based sky-segmentation in urban canyon

0
🤷
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Accurate and reliable positioning is essential for autonomous driving
- In urban environments, challenges like non-line-of-sight (NLOS) from buildings, trees, and structures can degrade positioning
- The paper proposes a sky-view image segmentation algorithm and a novel NLOS detection and mitigation (S-NDM) algorithm to address these challenges
- The system, called Sky-GVIO, combines Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), Inertial Measurement Units (IMU), and visual features for continuous and accurate positioning
- The system also harmonizes Single Point Positioning (SPP) and Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) approaches for versatility and resilience
Plain English Explanation
Autonomous vehicles need to know their precise location at all times to navigate safely. However, in dense urban areas with tall buildings, trees, and other structures, the signals from GPS satellites can get blocked, making it difficult for the vehicle to determine its position accurately.
To address this problem, the researchers developed a new algorithm that uses images of the sky to detect when the GPS signal is being obstructed. By combining this sky-view information with data from other sensors like inertial measurement units and cameras, the system can continuously track the vehicle's location, even in challenging urban environments.
The system also blends two different positioning techniques - single point positioning (SPP) and real-time kinematic (RTK) - to provide both meter-level accuracy under normal conditions and sub-decimeter precision when more detailed positioning is needed. This makes the system more versatile and reliable for autonomous driving applications.
The researchers have also made the dataset of sky-view images they used publicly available, so other researchers can build upon their work.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a sky-view images segmentation algorithm based on Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) for GNSS NLOS detection. Building on this, a novel NLOS detection and mitigation algorithm (S-NDM) is extended to a tightly coupled GNSS, IMU, and visual feature system called Sky-GVIO.
The Sky-GVIO system harmonizes Single Point Positioning (SPP) with Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) methodologies to bolster its operational versatility and resilience. In urban canyon environments, the positioning performance of the S-NDM algorithm is evaluated under different tightly coupled SPP-related and RTK-related models.
The results show that the Sky-GVIO system achieves meter-level accuracy under SPP mode and sub-decimeter precision with RTK, outperforming GNSS/INS/Vision frameworks without the S-NDM component. Additionally, the sky-view image dataset has been made publicly available for further research.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive approach to addressing the challenges of accurate positioning in urban environments. The use of sky-view image segmentation and the S-NDM algorithm to detect and mitigate the effects of NLOS is a novel and promising solution.
However, the paper does not fully address the computational and processing requirements of the proposed system. Integrating multiple sensor modalities and positioning techniques may increase the complexity and resource demands, which could be a limitation for real-world deployment in autonomous vehicles.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss the potential impact of environmental factors, such as weather conditions or seasonal changes, on the performance of the sky-view image segmentation and NLOS detection. Further research may be needed to evaluate the system's robustness under diverse urban environments and varying conditions.
Conclusion
The research presented in this paper offers a significant step towards achieving accurate and continuous positioning for autonomous driving in complex urban environments. The combination of sky-view image analysis, NLOS detection and mitigation, and the harmonization of SPP and RTK techniques demonstrates a promising approach to overcoming the limitations of standalone sensor systems.
By making the sky-view image dataset publicly available, the researchers have opened up opportunities for further exploration and advancements in this field. As autonomous driving technologies continue to evolve, the insights and methods presented in this paper may contribute to the development of more reliable and resilient positioning systems, ultimately enhancing the safety and performance of self-driving vehicles.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤷

0
Sky-GVIO: an enhanced GNSS/INS/Vision navigation with FCN-based sky-segmentation in urban canyon
Jingrong Wang, Bo Xu, Ronghe Jin, Shoujian Zhang, Kefu Gao, Jingnan Liu
Accurate, continuous, and reliable positioning is a critical component of achieving autonomous driving. However, in complex urban canyon environments, the vulnerability of a stand-alone sensor and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) caused by high buildings, trees, and elevated structures seriously affect positioning results. To address these challenges, a sky-view images segmentation algorithm based on Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) is proposed for GNSS NLOS detection. Building upon this, a novel NLOS detection and mitigation algorithm (named S-NDM) is extended to the tightly coupled Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), Inertial Measurement Units (IMU), and visual feature system which is called Sky-GVIO, with the aim of achieving continuous and accurate positioning in urban canyon environments. Furthermore, the system harmonizes Single Point Positioning (SPP) with Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) methodologies to bolster its operational versatility and resilience. In urban canyon environments, the positioning performance of S-NDM algorithm proposed in this paper is evaluated under different tightly coupled SPP-related and RTK-related models. The results exhibit that Sky-GVIO system achieves meter-level accuracy under SPP mode and sub-decimeter precision with RTK, surpassing the performance of GNSS/INS/Vision frameworks devoid of S-NDM. Additionally, the sky-view image dataset, inclusive of training and evaluation subsets, has been made publicly accessible for scholarly exploration at https://github.com/whuwangjr/sky-view-images .
Read more8/6/2024

0
Square-Root Inverse Filter-based GNSS-Visual-Inertial Navigation
Jun Hu, Xiaoming Lang, Feng Zhang, Yinian Mao, Guoquan Huang
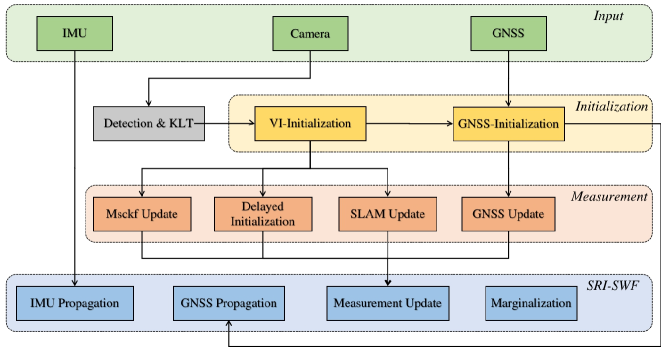
While Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is often used to provide global positioning if available, its intermittency and/or inaccuracy calls for fusion with other sensors. In this paper, we develop a novel GNSS-Visual-Inertial Navigation System (GVINS) that fuses visual, inertial, and raw GNSS measurements within the square-root inverse sliding window filtering (SRI-SWF) framework in a tightly coupled fashion, which thus is termed SRI-GVINS. In particular, for the first time, we deeply fuse the GNSS pseudorange, Doppler shift, single-differenced pseudorange, and double-differenced carrier phase measurements, along with the visual-inertial measurements. Inherited from the SRI-SWF, the proposed SRI-GVINS gains significant numerical stability and computational efficiency over the start-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we propose to use a filter to sequentially initialize the reference frame transformation till converges, rather than collecting measurements for batch optimization. We also perform online calibration of GNSS-IMU extrinsic parameters to mitigate the possible extrinsic parameter degradation. The proposed SRI-GVINS is extensively evaluated on our own collected UAV datasets and the results demonstrate that the proposed method is able to suppress VIO drift in real-time and also show the effectiveness of online GNSS-IMU extrinsic calibration. The experimental validation on the public datasets further reveals that the proposed SRI-GVINS outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of both accuracy and efficiency.
Read more5/20/2024


0
Geospecific View Generation -- Geometry-Context Aware High-resolution Ground View Inference from Satellite Views
Ningli Xu, Rongjun Qin
Predicting realistic ground views from satellite imagery in urban scenes is a challenging task due to the significant view gaps between satellite and ground-view images. We propose a novel pipeline to tackle this challenge, by generating geospecifc views that maximally respect the weak geometry and texture from multi-view satellite images. Different from existing approaches that hallucinate images from cues such as partial semantics or geometry from overhead satellite images, our method directly predicts ground-view images at geolocation by using a comprehensive set of information from the satellite image, resulting in ground-level images with a resolution boost at a factor of ten or more. We leverage a novel building refinement method to reduce geometric distortions in satellite data at ground level, which ensures the creation of accurate conditions for view synthesis using diffusion networks. Moreover, we proposed a novel geospecific prior, which prompts distribution learning of diffusion models to respect image samples that are closer to the geolocation of the predicted images. We demonstrate our pipeline is the first to generate close-to-real and geospecific ground views merely based on satellite images.
Read more9/16/2024


0
A Semantic Segmentation-guided Approach for Ground-to-Aerial Image Matching
Francesco Pro, Nikolaos Dionelis, Luca Maiano, Bertrand Le Saux, Irene Amerini
Nowadays the accurate geo-localization of ground-view images has an important role across domains as diverse as journalism, forensics analysis, transports, and Earth Observation. This work addresses the problem of matching a query ground-view image with the corresponding satellite image without GPS data. This is done by comparing the features from a ground-view image and a satellite one, innovatively leveraging the corresponding latter's segmentation mask through a three-stream Siamese-like network. The proposed method, Semantic Align Net (SAN), focuses on limited Field-of-View (FoV) and ground panorama images (images with a FoV of 360{deg}). The novelty lies in the fusion of satellite images in combination with their semantic segmentation masks, aimed at ensuring that the model can extract useful features and focus on the significant parts of the images. This work shows how SAN through semantic analysis of images improves the performance on the unlabelled CVUSA dataset for all the tested FoVs.
Read more5/24/2024