A Spatio-Temporal based Frame Indexing Algorithm for QoS Improvement in Live Low-Motion Video Streaming

0
🔍
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Real-time video streaming is becoming increasingly popular
- Ensuring efficient use of network bandwidth without compromising video quality is a key challenge
- The paper presents a spatio-temporal frame indexing approach to detect and eliminate redundancy in video frames before transmission
Plain English Explanation
The paper addresses the challenge of delivering high-quality real-time video streams over networks while efficiently using the available bandwidth. The proposed approach uses spatio-temporal frame indexing to identify and remove redundant video frames before transmitting them to clients. This helps reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent over the network without compromising the overall video quality.
The researchers evaluated the performance of their technique using two scenarios: standard video and local low-motion video. The results show that the proposed method achieved a 5.13% and 15.8% improvement in buffer size and compression ratio for standard videos, and a 5% and 15.6% improvement for local low-motion videos. However, there was a trade-off in terms of the time it takes to process the frames, with the proposed approach performing slightly worse than the baseline techniques.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a spatio-temporal frame indexing approach to detect and eliminate redundant video frames before transmission from the server to clients. This helps optimize the use of network bandwidth without compromising the Quality of Service (QoS) of the video stream.
The researchers consider two scenarios: standard videos and local low-motion videos. They evaluate the performance of the proposed approach in terms of buffer size, compression ratio, and frame-processing time. The results show that the spatio-temporal indexing method outperforms the baseline techniques in terms of buffer size and compression ratio, with improvements of up to 15.8%. However, there is a trade-off in terms of the time it takes to process the frames, where the proposed approach performs slightly worse than the baseline.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to optimizing real-time video streaming by leveraging spatio-temporal redundancy in video frames. However, the researchers acknowledge that there is a trade-off in terms of the frame-processing time. It would be interesting to see if this trade-off could be addressed through further optimizations or by leveraging advanced video processing techniques.
Additionally, the paper only evaluates the approach on two specific scenarios: standard videos and local low-motion videos. It would be valuable to assess the performance of the technique on a wider range of video content, including high-motion scenes and complex video events, to better understand its broader applicability and limitations.
Conclusion
The paper presents a spatio-temporal frame indexing approach to optimize real-time video streaming by detecting and eliminating redundant video frames before transmission. The results demonstrate that this technique can significantly improve the buffer size and compression ratio without compromising the overall video quality. While there is a trade-off in terms of frame-processing time, the proposed method shows promise as a way to enhance the efficiency of real-time video delivery over networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔍

0
A Spatio-Temporal based Frame Indexing Algorithm for QoS Improvement in Live Low-Motion Video Streaming
Adewale Emmanuel Adedokun, Muhammed Bashir Abdulrazak, Muyideen Momoh Omuya, Habeeb BelloSalau, Bashir Olaniyi Sadiq
Real-time video life streaming of events over a network continued to gain more popularity among the populace. However, there is need to ensure the judicious utilization of allocated bandwidth without compromising the Quality of Service (QoS) of the system. In this regard, this paper presents an approach based on spatio-temporal frame indexing that detects and eliminate redundancy within and across captured frame, prior transmission from the server to clients. The standard and local low motion videos were the two scenarios considered in evaluating the performance of the proposed algorithm. Results obtained showed that the proposed approach achieved an improvement of 5.13%, 15.8% and 5%, 15.6% improvement in terms of the buffer size and compression ratio. Though with a tradeoff of the frame-built time, where both the standard and local frame indexing outperforms the proposed scheme with 10.8% and 8.71% respectively.
Read more5/1/2024


0
Online Video Quality Enhancement with Spatial-Temporal Look-up Tables
Zefan Qu, Xinyang Jiang, Yifan Yang, Dongsheng Li, Cairong Zhao
Low latency rates are crucial for online video-based applications, such as video conferencing and cloud gaming, which make improving video quality in online scenarios increasingly important. However, existing quality enhancement methods are limited by slow inference speed and the requirement for temporal information contained in future frames, making it challenging to deploy them directly in online tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel method, STLVQE, specifically designed to address the rarely studied online video quality enhancement (Online-VQE) problem. Our STLVQE designs a new VQE framework which contains a Module-Agnostic Feature Extractor that greatly reduces the redundant computations and redesign the propagation, alignment, and enhancement module of the network. A Spatial-Temporal Look-up Tables (STL) is proposed, which extracts spatial-temporal information in videos while saving substantial inference time. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to exploit the LUT structure to extract temporal information in video tasks. Extensive experiments on the MFQE 2.0 dataset demonstrate that our STLVQE achieves a satisfactory performance-speed trade-off.
Read more7/11/2024

0
Space-time Reinforcement Network for Video Object Segmentation
Yadang Chen, Wentao Zhu, Zhi-Xin Yang, Enhua Wu
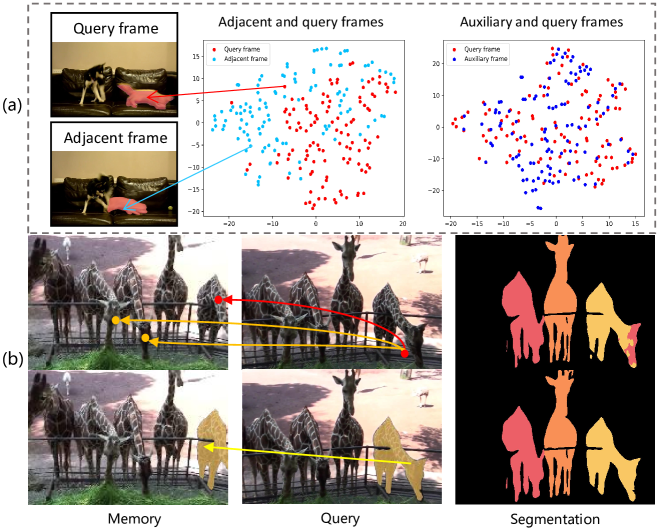
Recently, video object segmentation (VOS) networks typically use memory-based methods: for each query frame, the mask is predicted by space-time matching to memory frames. Despite these methods having superior performance, they suffer from two issues: 1) Challenging data can destroy the space-time coherence between adjacent video frames. 2) Pixel-level matching will lead to undesired mismatching caused by the noises or distractors. To address the aforementioned issues, we first propose to generate an auxiliary frame between adjacent frames, serving as an implicit short-temporal reference for the query one. Next, we learn a prototype for each video object and prototype-level matching can be implemented between the query and memory. The experiment demonstrated that our network outperforms the state-of-the-art method on the DAVIS 2017, achieving a J&F score of 86.4%, and attains a competitive result 85.0% on YouTube VOS 2018. In addition, our network exhibits a high inference speed of 32+ FPS.
Read more5/8/2024


0
Compressed Video Quality Enhancement with Temporal Group Alignment and Fusion
Qiang Zhu, Yajun Qiu, Yu Liu, Shuyuan Zhu, Bing Zeng
In this paper, we propose a temporal group alignment and fusion network to enhance the quality of compressed videos by using the long-short term correlations between frames. The proposed model consists of the intra-group feature alignment (IntraGFA) module, the inter-group feature fusion (InterGFF) module, and the feature enhancement (FE) module. We form the group of pictures (GoP) by selecting frames from the video according to their temporal distances to the target enhanced frame. With this grouping, the composed GoP can contain either long- or short-term correlated information of neighboring frames. We design the IntraGFA module to align the features of frames of each GoP to eliminate the motion existing between frames. We construct the InterGFF module to fuse features belonging to different GoPs and finally enhance the fused features with the FE module to generate high-quality video frames. The experimental results show that our proposed method achieves up to 0.05dB gain and lower complexity compared to the state-of-the-art method.
Read more6/17/2024