Story3D-Agent: Exploring 3D Storytelling Visualization with Large Language Models

0
💬
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This document provides instructions for authors using LaTeX to prepare an anonymous submission for AAAI Press.
- It covers guidelines for the camera-ready version and copyright information.
Plain English Explanation
The provided document is a set of instructions for authors who want to submit a paper to AAAI Press using the LaTeX typesetting system. It explains the steps required to ensure the submission remains anonymous during the review process, as well as the guidelines for preparing the final camera-ready version of the paper. The instructions also cover the copyright requirements authors must follow.
The key points are:
- Preparing an Anonymous Submission: Authors must remove their names and other identifying information from the paper to maintain anonymity during the review process.
- Camera-Ready Guidelines: There are specific formatting and layout requirements for the final version of the paper that will be published.
- Copyright: Authors must agree to transfer the copyright of their work to AAAI Press upon acceptance of their paper.
The instructions aim to ensure a smooth and standardized submission and publication process for AAAI Press.
Technical Explanation
The document outlines the guidelines for authors using LaTeX to prepare an anonymous submission for AAAI Press. It covers three main sections:
-
Preparing an Anonymous Submission: This section instructs authors on how to remove any identifying information from their paper, such as their names and affiliations, to maintain anonymity during the review process. It provides specific steps to take within the LaTeX code to ensure the paper is properly anonymized.
-
Camera-Ready Guidelines: This section details the formatting and layout requirements for the final camera-ready version of the paper. It covers aspects like page size, margins, font sizes, and the placement of figures and tables.
-
Copyright: This section explains that authors must agree to transfer the copyright of their work to AAAI Press upon acceptance of their paper. This is a standard practice for many academic publishers.
The instructions aim to ensure a consistent and professional presentation of accepted papers, while also protecting the anonymity of authors during the review process.
Critical Analysis
The instructions provided in this document are comprehensive and well-structured, covering the key aspects of preparing an anonymous submission and the final camera-ready version for AAAI Press. The guidelines seem reasonable and aligned with common practices in academic publishing.
One potential limitation is that the instructions are specifically tailored for authors using the LaTeX typesetting system. While LaTeX is widely used in the research community, some authors may prefer to use other tools, such as Microsoft Word, to prepare their submissions. It would be helpful if the instructions also provided guidance for authors using alternative software.
Additionally, the document does not address any potential issues or caveats that authors may encounter during the submission or publication process. It would be valuable for the instructions to include information on troubleshooting common problems or providing resources for authors to seek support if needed.
Conclusion
The AAAI Press Anonymous Submission Instructions for Authors Using LaTeX provide a clear and comprehensive guide for researchers submitting their work to AAAI Press. By following these guidelines, authors can ensure that their submissions maintain anonymity during the review process and meet the required formatting and copyright standards for publication.
The instructions cover the essential elements of preparing an anonymous submission, adhering to camera-ready guidelines, and understanding the copyright requirements. While the focus is on LaTeX users, the general principles and best practices outlined in the document can be applicable to authors using other tools as well.
Overall, these instructions serve as a valuable resource for researchers seeking to publish their work through AAAI Press, helping to streamline the submission and publication process.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬

0
Story3D-Agent: Exploring 3D Storytelling Visualization with Large Language Models
Yuzhou Huang, Yiran Qin, Shunlin Lu, Xintao Wang, Rui Huang, Ying Shan, Ruimao Zhang
Traditional visual storytelling is complex, requiring specialized knowledge and substantial resources, yet often constrained by human creativity and creation precision. While Large Language Models (LLMs) enhance visual storytelling, current approaches often limit themselves to 2D visuals or oversimplify stories through motion synthesis and behavioral simulation, failing to create comprehensive, multi-dimensional narratives. To this end, we present Story3D-Agent, a pioneering approach that leverages the capabilities of LLMs to transform provided narratives into 3D-rendered visualizations. By integrating procedural modeling, our approach enables precise control over multi-character actions and motions, as well as diverse decorative elements, ensuring the long-range and dynamic 3D representation. Furthermore, our method supports narrative extension through logical reasoning, ensuring that generated content remains consistent with existing conditions. We have thoroughly evaluated our Story3D-Agent to validate its effectiveness, offering a basic framework to advance 3D story representation.
Read more8/22/2024

0
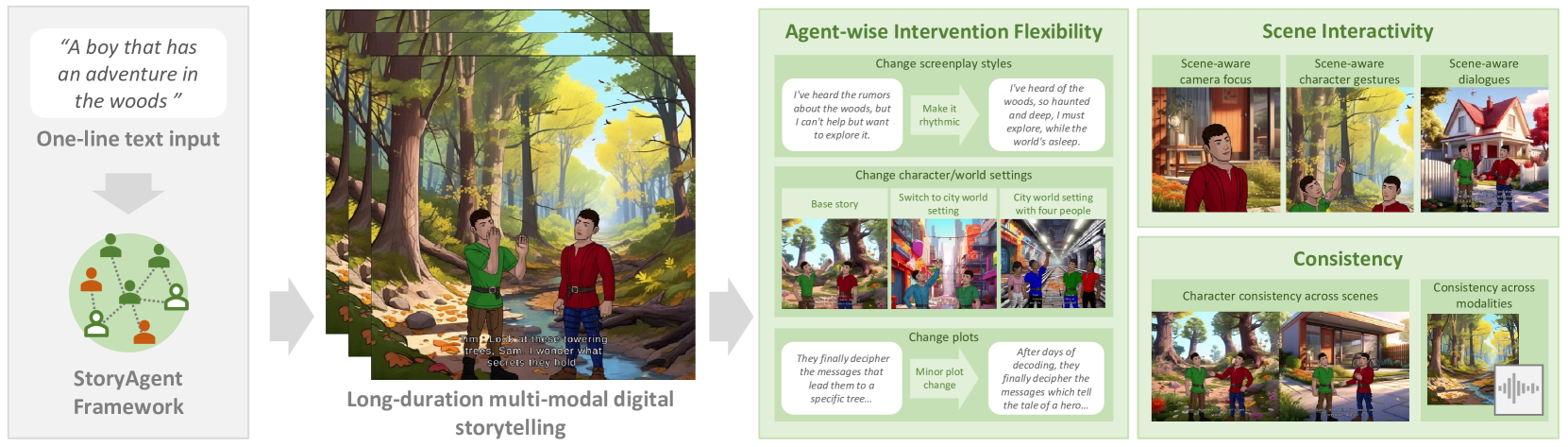
From Words to Worlds: Transforming One-line Prompt into Immersive Multi-modal Digital Stories with Communicative LLM Agent
Samuel S. Sohn, Danrui Li, Sen Zhang, Che-Jui Chang, Mubbasir Kapadia
Digital storytelling, essential in entertainment, education, and marketing, faces challenges in production scalability and flexibility. The StoryAgent framework, introduced in this paper, utilizes Large Language Models and generative tools to automate and refine digital storytelling. Employing a top-down story drafting and bottom-up asset generation approach, StoryAgent tackles key issues such as manual intervention, interactive scene orchestration, and narrative consistency. This framework enables efficient production of interactive and consistent narratives across multiple modalities, democratizing content creation and enhancing engagement. Our results demonstrate the framework's capability to produce coherent digital stories without reference videos, marking a significant advancement in automated digital storytelling.
Read more6/24/2024
💬

0
Improving Visual Storytelling with Multimodal Large Language Models
Xiaochuan Lin, Xiangyong Chen
Visual storytelling is an emerging field that combines images and narratives to create engaging and contextually rich stories. Despite its potential, generating coherent and emotionally resonant visual stories remains challenging due to the complexity of aligning visual and textual information. This paper presents a novel approach leveraging large language models (LLMs) and large vision-language models (LVLMs) combined with instruction tuning to address these challenges. We introduce a new dataset comprising diverse visual stories, annotated with detailed captions and multimodal elements. Our method employs a combination of supervised and reinforcement learning to fine-tune the model, enhancing its narrative generation capabilities. Quantitative evaluations using GPT-4 and qualitative human assessments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing models, achieving higher scores in narrative coherence, relevance, emotional depth, and overall quality. The results underscore the effectiveness of instruction tuning and the potential of LLMs/LVLMs in advancing visual storytelling.
Read more7/4/2024


0
When LLMs step into the 3D World: A Survey and Meta-Analysis of 3D Tasks via Multi-modal Large Language Models
Xianzheng Ma, Yash Bhalgat, Brandon Smart, Shuai Chen, Xinghui Li, Jian Ding, Jindong Gu, Dave Zhenyu Chen, Songyou Peng, Jia-Wang Bian, Philip H Torr, Marc Pollefeys, Matthias Nie{ss}ner, Ian D Reid, Angel X. Chang, Iro Laina, Victor Adrian Prisacariu
As large language models (LLMs) evolve, their integration with 3D spatial data (3D-LLMs) has seen rapid progress, offering unprecedented capabilities for understanding and interacting with physical spaces. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of the methodologies enabling LLMs to process, understand, and generate 3D data. Highlighting the unique advantages of LLMs, such as in-context learning, step-by-step reasoning, open-vocabulary capabilities, and extensive world knowledge, we underscore their potential to significantly advance spatial comprehension and interaction within embodied Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems. Our investigation spans various 3D data representations, from point clouds to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs). It examines their integration with LLMs for tasks such as 3D scene understanding, captioning, question-answering, and dialogue, as well as LLM-based agents for spatial reasoning, planning, and navigation. The paper also includes a brief review of other methods that integrate 3D and language. The meta-analysis presented in this paper reveals significant progress yet underscores the necessity for novel approaches to harness the full potential of 3D-LLMs. Hence, with this paper, we aim to chart a course for future research that explores and expands the capabilities of 3D-LLMs in understanding and interacting with the complex 3D world. To support this survey, we have established a project page where papers related to our topic are organized and listed: https://github.com/ActiveVisionLab/Awesome-LLM-3D.
Read more5/17/2024