Storypark: Leveraging Large Language Models to Enhance Children Story Learning Through Child-AI collaboration Storytelling
2405.06495

0
0
Abstract
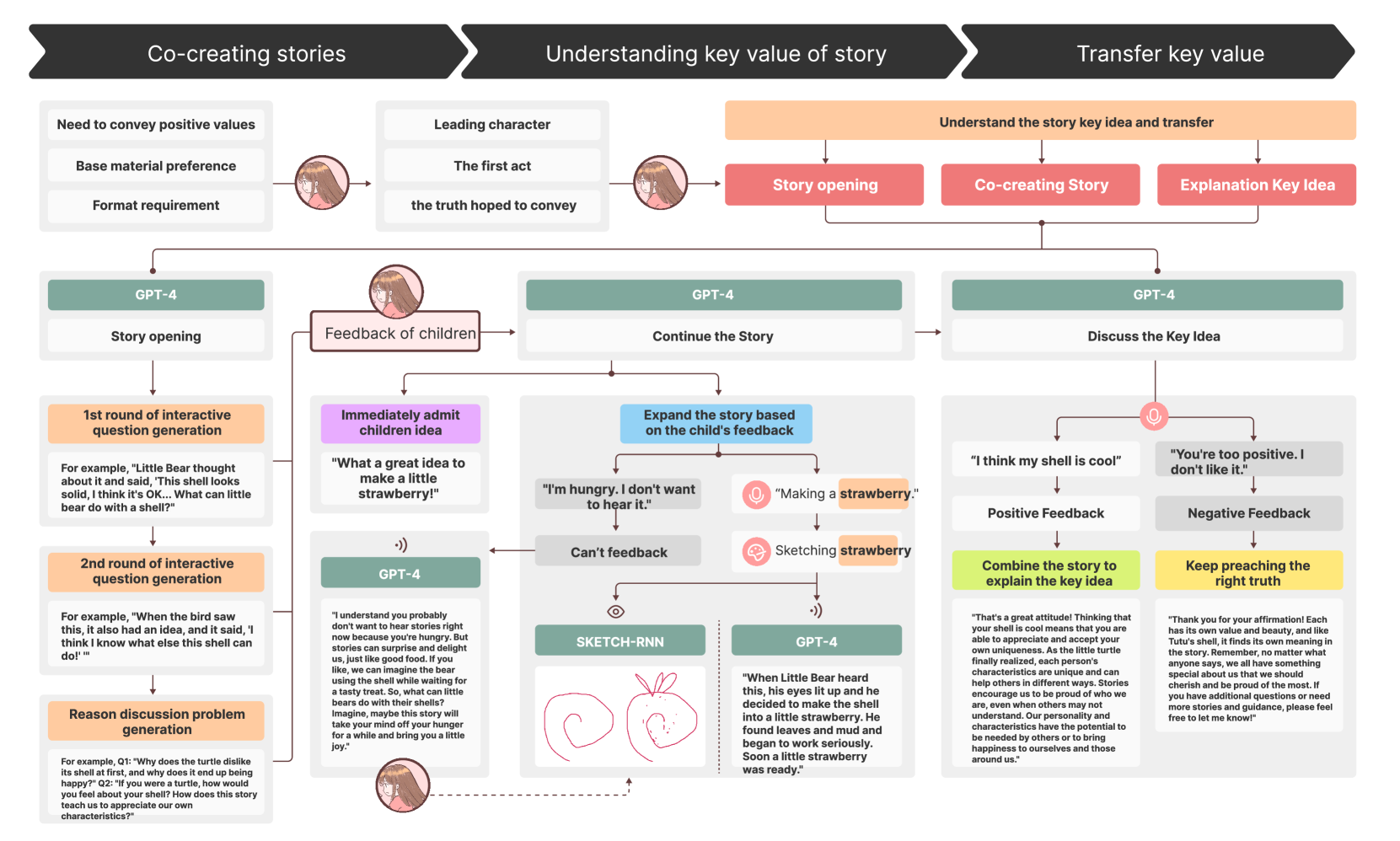
Interactive storytelling has been widely adopted by educators in teaching activities of young children. Such a teaching method combines storytelling with active child participation, benefiting their expressive abilities, creative thinking, and understanding of stories. Interactive storytelling requires facilitators to unidirectionally narrate the story content and encourage children's participation in story plot creation and interpretation of central themes through multi-sensory interactive methods such as questioning and drawing. However, providing tailored guidance based on diverse feedback from children during interactive storytelling poses challenges for most facilitators. These challenges include expanding story plot development based on children's ideas, using drawings to visualize children's thoughts, and interpreting the story's central themes based on children's thinking. This necessitates facilitators to possess strong imaginative, associative, domain knowledge, and drawing skills. Large language models have demonstrated their potential in facilitating responsive and participatory dialogues, offering new design possibilities to address the challenges faced by facilitators in interactive storytelling. In this study, our goal is to leverage large language models to design an interactive storytelling system that provides children with plot frameworks and interpretations of central themes during the interactive storytelling process. Through user experiments involving 20 child participants, we evaluate this interactive system's usability, learning effectiveness, and user experience. The user study shows that Storypark improves learning outcomes in understanding story key ideas, generalization, and transfer. And high engagement and willingness to use of participants demonstrate that StoryPark provides children with a positive learning experience.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces Storypark, a system that leverages large language models to enhance children's story learning through a collaborative storytelling experience between the child and an AI assistant.
- The key objectives are to foster children's creativity, language skills, and engagement in the storytelling process by combining their own ideas with the capabilities of large language models.
- The system is designed to be child-centric, providing a safe and engaging environment for children to explore and co-create stories with the AI.
Plain English Explanation
Storypark: Leveraging Large Language Models to Enhance Children Story Learning Through Child-AI collaboration Storytelling is a system that aims to help children learn and engage with stories in a more interactive and collaborative way. The idea is to combine the creative abilities of children with the powerful language capabilities of large language models, like GPT-3, to co-create stories together.
The system provides a child-friendly interface where children can contribute their own ideas and storylines. The AI assistant then builds on these contributions, suggesting new plot points, characters, or narrative directions. This back-and-forth collaboration allows children to explore their imagination while also learning new vocabulary, sentence structures, and storytelling techniques from the AI.
The researchers behind Storypark believe that this kind of child-centric AI learning environment can foster children's creativity, language skills, and overall engagement with the storytelling process. By giving children a more active role in shaping the narrative, the system aims to make the learning experience more fun and meaningful for them.
Technical Explanation
Storypark: Leveraging Large Language Models to Enhance Children Story Learning Through Child-AI collaboration Storytelling describes a system that combines a child-friendly interface with the capabilities of large language models to enable a collaborative storytelling experience between children and an AI assistant.
The system architecture includes a natural language processing module that can understand and interpret the child's story contributions, as well as a large language model-based situational dialogue component that generates relevant responses and narrative extensions. These components work together to create a back-and-forth storytelling flow, where the child's ideas inform the AI's contributions, and the AI's suggestions inspire the child to further develop the story.
The researchers conducted a series of user studies to evaluate the effectiveness of Storypark in enhancing children's creativity, language skills, and engagement in the storytelling process. The results showed that the child-AI collaboration led to more diverse and imaginative story outcomes, as well as increased enthusiasm and language development among the participating children.
Critical Analysis
The Storypark system presents an innovative approach to leveraging large language models to support children's story learning and creativity. By focusing on a collaborative storytelling experience, the researchers have addressed some of the potential limitations of using large language models in synthetic participatory planning, where the AI may dominate the creative process.
However, the paper acknowledges that further research is needed to fully understand the long-term impacts of this child-AI collaboration on children's cognitive and social development. Additionally, the system's reliance on large language models means that it may be susceptible to biases or inconsistencies inherent in those models, which could inadvertently influence the stories being co-created.
It would also be valuable to explore ways to make the system even more child-centric, such as incorporating multimodal inputs (e.g., drawings, audio recordings) or adapting the language and tone of the AI assistant to better match the child's developmental stage and preferences.
Conclusion
The Storypark system represents a promising approach to leveraging large language models to enhance children's story learning and creativity. By enabling a collaborative storytelling experience between children and an AI assistant, the system aims to foster children's imagination, language skills, and overall engagement with the storytelling process.
The positive results from the user studies suggest that this type of child-centric AI learning environment could have significant benefits for children's cognitive and social development. As the researchers continue to refine and expand the Storypark system, it will be important to carefully consider the ethical implications and potential biases associated with the use of large language models, ensuring that the technology remains a supportive and empowering tool for children's learning and creativity.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
From Words to Worlds: Transforming One-line Prompt into Immersive Multi-modal Digital Stories with Communicative LLM Agent
Samuel S. Sohn, Danrui Li, Sen Zhang, Che-Jui Chang, Mubbasir Kapadia

0
0
Digital storytelling, essential in entertainment, education, and marketing, faces challenges in production scalability and flexibility. The StoryAgent framework, introduced in this paper, utilizes Large Language Models and generative tools to automate and refine digital storytelling. Employing a top-down story drafting and bottom-up asset generation approach, StoryAgent tackles key issues such as manual intervention, interactive scene orchestration, and narrative consistency. This framework enables efficient production of interactive and consistent narratives across multiple modalities, democratizing content creation and enhancing engagement. Our results demonstrate the framework's capability to produce coherent digital stories without reference videos, marking a significant advancement in automated digital storytelling.
6/24/2024

Leveraging Large Language Models for Learning Complex Legal Concepts through Storytelling
Hang Jiang, Xiajie Zhang, Robert Mahari, Daniel Kessler, Eric Ma, Tal August, Irene Li, Alex 'Sandy' Pentland, Yoon Kim, Jad Kabbara, Deb Roy

0
0
Making legal knowledge accessible to non-experts is crucial for enhancing general legal literacy and encouraging civic participation in democracy. However, legal documents are often challenging to understand for people without legal backgrounds. In this paper, we present a novel application of large language models (LLMs) in legal education to help non-experts learn intricate legal concepts through storytelling, an effective pedagogical tool in conveying complex and abstract concepts. We also introduce a new dataset LegalStories, which consists of 294 complex legal doctrines, each accompanied by a story and a set of multiple-choice questions generated by LLMs. To construct the dataset, we experiment with various LLMs to generate legal stories explaining these concepts. Furthermore, we use an expert-in-the-loop approach to iteratively design multiple-choice questions. Then, we evaluate the effectiveness of storytelling with LLMs through randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with legal novices on 10 samples from the dataset. We find that LLM-generated stories enhance comprehension of legal concepts and interest in law among non-native speakers compared to only definitions. Moreover, stories consistently help participants relate legal concepts to their lives. Finally, we find that learning with stories shows a higher retention rate for non-native speakers in the follow-up assessment. Our work has strong implications for using LLMs in promoting teaching and learning in the legal field and beyond.
6/17/2024
📉
Metabook: An Automatically Generated Augmented Reality Storybook Interaction System to Improve Children's Engagement in Storytelling
Yibo Wang, Yuanyuan Mao, Shi-ting Ni

0
0
Storytelling serves as a crucial avenue for children to acquire knowledge, offering numerous benefits such as enhancing children's sensitivity to various forms of syntax, diction, and rhetoric; recognizing patterns in language and human experience; stimulating creativity; and providing practice in problem-solving, decision-making, and evaluation. However, current storytelling book facing these problems:1.Traditional 3D storybooks lack flexibility in dealing with text changing, as adding a new story requires remaking of the 3D book by artists. 2. Children often have many questions after reading stories, but traditional 3D books are unable to provide answers or explanations for children.3.Children can easily feel bored when reading text, and traditional 3D books still rely on text to tell stories, thus limiting their ability to increase children's enthusiasm for reading. So, we propose the Metabook: an automatically generated interactive 3D storybook. Our main contributions are as follows: First, we propose a story to 3D generation scheme, enabling 3D books to be automatically generated based on stories. Next, we introduce cartoon Metahumans for storytelling, utilizing lip-syncing and eye-tracking technology to enable facial interaction with children, enhancing the fun of reading. Last but not least, we connect GPT-4 to the brain of the metahuman, which provides answers and explanations to the questions children have after reading.
5/24/2024
💬
Tell Me a Story! Narrative-Driven XAI with Large Language Models
David Martens, James Hinns, Camille Dams, Mark Vergouwen, Theodoros Evgeniou

0
0
In many AI applications today, the predominance of black-box machine learning models, due to their typically higher accuracy, amplifies the need for Explainable AI (XAI). Existing XAI approaches, such as the widely used SHAP values or counterfactual (CF) explanations, are arguably often too technical for users to understand and act upon. To enhance comprehension of explanations of AI decisions and the overall user experience, we introduce XAIstories, which leverage Large Language Models to provide narratives about how AI predictions are made: SHAPstories do so based on SHAP explanations, while CFstories do so for CF explanations. We study the impact of our approach on users' experience and understanding of AI predictions. Our results are striking: over 90% of the surveyed general audience finds the narratives generated by SHAPstories convincing. Data scientists primarily see the value of SHAPstories in communicating explanations to a general audience, with 83% of data scientists indicating they are likely to use SHAPstories for this purpose. In an image classification setting, CFstories are considered more or equally convincing as the users' own crafted stories by more than 75% of the participants. CFstories additionally bring a tenfold speed gain in creating a narrative. We also find that SHAPstories help users to more accurately summarize and understand AI decisions, in a credit scoring setting we test, correctly answering comprehension questions significantly more often than they do when only SHAP values are provided. The results thereby suggest that XAIstories may significantly help explaining and understanding AI predictions, ultimately supporting better decision-making in various applications.
6/14/2024