A Survey of Language-Based Communication in Robotics
2406.04086

0
0
Abstract
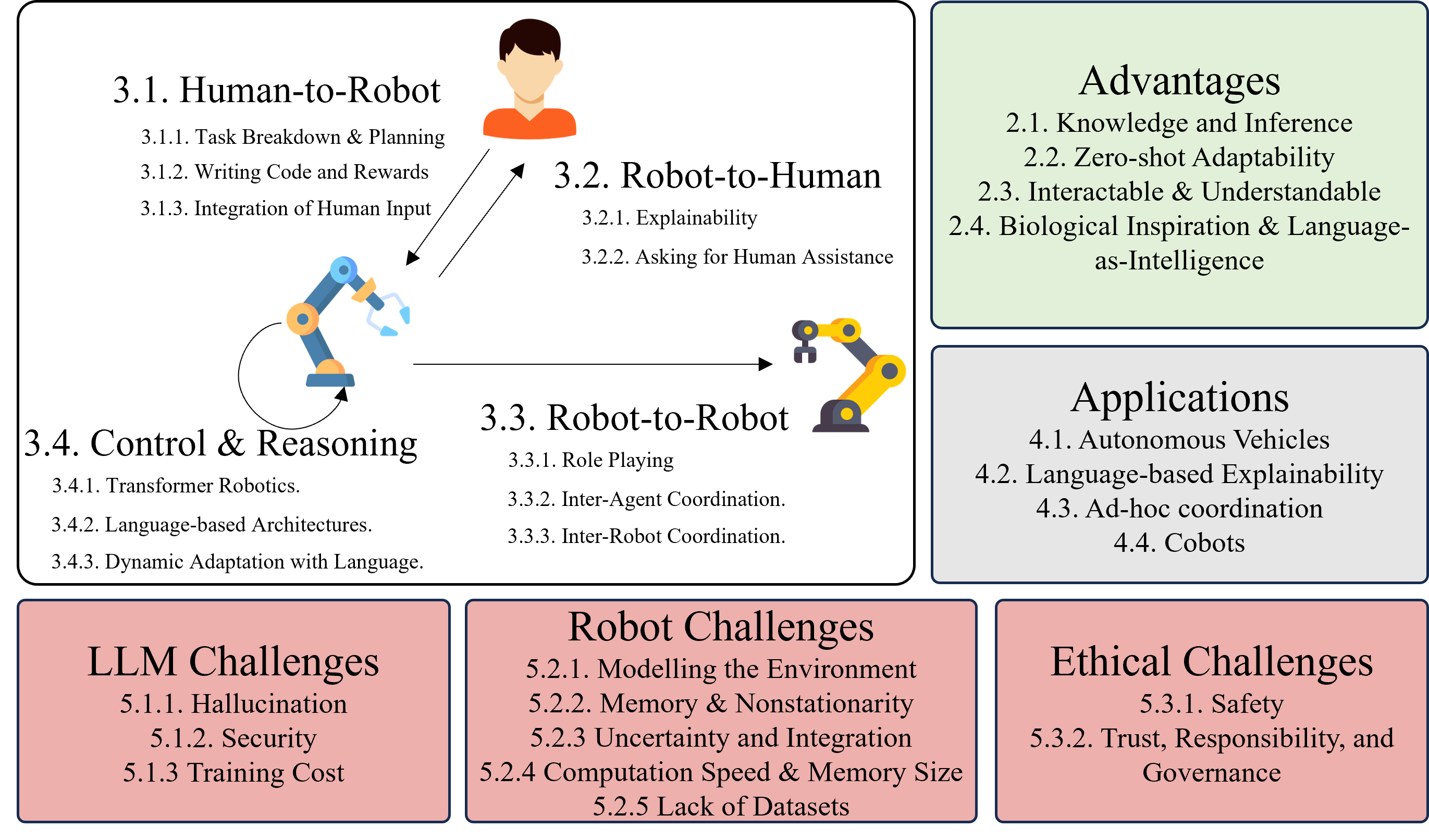
Embodied robots which can interact with their environment and neighbours are increasingly being used as a test case to develop Artificial Intelligence. This creates a need for multimodal robot controllers which can operate across different types of information including text. Large Language Models are able to process and generate textual as well as audiovisual data and, more recently, robot actions. Language Models are increasingly being applied to robotic systems; these Language-Based robots leverage the power of language models in a variety of ways. Additionally, the use of language opens up multiple forms of information exchange between members of a human-robot team. This survey motivates the use of language models in robotics, and then delineates works based on the part of the overall control flow in which language is incorporated. Language can be used by human to task a robot, by a robot to inform a human, between robots as a human-like communication medium, and internally for a robot's planning and control. Applications of language-based robots are explored, and finally numerous limitations and challenges are discussed to provide a summary of the development needed for language-based robotics moving forward. Links to each paper and, if available, source code are made available in the accompanying site at https://uos-haris.online/sooratilab/papers/WillSurvey/LangRobotSurvey.php
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of language-based communication in robotics.
- It explores the benefits of using language for robot-human interaction and the various techniques and approaches that have been developed in this field.
- The paper covers key topics such as natural language processing, dialog systems, and multimodal interaction.
Plain English Explanation
Language is a powerful tool for robots to interact with humans in a more natural and intuitive way. By using language, robots can understand and respond to human instructions, ask for clarification, and engage in back-and-forth communication. This can be especially useful in collaborative tasks where robots need to work alongside humans.
The paper explores various techniques that have been developed to enable language-based communication in robotics. This includes natural language processing algorithms to understand human speech and language, as well as dialog systems that allow robots to engage in conversational exchanges. The paper also discusses multimodal interaction, where robots combine language with other forms of communication, such as gestures and visual cues, to enhance their understanding and interaction with humans.
Overall, the paper highlights the significant potential of language-based communication in robotics, and how it can enable more natural and effective human-robot collaboration across a wide range of applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides a comprehensive survey of the current state of language-based communication in robotics. It begins by outlining the key benefits of using language for robot-human interaction, including improved understanding, more natural communication, and the ability to engage in back-and-forth dialog.
The paper then delves into the various techniques and approaches that have been developed to enable language-based communication in robotics. This includes advances in natural language processing, which allow robots to understand and interpret human speech and language, as well as dialog systems that enable robots to engage in conversational exchanges.
The paper also discusses the importance of multimodal interaction, where robots combine language with other forms of communication, such as gestures and visual cues, to enhance their understanding and interaction with humans. This can be particularly useful in collaborative tasks, where robots need to work seamlessly alongside human partners.
Throughout the paper, the authors provide a detailed overview of the various techniques and approaches that have been developed, including the key challenges and limitations that researchers have faced, as well as the potential future directions for this field.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-researched survey of the current state of language-based communication in robotics. It acknowledges the significant progress that has been made in this area, while also highlighting the ongoing challenges and limitations that researchers continue to grapple with.
One potential area for further research that the paper does not address in depth is the ethical and societal implications of language-based communication in robotics. As these technologies become more advanced and widespread, it will be important to consider issues such as privacy, bias, and the potential impact on human-robot relationships.
Additionally, the paper could have delved deeper into the practical applications and real-world use cases of language-based communication in robotics. While it touches on some examples, such as collaborative tasks, a more comprehensive discussion of the diverse ways in which these technologies are being leveraged across different industries and domains would have further strengthened the paper's impact.
Overall, the paper provides a valuable and informative resource for researchers and practitioners working in the field of language-based communication in robotics. Its detailed technical explanations and critical analysis offer a solid foundation for understanding the current state of the art and future directions in this rapidly evolving field.
Conclusion
This paper offers a comprehensive survey of language-based communication in robotics, highlighting the significant benefits and the various techniques and approaches that have been developed to enable more natural and effective human-robot interaction.
By exploring the advancements in natural language processing, dialog systems, and multimodal interaction, the paper highlights the significant potential of language-based communication in robotics, and how it can enable more collaborative and intuitive human-robot partnerships across a wide range of applications.
While the paper provides a thorough technical analysis, it also acknowledges the ongoing challenges and limitations in this field, and suggests areas for further research and exploration. As language-based communication in robotics continues to evolve, this paper serves as an invaluable resource for understanding the current state of the art and the exciting future developments that lie ahead.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
A Survey on Integration of Large Language Models with Intelligent Robots
Yeseung Kim, Dohyun Kim, Jieun Choi, Jisang Park, Nayoung Oh, Daehyung Park

0
0
In recent years, the integration of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized the field of robotics, enabling robots to communicate, understand, and reason with human-like proficiency. This paper explores the multifaceted impact of LLMs on robotics, addressing key challenges and opportunities for leveraging these models across various domains. By categorizing and analyzing LLM applications within core robotics elements -- communication, perception, planning, and control -- we aim to provide actionable insights for researchers seeking to integrate LLMs into their robotic systems. Our investigation focuses on LLMs developed post-GPT-3.5, primarily in text-based modalities while also considering multimodal approaches for perception and control. We offer comprehensive guidelines and examples for prompt engineering, facilitating beginners' access to LLM-based robotics solutions. Through tutorial-level examples and structured prompt construction, we illustrate how LLM-guided enhancements can be seamlessly integrated into robotics applications. This survey serves as a roadmap for researchers navigating the evolving landscape of LLM-driven robotics, offering a comprehensive overview and practical guidance for harnessing the power of language models in robotics development.
6/26/2024
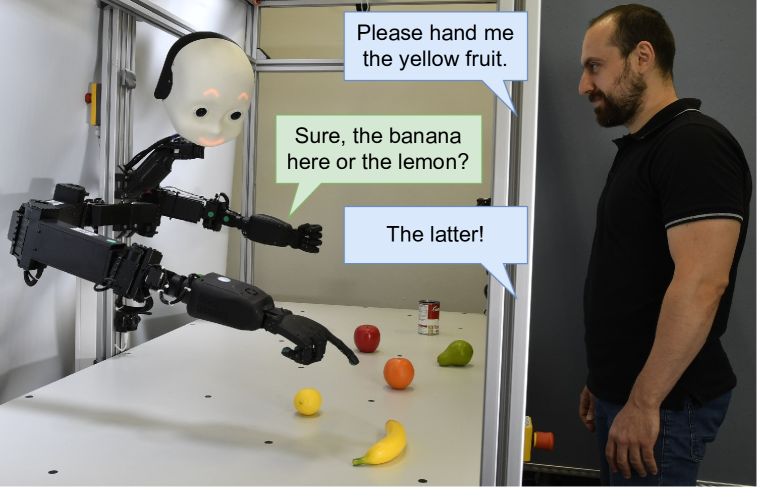

New!When Robots Get Chatty: Grounding Multimodal Human-Robot Conversation and Collaboration
Philipp Allgeuer, Hassan Ali, Stefan Wermter

0
0
We investigate the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) to equip neural robotic agents with human-like social and cognitive competencies, for the purpose of open-ended human-robot conversation and collaboration. We introduce a modular and extensible methodology for grounding an LLM with the sensory perceptions and capabilities of a physical robot, and integrate multiple deep learning models throughout the architecture in a form of system integration. The integrated models encompass various functions such as speech recognition, speech generation, open-vocabulary object detection, human pose estimation, and gesture detection, with the LLM serving as the central text-based coordinating unit. The qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate the huge potential of LLMs in providing emergent cognition and interactive language-oriented control of robots in a natural and social manner.
7/2/2024
💬
Large Language Models for Human-Robot Interaction: Opportunities and Risks
Jesse Atuhurra

0
0
The tremendous development in large language models (LLM) has led to a new wave of innovations and applications and yielded research results that were initially forecast to take longer. In this work, we tap into these recent developments and present a meta-study about the potential of large language models if deployed in social robots. We place particular emphasis on the applications of social robots: education, healthcare, and entertainment. Before being deployed in social robots, we also study how these language models could be safely trained to ``understand'' societal norms and issues, such as trust, bias, ethics, cognition, and teamwork. We hope this study provides a resourceful guide to other robotics researchers interested in incorporating language models in their robots.
5/3/2024
💬
How Can Large Language Models Enable Better Socially Assistive Human-Robot Interaction: A Brief Survey
Zhonghao Shi, Ellen Landrum, Amy O' Connell, Mina Kian, Leticia Pinto-Alva, Kaleen Shrestha, Xiaoyuan Zhu, Maja J Matari'c

0
0
Socially assistive robots (SARs) have shown great success in providing personalized cognitive-affective support for user populations with special needs such as older adults, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and individuals with mental health challenges. The large body of work on SAR demonstrates its potential to provide at-home support that complements clinic-based interventions delivered by mental health professionals, making these interventions more effective and accessible. However, there are still several major technical challenges that hinder SAR-mediated interactions and interventions from reaching human-level social intelligence and efficacy. With the recent advances in large language models (LLMs), there is an increased potential for novel applications within the field of SAR that can significantly expand the current capabilities of SARs. However, incorporating LLMs introduces new risks and ethical concerns that have not yet been encountered, and must be carefully be addressed to safely deploy these more advanced systems. In this work, we aim to conduct a brief survey on the use of LLMs in SAR technologies, and discuss the potentials and risks of applying LLMs to the following three major technical challenges of SAR: 1) natural language dialog; 2) multimodal understanding; 3) LLMs as robot policies.
4/9/2024