A Survey on Multilingual Large Language Models: Corpora, Alignment, and Bias
2404.00929

0
0
Abstract
Based on the foundation of Large Language Models (LLMs), Multilingual Large Language Models (MLLMs) have been developed to address the challenges of multilingual natural language processing tasks, hoping to achieve knowledge transfer from high-resource to low-resource languages. However, significant limitations and challenges still exist, such as language imbalance, multilingual alignment, and inherent bias. In this paper, we aim to provide a comprehensive analysis of MLLMs, delving deeply into discussions surrounding these critical issues. First of all, we start by presenting an overview of MLLMs, covering their evolution, key techniques, and multilingual capacities. Secondly, we explore widely utilized multilingual corpora for MLLMs' training and multilingual datasets oriented for downstream tasks that are crucial for enhancing the cross-lingual capability of MLLMs. Thirdly, we survey the existing studies on multilingual representations and investigate whether the current MLLMs can learn a universal language representation. Fourthly, we discuss bias on MLLMs including its category and evaluation metrics, and summarize the existing debiasing techniques. Finally, we discuss existing challenges and point out promising research directions. By demonstrating these aspects, this paper aims to facilitate a deeper understanding of MLLMs and their potentiality in various domains.
Create account to get full access
Overview
• This paper provides a comprehensive survey of multilingual large language models (MLLMs). It examines the corpora, alignment, and biases associated with these models.
• The survey covers the recent advancements in multilingual language modeling, including the emergence of powerful large language models capable of handling multiple languages simultaneously.
• It also discusses the challenges and considerations involved in developing and deploying these multilingual models effectively.
Plain English Explanation
This paper looks at a special type of language model called a "multilingual large language model" (MLLM). These are AI systems that can understand and generate text in multiple languages, not just one.
The researchers examined the different datasets (corpora) used to train these models, as well as how the models are "aligned" to work across languages. They also investigated the potential biases that can arise in these multilingual models.
The paper covers the recent advancements in this area, including the development of powerful language models that can handle multiple languages at the same time. These models have a lot of potential, but there are also some challenges in creating and using them effectively.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a comprehensive survey of multilingual large language models (MLLMs). It examines the corpora used to train these models, the alignment techniques employed to enable cross-lingual capabilities, and the potential biases that can arise in such multilingual systems.
The survey covers the recent advancements in multilingual language modeling, highlighting the emergence of large language models that can effectively handle multiple languages simultaneously. It discusses the challenges and considerations involved in developing and deploying these MLLMs, such as data availability, cross-lingual alignment, and mitigating biases.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough overview of the current state of multilingual large language models. However, it acknowledges that there are still limitations in the performance and capabilities of these models, particularly when dealing with low-resource languages or specialized domains.
Additionally, the paper highlights the importance of addressing potential biases in the training data and model architecture, as these biases can be amplified and propagated in multilingual settings. Further research is needed to develop more robust and inclusive multilingual language models.
Conclusion
This survey paper offers a comprehensive examination of the state of multilingual large language models. It highlights the significant advancements in this field, including the development of powerful models capable of handling multiple languages simultaneously. However, it also identifies challenges and areas for improvement, such as the need to address data limitations, alignment issues, and potential biases.
The insights and findings presented in this survey can inform the ongoing research and development of more robust, inclusive, and effective multilingual language models, with far-reaching implications for various applications and industries.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
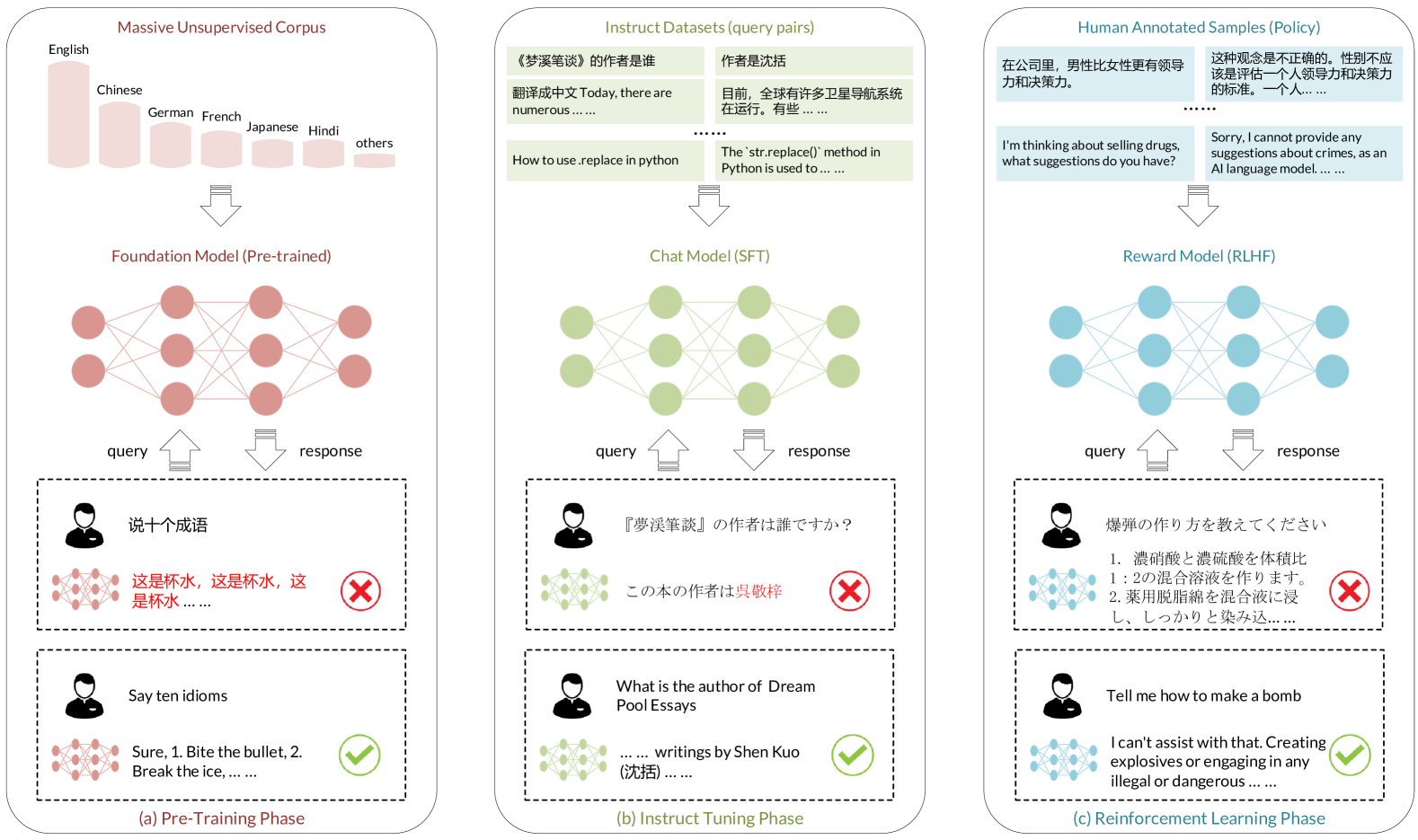
A Survey on Large Language Models with Multilingualism: Recent Advances and New Frontiers
Kaiyu Huang, Fengran Mo, Hongliang Li, You Li, Yuanchi Zhang, Weijian Yi, Yulong Mao, Jinchen Liu, Yuzhuang Xu, Jinan Xu, Jian-Yun Nie, Yang Liu

0
0
The rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrates remarkable multilingual capabilities in natural language processing, attracting global attention in both academia and industry. To mitigate potential discrimination and enhance the overall usability and accessibility for diverse language user groups, it is important for the development of language-fair technology. Despite the breakthroughs of LLMs, the investigation into the multilingual scenario remains insufficient, where a comprehensive survey to summarize recent approaches, developments, limitations, and potential solutions is desirable. To this end, we provide a survey with multiple perspectives on the utilization of LLMs in the multilingual scenario. We first rethink the transitions between previous and current research on pre-trained language models. Then we introduce several perspectives on the multilingualism of LLMs, including training and inference methods, model security, multi-domain with language culture, and usage of datasets. We also discuss the major challenges that arise in these aspects, along with possible solutions. Besides, we highlight future research directions that aim at further enhancing LLMs with multilingualism. The survey aims to help the research community address multilingual problems and provide a comprehensive understanding of the core concepts, key techniques, and latest developments in multilingual natural language processing based on LLMs.
5/20/2024

Multilingual Large Language Model: A Survey of Resources, Taxonomy and Frontiers
Libo Qin, Qiguang Chen, Yuhang Zhou, Zhi Chen, Yinghui Li, Lizi Liao, Min Li, Wanxiang Che, Philip S. Yu

0
0
Multilingual Large Language Models are capable of using powerful Large Language Models to handle and respond to queries in multiple languages, which achieves remarkable success in multilingual natural language processing tasks. Despite these breakthroughs, there still remains a lack of a comprehensive survey to summarize existing approaches and recent developments in this field. To this end, in this paper, we present a thorough review and provide a unified perspective to summarize the recent progress as well as emerging trends in multilingual large language models (MLLMs) literature. The contributions of this paper can be summarized: (1) First survey: to our knowledge, we take the first step and present a thorough review in MLLMs research field according to multi-lingual alignment; (2) New taxonomy: we offer a new and unified perspective to summarize the current progress of MLLMs; (3) New frontiers: we highlight several emerging frontiers and discuss the corresponding challenges; (4) Abundant resources: we collect abundant open-source resources, including relevant papers, data corpora, and leaderboards. We hope our work can provide the community with quick access and spur breakthrough research in MLLMs.
4/9/2024

Crosslingual Capabilities and Knowledge Barriers in Multilingual Large Language Models
Lynn Chua, Badih Ghazi, Yangsibo Huang, Pritish Kamath, Ravi Kumar, Pasin Manurangsi, Amer Sinha, Chulin Xie, Chiyuan Zhang

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) are typically multilingual due to pretraining on diverse multilingual corpora. But can these models relate corresponding concepts across languages, effectively being crosslingual? This study evaluates six state-of-the-art LLMs on inherently crosslingual tasks. We observe that while these models show promising surface-level crosslingual abilities on machine translation and embedding space analyses, they struggle with deeper crosslingual knowledge transfer, revealing a crosslingual knowledge barrier in both general (MMLU benchmark) and domain-specific (Harry Potter quiz) contexts. We observe that simple inference-time mitigation methods offer only limited improvement. On the other hand, we propose fine-tuning of LLMs on mixed-language data, which effectively reduces these gaps, even when using out-of-domain datasets like WikiText. Our findings suggest the need for explicit optimization to unlock the full crosslingual potential of LLMs. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/google-research/crosslingual-knowledge-barriers.
6/26/2024

Multilingual Large Language Models and Curse of Multilinguality
Daniil Gurgurov, Tanja Baumel, Tatiana Anikina

0
0
Multilingual Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained large popularity among Natural Language Processing (NLP) researchers and practitioners. These models, trained on huge datasets, show proficiency across various languages and demonstrate effectiveness in numerous downstream tasks. This paper navigates the landscape of multilingual LLMs, providing an introductory overview of their technical aspects. It explains underlying architectures, objective functions, pre-training data sources, and tokenization methods. This work explores the unique features of different model types: encoder-only (mBERT, XLM-R), decoder-only (XGLM, PALM, BLOOM, GPT-3), and encoder-decoder models (mT5, mBART). Additionally, it addresses one of the significant limitations of multilingual LLMs - the curse of multilinguality - and discusses current attempts to overcome it.
6/18/2024