Multilingual Large Language Model: A Survey of Resources, Taxonomy and Frontiers
2404.04925

0
0

Abstract
Multilingual Large Language Models are capable of using powerful Large Language Models to handle and respond to queries in multiple languages, which achieves remarkable success in multilingual natural language processing tasks. Despite these breakthroughs, there still remains a lack of a comprehensive survey to summarize existing approaches and recent developments in this field. To this end, in this paper, we present a thorough review and provide a unified perspective to summarize the recent progress as well as emerging trends in multilingual large language models (MLLMs) literature. The contributions of this paper can be summarized: (1) First survey: to our knowledge, we take the first step and present a thorough review in MLLMs research field according to multi-lingual alignment; (2) New taxonomy: we offer a new and unified perspective to summarize the current progress of MLLMs; (3) New frontiers: we highlight several emerging frontiers and discuss the corresponding challenges; (4) Abundant resources: we collect abundant open-source resources, including relevant papers, data corpora, and leaderboards. We hope our work can provide the community with quick access and spur breakthrough research in MLLMs.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Provides a comprehensive survey of multilingual large language models (LLMs), including resources, taxonomy, and emerging frontiers
- Examines the progress and challenges in developing LLMs that can understand and generate text across multiple languages
- Discusses the potential applications and societal impact of multilingual LLMs
Plain English Explanation
Multilingual large language models are powerful artificial intelligence systems that can understand and generate text in many different languages. This paper reviews the current state of this technology, including the available resources, how these models are categorized, and the exciting new developments on the horizon.
Large language models are AI systems that have been trained on vast amounts of text data, allowing them to understand and generate human-like language. Traditionally, these models have been developed for individual languages, but there is growing interest in creating multilingual models that can work across multiple languages.
The paper explores the benefits of multilingual LLMs, such as the ability to communicate more effectively in a globalized world and support language preservation efforts. It also discusses the technical challenges, such as balancing performance across many languages and dealing with linguistic diversity.
The authors provide a detailed taxonomy of the different types of multilingual LLMs, ranging from models that can handle a handful of languages to those that can understand hundreds. They also highlight some of the cutting-edge research in this area, including the development of autonomous agents that can use these models for complex reasoning and problem-solving.
Overall, this paper offers a comprehensive overview of the state of the art in multilingual large language models, and the significant potential of this technology to transform how we communicate and interact with technology across languages.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a thorough survey of the current landscape of multilingual large language models (LLMs). The authors begin by providing an overview of monolingual LLMs, which are AI systems trained on large amounts of text data in a single language, and then delve into the challenges and opportunities of developing multilingual models.
One of the key challenges addressed is the need to balance performance across multiple languages, as well as handling linguistic diversity, such as different writing systems and grammatical structures. The paper outlines a taxonomy of multilingual LLMs, ranging from models that can handle a small number of languages to those that are capable of understanding hundreds of languages.
The authors also highlight some of the recent advancements in this field, including the development of multimodal LLMs that can process not only text, but also images, audio, and other forms of data. These models have the potential to enable more natural and contextual language understanding and generation across languages.
Furthermore, the paper discusses the application of multilingual LLMs in autonomous agents and mathematical reasoning, highlighting the opportunities for these models to support complex problem-solving and decision-making in a multilingual context.
Overall, the survey provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of multilingual LLMs, the challenges and opportunities in this field, and the potential implications for various applications, such as language education and spoken language understanding.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-researched overview of the current state of multilingual large language models, highlighting both the progress and the remaining challenges in this field. One key limitation discussed is the need to balance performance across multiple languages, as well as the difficulty of handling linguistic diversity.
The authors also acknowledge that the development of these models is still in its early stages, and there is a need for further research and experimentation to fully unlock the potential of multilingual LLMs. For example, the paper suggests that more work is needed to improve the robustness and generalization capabilities of these models, as well as to address potential biases and ethical concerns that may arise from their deployment.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific use cases and societal implications of multilingual LLMs. While it mentions potential applications in areas like language education and autonomous agents, a more in-depth discussion of the broader impact of this technology on communication, collaboration, and cross-cultural understanding could have been valuable.
Overall, the paper serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working in the field of multilingual language models, providing a solid foundation for understanding the current state of the art and the key challenges that remain to be addressed.
Conclusion
This comprehensive survey paper provides a detailed overview of the current state of multilingual large language models, including the available resources, a taxonomy of the different types of models, and an examination of the emerging frontiers in this field.
The paper highlights the significant potential of multilingual LLMs to enable more effective communication and collaboration in a globalized world, as well as support language preservation efforts and the development of autonomous agents capable of complex reasoning and problem-solving.
While the development of these models is still in its early stages, the paper suggests that continued research and innovation in areas like performance balancing, linguistic diversity handling, and ethical considerations will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of multilingual large language models and their applications across various domains.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
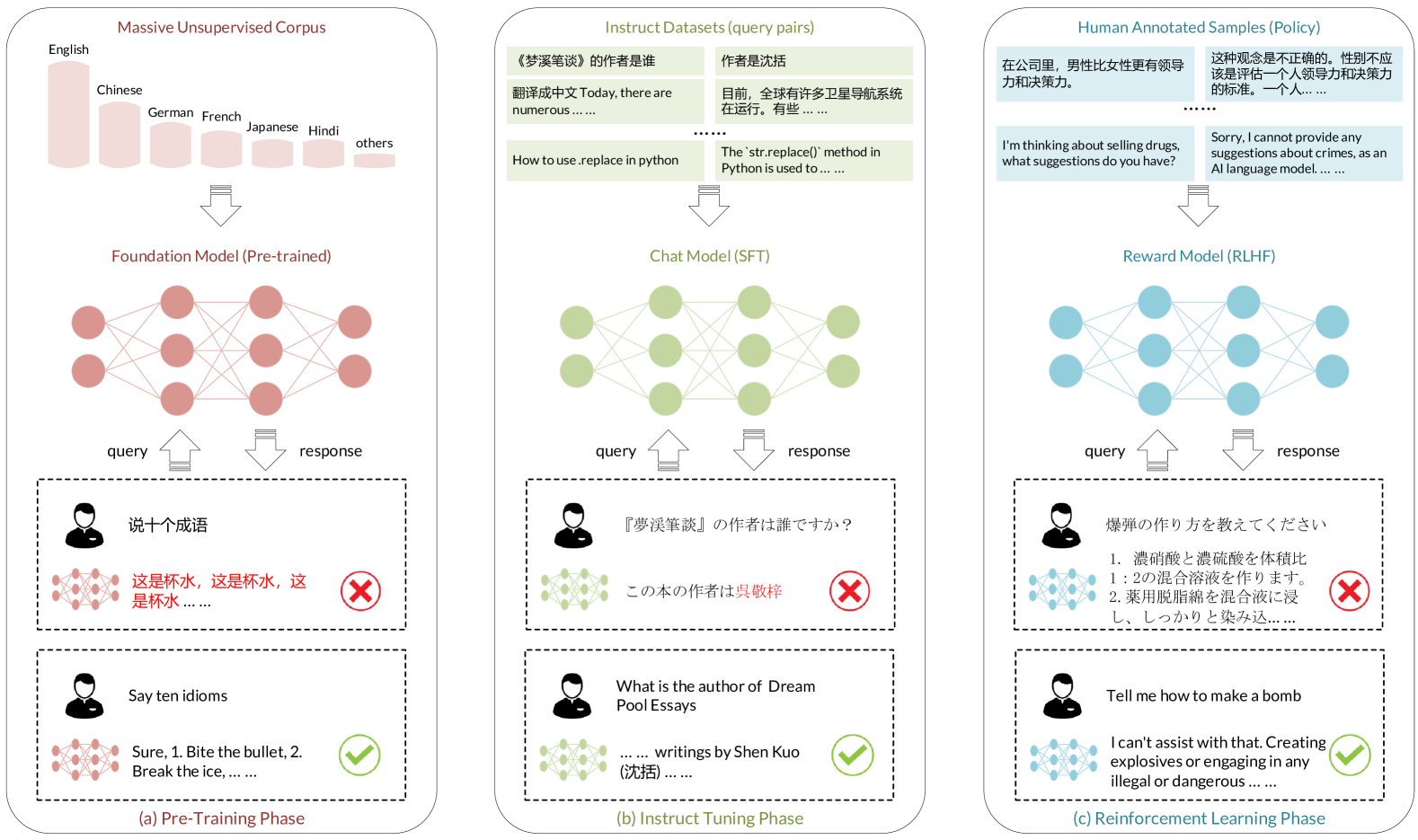
A Survey on Large Language Models with Multilingualism: Recent Advances and New Frontiers
Kaiyu Huang, Fengran Mo, Hongliang Li, You Li, Yuanchi Zhang, Weijian Yi, Yulong Mao, Jinchen Liu, Yuzhuang Xu, Jinan Xu, Jian-Yun Nie, Yang Liu

0
0
The rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrates remarkable multilingual capabilities in natural language processing, attracting global attention in both academia and industry. To mitigate potential discrimination and enhance the overall usability and accessibility for diverse language user groups, it is important for the development of language-fair technology. Despite the breakthroughs of LLMs, the investigation into the multilingual scenario remains insufficient, where a comprehensive survey to summarize recent approaches, developments, limitations, and potential solutions is desirable. To this end, we provide a survey with multiple perspectives on the utilization of LLMs in the multilingual scenario. We first rethink the transitions between previous and current research on pre-trained language models. Then we introduce several perspectives on the multilingualism of LLMs, including training and inference methods, model security, multi-domain with language culture, and usage of datasets. We also discuss the major challenges that arise in these aspects, along with possible solutions. Besides, we highlight future research directions that aim at further enhancing LLMs with multilingualism. The survey aims to help the research community address multilingual problems and provide a comprehensive understanding of the core concepts, key techniques, and latest developments in multilingual natural language processing based on LLMs.
5/20/2024
A Survey on Multilingual Large Language Models: Corpora, Alignment, and Bias
Yuemei Xu, Ling Hu, Jiayi Zhao, Zihan Qiu, Yuqi Ye, Hanwen Gu

0
0
Based on the foundation of Large Language Models (LLMs), Multilingual Large Language Models (MLLMs) have been developed to address the challenges of multilingual natural language processing tasks, hoping to achieve knowledge transfer from high-resource to low-resource languages. However, significant limitations and challenges still exist, such as language imbalance, multilingual alignment, and inherent bias. In this paper, we aim to provide a comprehensive analysis of MLLMs, delving deeply into discussions surrounding these critical issues. First of all, we start by presenting an overview of MLLMs, covering their evolution, key techniques, and multilingual capacities. Secondly, we explore widely utilized multilingual corpora for MLLMs' training and multilingual datasets oriented for downstream tasks that are crucial for enhancing the cross-lingual capability of MLLMs. Thirdly, we survey the existing studies on multilingual representations and investigate whether the current MLLMs can learn a universal language representation. Fourthly, we discuss bias on MLLMs including its category and evaluation metrics, and summarize the existing debiasing techniques. Finally, we discuss existing challenges and point out promising research directions. By demonstrating these aspects, this paper aims to facilitate a deeper understanding of MLLMs and their potentiality in various domains.
6/7/2024
💬
Efficient Large Language Models: A Survey
Zhongwei Wan, Xin Wang, Che Liu, Samiul Alam, Yu Zheng, Jiachen Liu, Zhongnan Qu, Shen Yan, Yi Zhu, Quanlu Zhang, Mosharaf Chowdhury, Mi Zhang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in important tasks such as natural language understanding and language generation, and thus have the potential to make a substantial impact on our society. Such capabilities, however, come with the considerable resources they demand, highlighting the strong need to develop effective techniques for addressing their efficiency challenges. In this survey, we provide a systematic and comprehensive review of efficient LLMs research. We organize the literature in a taxonomy consisting of three main categories, covering distinct yet interconnected efficient LLMs topics from model-centric, data-centric, and framework-centric perspective, respectively. We have also created a GitHub repository where we organize the papers featured in this survey at https://github.com/AIoT-MLSys-Lab/Efficient-LLMs-Survey. We will actively maintain the repository and incorporate new research as it emerges. We hope our survey can serve as a valuable resource to help researchers and practitioners gain a systematic understanding of efficient LLMs research and inspire them to contribute to this important and exciting field.
5/24/2024

A Comprehensive Survey of Scientific Large Language Models and Their Applications in Scientific Discovery
Yu Zhang, Xiusi Chen, Bowen Jin, Sheng Wang, Shuiwang Ji, Wei Wang, Jiawei Han

0
0
In many scientific fields, large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the way with which text and other modalities of data (e.g., molecules and proteins) are dealt, achieving superior performance in various applications and augmenting the scientific discovery process. Nevertheless, previous surveys on scientific LLMs often concentrate on one to two fields or a single modality. In this paper, we aim to provide a more holistic view of the research landscape by unveiling cross-field and cross-modal connections between scientific LLMs regarding their architectures and pre-training techniques. To this end, we comprehensively survey over 250 scientific LLMs, discuss their commonalities and differences, as well as summarize pre-training datasets and evaluation tasks for each field and modality. Moreover, we investigate how LLMs have been deployed to benefit scientific discovery. Resources related to this survey are available at https://github.com/yuzhimanhua/Awesome-Scientific-Language-Models.
6/18/2024