Synergistic Simulations: Multi-Agent Problem Solving with Large Language Models

0
💬
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) to facilitate the development of multi-agent systems.
- It aims to integrate agent-based modeling and interaction with simulated environments into a single simulation.
- The goal is to understand whether LLMs can demonstrate the synergy of human collaboration in problem-solving.
- The researchers implemented two simulations: a physical studio apartment with two roommates, and a collaboration to complete a programming task.
Plain English Explanation
The paper investigates how large language models (LLMs) can be used to create multi-agent systems - systems with multiple intelligent agents that can work together. The researchers were curious to see if these LLM-powered agents could replicate the way groups of humans often solve problems better than individuals working alone.
To explore this, they set up two different simulated scenarios. In the first, they created a virtual studio apartment with two roommates who had to work together to complete everyday tasks. In the second, the agents had to collaborate on a programming project.
By observing how the agents performed in these simulated environments, the researchers hoped to gain insights that could lead to advancements in the applications of LLMs. If the agents could demonstrate the kind of synergy seen in human collaboration, it could open up new ways to use these powerful language models.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a multi-agent framework that integrates agent-based modeling and interaction with simulated environments. The researchers implemented two specific simulations to test the capabilities of LLM-powered agents:
-
Physical Studio Apartment: This simulation featured a virtual studio apartment with two roommates who had to collaborate on everyday tasks like cleaning, cooking, and managing their shared living space.
-
Programming Collaboration: In this scenario, the agents had to work together to complete a programming project, dividing up tasks and coordinating their efforts.
By observing the agents' performance in these simulated environments, the researchers aimed to understand whether LLMs can demonstrate the synergistic problem-solving capabilities often seen in human groups. The paper discusses the agents' behaviors and outcomes in each simulation, providing insights into the potential of LLM-based multi-agent systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents an interesting exploration of using LLMs to power multi-agent systems and simulate collaborative problem-solving. However, the researchers acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research:
- The simulations were relatively simple and may not fully capture the complexity of real-world human collaboration.
- The agents' decision-making and communication processes were not thoroughly examined, and their inner workings were not fully explained.
- The paper does not provide a robust quantitative evaluation of the agents' performance, relying more on qualitative observations.
- Further research is needed to understand how LLM-based agents can be scaled up to handle more complex tasks and environments.
Additionally, one could question whether the simulated scenarios adequately represent the nuances of human collaboration, which often involves factors like social dynamics, emotional intelligence, and contextual understanding that may not be fully captured by current LLM-based approaches.
Conclusion
This paper represents an important step in exploring the potential of using large language models to power multi-agent systems and simulate collaborative problem-solving. The researchers have demonstrated the feasibility of this approach and provided some initial insights into the capabilities of LLM-based agents.
However, further research is needed to fully understand the limitations and potential applications of this technology. As the field of multi-agent systems and LLM-based modeling continues to evolve, the insights from this paper could contribute to advancements that may one day lead to more sophisticated simulations and applications that mirror the synergistic problem-solving abilities of human teams.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬

0
Synergistic Simulations: Multi-Agent Problem Solving with Large Language Models
Asher Sprigler, Alexander Drobek, Keagan Weinstock, Wendpanga Tapsoba, Gavin Childress, Andy Dao, Lucas Gral
Large Language Models (LLMs) have increasingly demonstrated the ability to facilitate the development of multi-agent systems that allow the interpretation of thoughts and actions generated by each individual. Promising advancements have also been made in LLM-based interaction with existing worlds, particularly in interacting with simulated environments. This paper aims to integrate both aforementioned topics (agents & world interaction) into a single simulation where multiple agents can work together to solve a problem, modeling how groups of humans can often solve problems better than individuals. By showing whether LLMs demonstrate the synergy of human collaboration, it could lead to advancements in the applications of LLMs. We implemented two simulations: a physical studio apartment with two roommates, and another where agents collaborate to complete a programming task. We provide a multi-agent framework, discuss the performance of the agents in each simulation, and discuss potential future additions.
Read more9/24/2024

0
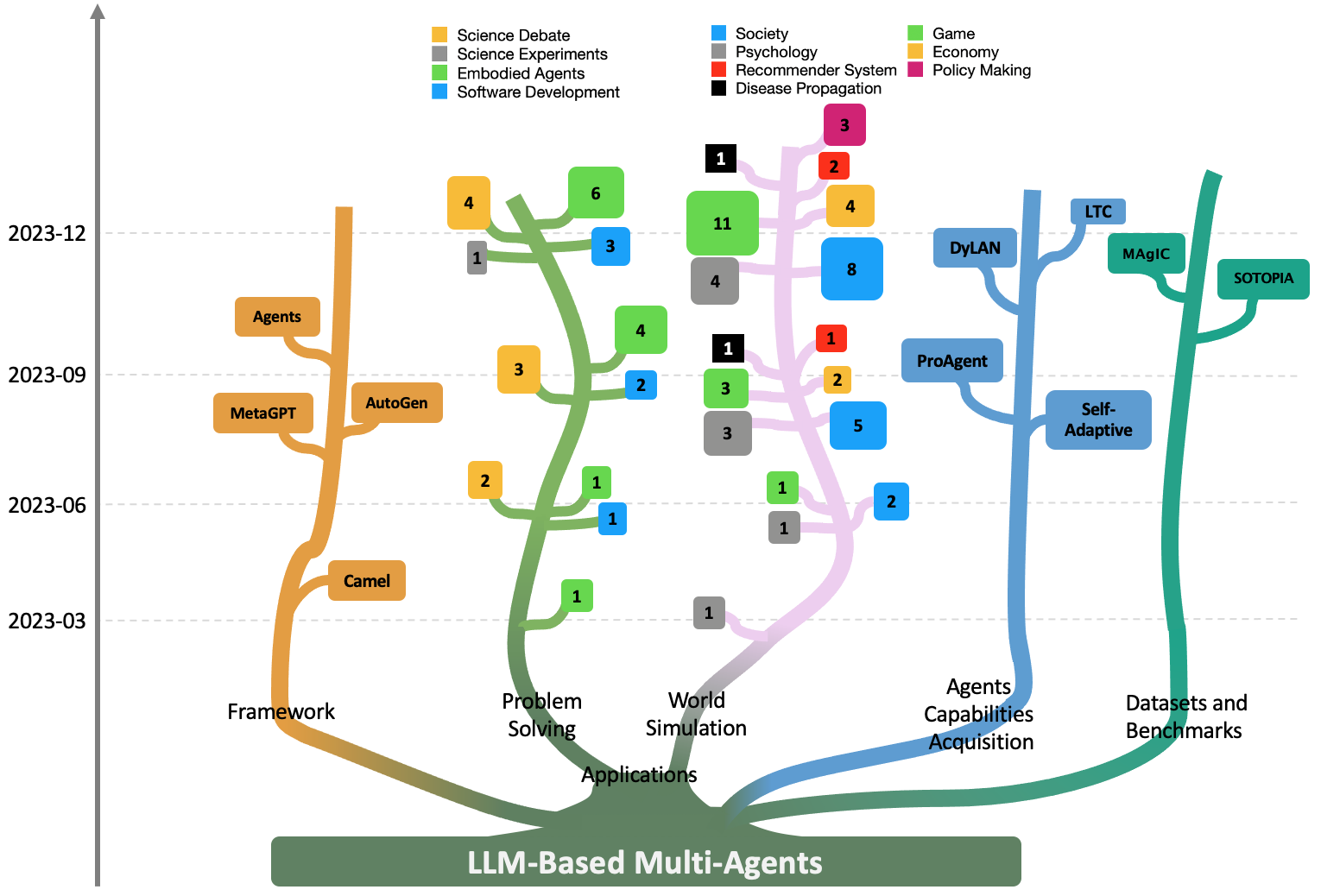
Large Language Model based Multi-Agents: A Survey of Progress and Challenges
Taicheng Guo, Xiuying Chen, Yaqi Wang, Ruidi Chang, Shichao Pei, Nitesh V. Chawla, Olaf Wiest, Xiangliang Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across a wide array of tasks. Due to the impressive planning and reasoning abilities of LLMs, they have been used as autonomous agents to do many tasks automatically. Recently, based on the development of using one LLM as a single planning or decision-making agent, LLM-based multi-agent systems have achieved considerable progress in complex problem-solving and world simulation. To provide the community with an overview of this dynamic field, we present this survey to offer an in-depth discussion on the essential aspects of multi-agent systems based on LLMs, as well as the challenges. Our goal is for readers to gain substantial insights on the following questions: What domains and environments do LLM-based multi-agents simulate? How are these agents profiled and how do they communicate? What mechanisms contribute to the growth of agents' capacities? For those interested in delving into this field of study, we also summarize the commonly used datasets or benchmarks for them to have convenient access. To keep researchers updated on the latest studies, we maintain an open-source GitHub repository, dedicated to outlining the research on LLM-based multi-agent systems.
Read more4/22/2024
✨

0
LLM-Augmented Agent-Based Modelling for Social Simulations: Challenges and Opportunities
Onder Gurcan
As large language models (LLMs) continue to make significant strides, their better integration into agent-based simulations offers a transformational potential for understanding complex social systems. However, such integration is not trivial and poses numerous challenges. Based on this observation, in this paper, we explore architectures and methods to systematically develop LLM-augmented social simulations and discuss potential research directions in this field. We conclude that integrating LLMs with agent-based simulations offers a powerful toolset for researchers and scientists, allowing for more nuanced, realistic, and comprehensive models of complex systems and human behaviours.
Read more5/14/2024
💬

0
LLM experiments with simulation: Large Language Model Multi-Agent System for Process Simulation Parametrization in Digital Twins
Yuchen Xia, Daniel Dittler, Nasser Jazdi, Haonan Chen, Michael Weyrich
This paper presents a novel design of a multi-agent system framework that applies large language models (LLMs) to automate the parametrization of simulation models in digital twins. This framework features specialized LLM agents tasked with observing, reasoning, decision-making, and summarizing, enabling them to dynamically interact with digital twin simulations to explore parametrization possibilities and determine feasible parameter settings to achieve an objective. The proposed approach enhances the usability of simulation model by infusing it with knowledge heuristics from LLM and enables autonomous search for feasible parametrization to solve a user task. Furthermore, the system has the potential to increase user-friendliness and reduce the cognitive load on human users by assisting in complex decision-making processes. The effectiveness and functionality of the system are demonstrated through a case study, and the visualized demos and codes are available at a GitHub Repository: https://github.com/YuchenXia/LLMDrivenSimulation
Read more7/23/2024