A Systematic Literature Map on Big Data

0
📊
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper examines the field of Big Data and its applications across various domains.
- It aims to provide an analytical view of the research conducted and published on the Big Data paradigm.
- The study uses a systematic mapping approach, combining bibliometric and content analysis, to identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing literature.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the concept of Big Data, which has become a significant field of study in many areas, such as healthcare, science, transport, education, and government services. Despite its widespread adoption, there is no universally agreed-upon definition of the Big Data paradigm, although various concepts have been proposed by academia and industry.
The researchers conducted a systematic review of the literature, combining bibliometric analysis and content analysis, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the research on Big Data. This approach allowed them to identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing studies on this topic.
The findings suggest that there is still a long way to go in both research and conceptual development to fully address the challenges and realize the expected benefits of the Big Data paradigm. Key areas that require further attention include building and defining adequate infrastructures and standards to support the effective implementation of Big Data solutions.
Technical Explanation
The researchers employed a systematic mapping approach to analyze the existing literature on the Big Data paradigm. This method combined bibliometric analysis, which examines the publication patterns and trends, with content analysis, which delves into the substance of the research articles.
The bibliometric analysis allowed the researchers to identify the key institutions, authors, and publication outlets contributing to the field of Big Data research. This provided insights into the academic landscape and the evolution of the field over time.
The content analysis, on the other hand, enabled the researchers to explore the conceptual foundations, methodologies, and focus areas of the existing studies. This helped them to uncover the patterns, trends, and gaps in the research, as well as the challenges and opportunities associated with the Big Data paradigm.
By integrating these two complementary analytical techniques, the researchers were able to develop a comprehensive understanding of the state of the art in Big Data research, including the progress made, the unresolved issues, and the potential future directions for the field.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable overview of the current research landscape on the Big Data paradigm, highlighting the progress made and the areas that require further attention. However, the study does not delve deeply into the specific challenges and limitations of the existing research, nor does it offer a critical assessment of the methodologies and approaches commonly used in this field.
One potential limitation of the study is the scope of the literature review, as it may not have captured all the relevant research articles, particularly those published in non-English or lesser-known outlets. Additionally, the paper does not address the potential biases or limitations inherent in the bibliometric and content analysis techniques employed.
Future research in this area could benefit from a more in-depth examination of the technological, organizational, and societal factors that influence the adoption and implementation of Big Data solutions. It could also explore the ethical and privacy concerns associated with the collection and use of large-scale data, as well as the potential unintended consequences of the Big Data paradigm.
Conclusion
The systematic review of the Big Data literature presented in this paper provides a valuable snapshot of the current state of research in this rapidly evolving field. While the findings suggest that significant progress has been made, the researchers highlight the need for continued efforts to address the challenges and realize the full potential of the Big Data paradigm.
By identifying the patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing studies, the paper paves the way for future research that can build upon the existing knowledge and tackle the unresolved issues. As the adoption of Big Data solutions continues to grow across various sectors, this type of comprehensive analysis can inform the development of more effective and impactful data-driven strategies and technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📊

0
A Systematic Literature Map on Big Data
Rogerio Rossi, Kechi Hirama, Eduardo Ferreira Franco
The paradigm of Big Data has been established as a solid field of studies in many areas such as healthcare, science, transport, education, government services, among others. Despite widely discussed, there is no agreed definition about the paradigm although there are many concepts proposed by the academy and industry. This work aims to provide an analytical view of the studies conducted and published regarding the Big Data paradigm. The approach used is the systematic map of the literature, combining bibliometric analysis and content analysis to depict the panorama of research works, identifying patterns, trends, and gaps. The results indicate that there is still a long way to go, both in research and in concepts, such as building and defining adequate infrastructures and standards, to meet future challenges and for the paradigm to become effective and bring the expected benefits.
Read more8/13/2024
📊

0
Towards a potential paradigm shift in health data collection and analysis
David Josef Herzog, Nitsa Judith Herzog
Industrial Revolution 4.0 transforms healthcare systems. The first three technological revolutions changed the relationship between human and machine interaction due to the exponential growth of machine numbers. The fourth revolution put humans into a situation where heterogeneous data is produced with unmatched quantity and quality not only by traditional methods, enforced by digitization, but also by ubiquitous computing, machine-to-machine interactions and smart environment. The modern cyber-physical space underlines the role of the person in the expanding context of computerization and big data processing. In healthcare, where data collection and analysis particularly depend on human efforts, the disruptive nature of these developments is evident. Adaptation to this process requires deep scrutiny of the trends and recognition of future medical data technologies` evolution. Significant difficulties arise from discrepancies in requirements by healthcare, administrative and technology stakeholders. Black box and grey box decisions made in medical imaging and diagnostic Decision Support Software are often not transparent enough for the professional, social and medico-legal requirements. While Explainable AI proposes a partial solution for AI applications in medicine, the approach has to be wider and multiplex. LLM potential and limitations are also discussed. This paper lists the most significant issues in these topics and describes possible solutions.
Read more4/3/2024
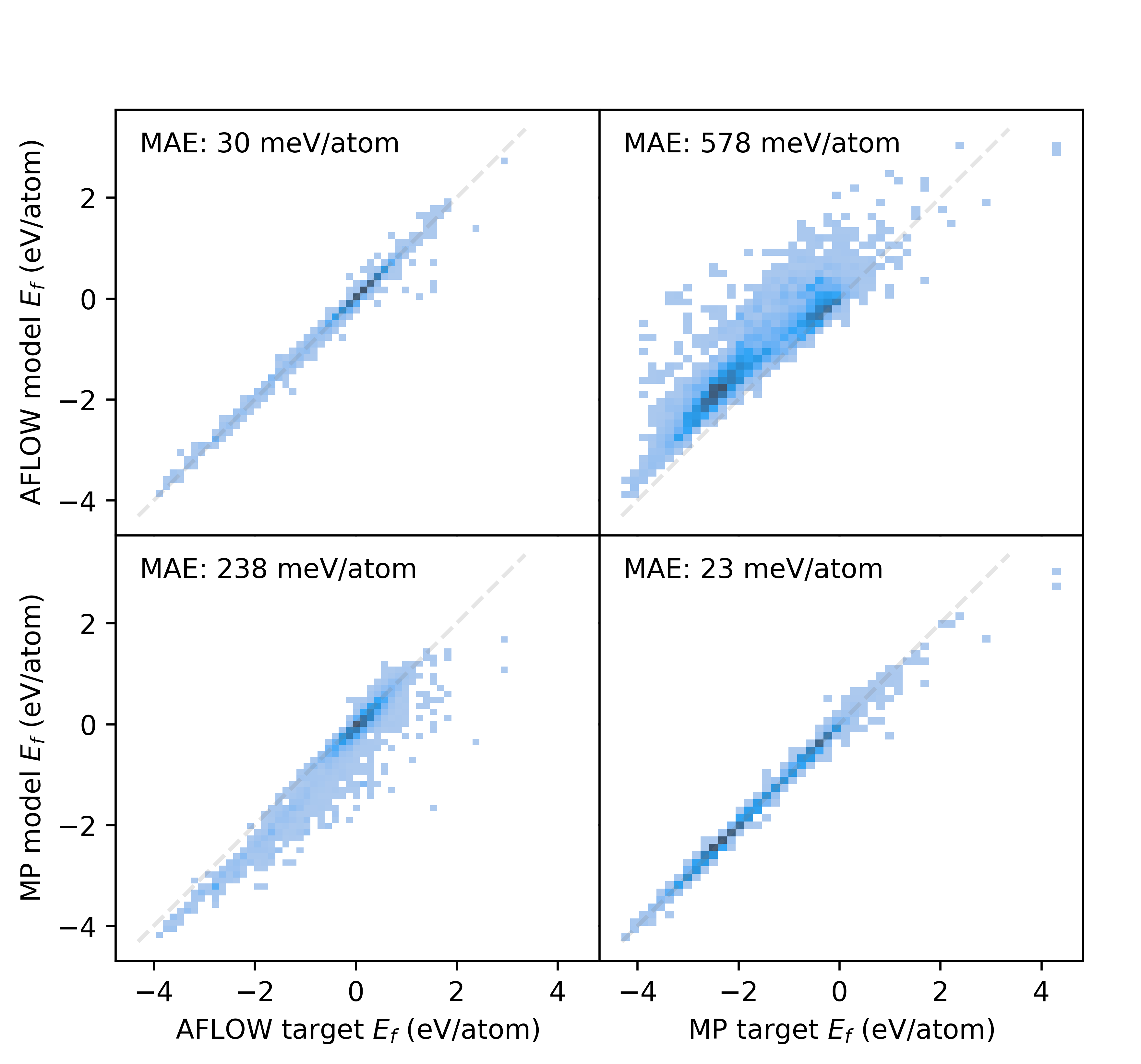

0
How big is Big Data?
Daniel T. Speckhard, Tim Bechtel, Luca M. Ghiringhelli, Martin Kuban, Santiago Rigamonti, Claudia Draxl
Big data has ushered in a new wave of predictive power using machine learning models. In this work, we assess what {it big} means in the context of typical materials-science machine-learning problems. This concerns not only data volume, but also data quality and veracity as much as infrastructure issues. With selected examples, we ask (i) how models generalize to similar datasets, (ii) how high-quality datasets can be gathered from heterogenous sources, (iii) how the feature set and complexity of a model can affect expressivity, and (iv) what infrastructure requirements are needed to create larger datasets and train models on them. In sum, we find that big data present unique challenges along very different aspects that should serve to motivate further work.
Read more5/21/2024


0
Demystifying Object-based Big Data Storage Systems
Anindita Sarkar Mondal, Madhupa Sanyal, Ari Kusumastuti, Hrishav Bakul Barua, Kartick Chandra Mondal
Today's era is the digitized era. Managing such generated big data is an important factor for data scientists. Day by day, it increases the demand for big data storage systems. Different organizations are involved in providing storage-related services. They follow the different architectures or storage models for storing big data. In this survey paper, our target is to highlight such storage architectures which provided by different renowned storage service providers. On an architectural basis, we divide the big data storage systems into five parts, Distributed file systems (DFS), Clustered File Systems (CFS), Cloud Storage, Archive Storage, and Object Storage Systems (OSS). Also, we reveal a detailed architectural view of the big data storage systems provided by the different organizations under these parts.
Read more6/4/2024