Text-guided Controllable Mesh Refinement for Interactive 3D Modeling

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
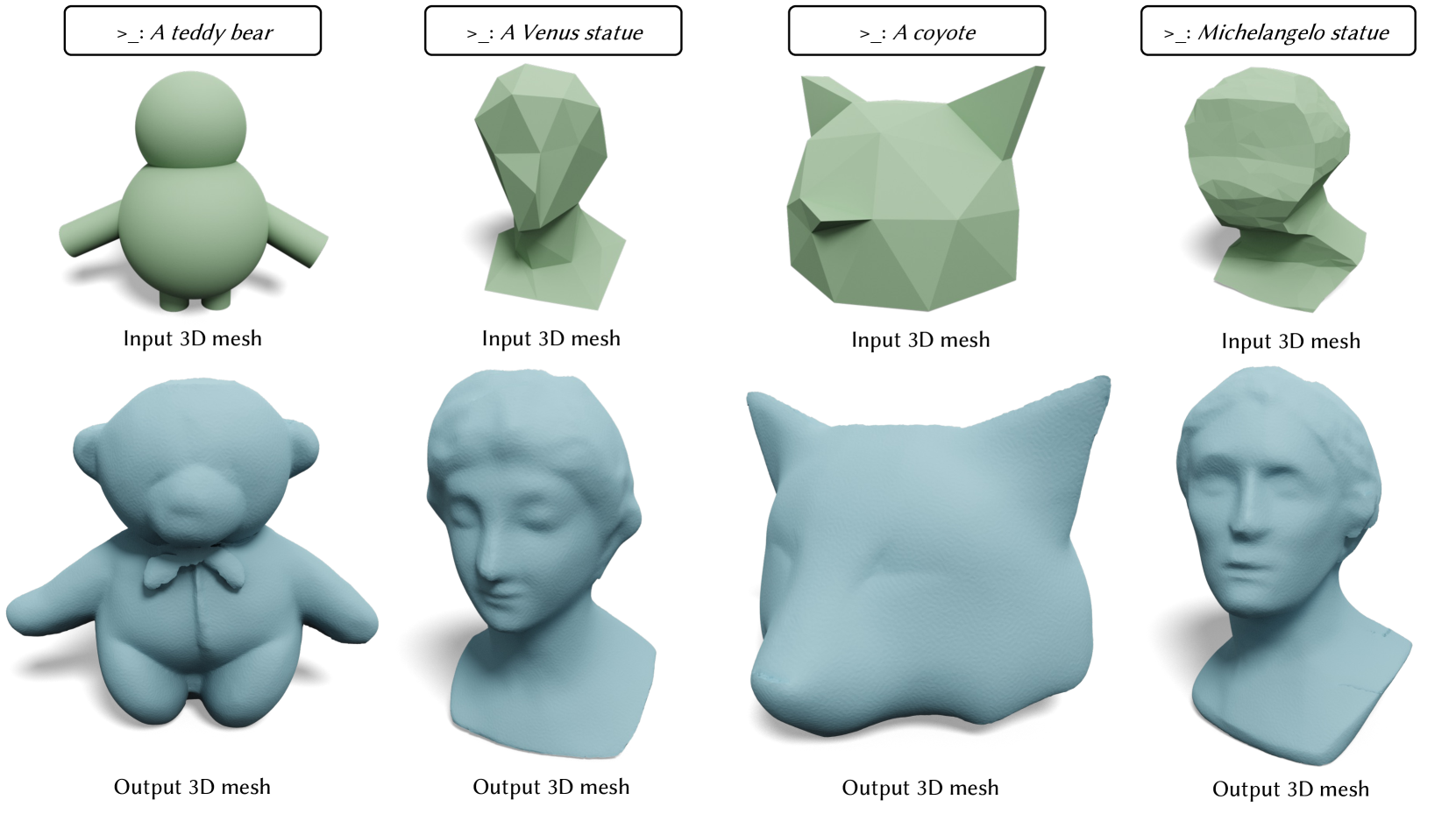
- This paper presents a text-guided system for interactively refining 3D mesh models.
- The system allows users to provide natural language descriptions to guide the refinement process, enabling them to create complex 3D shapes with fine-grained control.
- The approach leverages large language models to translate text prompts into geometric edits, enabling interactive 3D modeling that is guided by user input.
Plain English Explanation
This research describes a new way to create and edit 3D models using words instead of just clicking and dragging. Typically, 3D modeling can be quite complex, requiring specialized skills and a lot of manual adjustments. However, this system lets you simply describe what you want the 3D model to look like, and the computer will automatically update the model accordingly.
For example, you could say "make the object taller and rounder" or "add more detailed features on the surface." The system would then intelligently modify the 3D mesh to match your text description. This text-guided approach allows even novice users to interactively sculpt detailed 3D shapes, as the system translates natural language prompts into the appropriate geometric changes.
The key innovation is leveraging powerful language models, which are trained on vast amounts of text data, to interpret the user's instructions and map them to specific mesh refinement operations. This tight coupling of language understanding and 3D geometry editing enables a new level of intuitive 3D modeling that could be transformative for fields like digital art, product design, and architectural visualization.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces a text-guided 3D mesh refinement system that allows users to interactively create complex 3D shapes by providing natural language descriptions. The system consists of two key components:
-
A text-to-geometry translation module that uses large language models to map text prompts to specific mesh editing operations, such as adding detail, changing the shape, or modifying the surface.
-
A real-time 3D mesh editing engine that can efficiently apply these text-guided refinements to the 3D model, enabling interactive modeling.
The authors demonstrate the capability of their approach through a series of experiments, showing how users can create a diverse range of 3D shapes by providing high-level text instructions. They also compare their system to alternative 3D modeling approaches, highlighting the benefits of the text-guided interface for intuitive and expressive 3D creation.
The research builds upon recent advancements in large language models and interactive 3D modeling, combining these technologies to enable a novel text-driven 3D modeling workflow. This work could have significant implications for making 3D content creation more accessible and intuitive for a broader range of users.
Critical Analysis
The proposed text-guided mesh refinement system presents a compelling approach to interactive 3D modeling, but there are a few potential limitations and areas for further research:
-
The system's performance and ability to handle complex geometric transformations may be constrained by the underlying language model's capabilities. More research is needed to understand the limits of this approach and how it can be scaled to support increasingly intricate 3D shapes.
-
The paper does not provide a detailed analysis of the types of text prompts that the system can effectively handle. Understanding the breadth and limitations of the language understanding module would be valuable for users to assess the system's practical utility.
-
While the authors demonstrate the system's ability to create a diverse range of 3D models, it is unclear how the text-guided approach compares to traditional 3D modeling workflows in terms of efficiency, precision, and the range of possible outcomes. Further comparative studies would help contextualize the benefits and trade-offs of this new interaction paradigm.
-
The paper does not address potential issues related to the interpretability and controllability of the text-to-geometry translation process. Exploring ways to provide users with more transparency and control over the system's decision-making could enhance trust and enable more nuanced 3D modeling.
Despite these areas for improvement, the text-guided 3D mesh refinement system represents a promising step towards more intuitive and accessible 3D content creation, with potential applications across various industries and creative domains.
Conclusion
The research presented in this paper introduces a novel text-guided approach to 3D mesh refinement, allowing users to interactively create complex shapes by providing natural language descriptions. By leveraging powerful language models to translate text prompts into geometric edits, the system enables a new level of intuitive 3D modeling that could significantly lower the barrier to entry for 3D content creation.
While the proposed system has some limitations and areas for further research, it represents an important advancement in the field of interactive 3D modeling. By bridging the gap between language and 3D geometry, this work could pave the way for more accessible and expressive 3D modeling tools, with potential applications in digital art, product design, architectural visualization, and beyond.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Text-guided Controllable Mesh Refinement for Interactive 3D Modeling
Yun-Chun Chen, Selena Ling, Zhiqin Chen, Vladimir G. Kim, Matheus Gadelha, Alec Jacobson
We propose a novel technique for adding geometric details to an input coarse 3D mesh guided by a text prompt. Our method is composed of three stages. First, we generate a single-view RGB image conditioned on the input coarse geometry and the input text prompt. This single-view image generation step allows the user to pre-visualize the result and offers stronger conditioning for subsequent multi-view generation. Second, we use our novel multi-view normal generation architecture to jointly generate six different views of the normal images. The joint view generation reduces inconsistencies and leads to sharper details. Third, we optimize our mesh with respect to all views and generate a fine, detailed geometry as output. The resulting method produces an output within seconds and offers explicit user control over the coarse structure, pose, and desired details of the resulting 3D mesh.
Read more9/12/2024


0
FlashTex: Fast Relightable Mesh Texturing with LightControlNet
Kangle Deng, Timothy Omernick, Alexander Weiss, Deva Ramanan, Jun-Yan Zhu, Tinghui Zhou, Maneesh Agrawala
Manually creating textures for 3D meshes is time-consuming, even for expert visual content creators. We propose a fast approach for automatically texturing an input 3D mesh based on a user-provided text prompt. Importantly, our approach disentangles lighting from surface material/reflectance in the resulting texture so that the mesh can be properly relit and rendered in any lighting environment. We introduce LightControlNet, a new text-to-image model based on the ControlNet architecture, which allows the specification of the desired lighting as a conditioning image to the model. Our text-to-texture pipeline then constructs the texture in two stages. The first stage produces a sparse set of visually consistent reference views of the mesh using LightControlNet. The second stage applies a texture optimization based on Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) that works with LightControlNet to increase the texture quality while disentangling surface material from lighting. Our algorithm is significantly faster than previous text-to-texture methods, while producing high-quality and relightable textures.
Read more4/24/2024
🔮

0
GTR: Improving Large 3D Reconstruction Models through Geometry and Texture Refinement
Peiye Zhuang, Songfang Han, Chaoyang Wang, Aliaksandr Siarohin, Jiaxu Zou, Michael Vasilkovsky, Vladislav Shakhrai, Sergey Korolev, Sergey Tulyakov, Hsin-Ying Lee
We propose a novel approach for 3D mesh reconstruction from multi-view images. Our method takes inspiration from large reconstruction models like LRM that use a transformer-based triplane generator and a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) model trained on multi-view images. However, in our method, we introduce several important modifications that allow us to significantly enhance 3D reconstruction quality. First of all, we examine the original LRM architecture and find several shortcomings. Subsequently, we introduce respective modifications to the LRM architecture, which lead to improved multi-view image representation and more computationally efficient training. Second, in order to improve geometry reconstruction and enable supervision at full image resolution, we extract meshes from the NeRF field in a differentiable manner and fine-tune the NeRF model through mesh rendering. These modifications allow us to achieve state-of-the-art performance on both 2D and 3D evaluation metrics, such as a PSNR of 28.67 on Google Scanned Objects (GSO) dataset. Despite these superior results, our feed-forward model still struggles to reconstruct complex textures, such as text and portraits on assets. To address this, we introduce a lightweight per-instance texture refinement procedure. This procedure fine-tunes the triplane representation and the NeRF color estimation model on the mesh surface using the input multi-view images in just 4 seconds. This refinement improves the PSNR to 29.79 and achieves faithful reconstruction of complex textures, such as text. Additionally, our approach enables various downstream applications, including text- or image-to-3D generation.
Read more6/17/2024


0
Interactive3D: Create What You Want by Interactive 3D Generation
Shaocong Dong, Lihe Ding, Zhanpeng Huang, Zibin Wang, Tianfan Xue, Dan Xu
3D object generation has undergone significant advancements, yielding high-quality results. However, fall short of achieving precise user control, often yielding results that do not align with user expectations, thus limiting their applicability. User-envisioning 3D object generation faces significant challenges in realizing its concepts using current generative models due to limited interaction capabilities. Existing methods mainly offer two approaches: (i) interpreting textual instructions with constrained controllability, or (ii) reconstructing 3D objects from 2D images. Both of them limit customization to the confines of the 2D reference and potentially introduce undesirable artifacts during the 3D lifting process, restricting the scope for direct and versatile 3D modifications. In this work, we introduce Interactive3D, an innovative framework for interactive 3D generation that grants users precise control over the generative process through extensive 3D interaction capabilities. Interactive3D is constructed in two cascading stages, utilizing distinct 3D representations. The first stage employs Gaussian Splatting for direct user interaction, allowing modifications and guidance of the generative direction at any intermediate step through (i) Adding and Removing components, (ii) Deformable and Rigid Dragging, (iii) Geometric Transformations, and (iv) Semantic Editing. Subsequently, the Gaussian splats are transformed into InstantNGP. We introduce a novel (v) Interactive Hash Refinement module to further add details and extract the geometry in the second stage. Our experiments demonstrate that Interactive3D markedly improves the controllability and quality of 3D generation. Our project webpage is available at url{https://interactive-3d.github.io/}.
Read more4/26/2024