Towards Bidirectional Human-AI Alignment: A Systematic Review for Clarifications, Framework, and Future Directions
2406.09264

0
0
Abstract
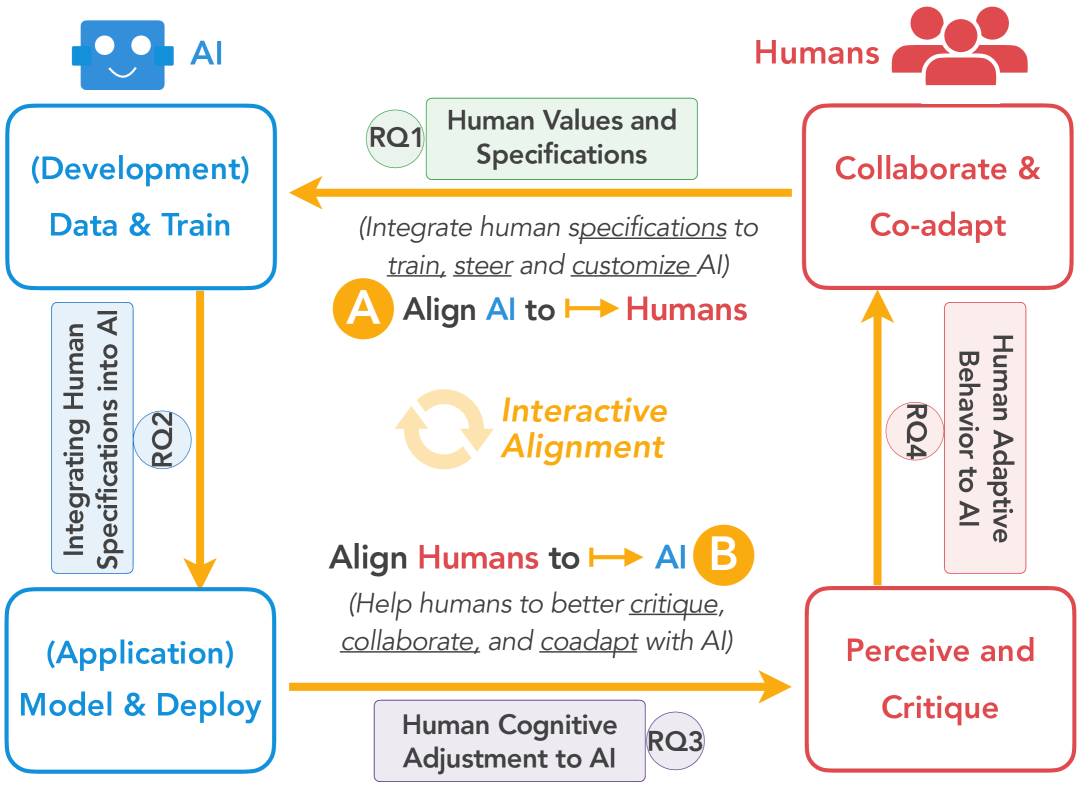
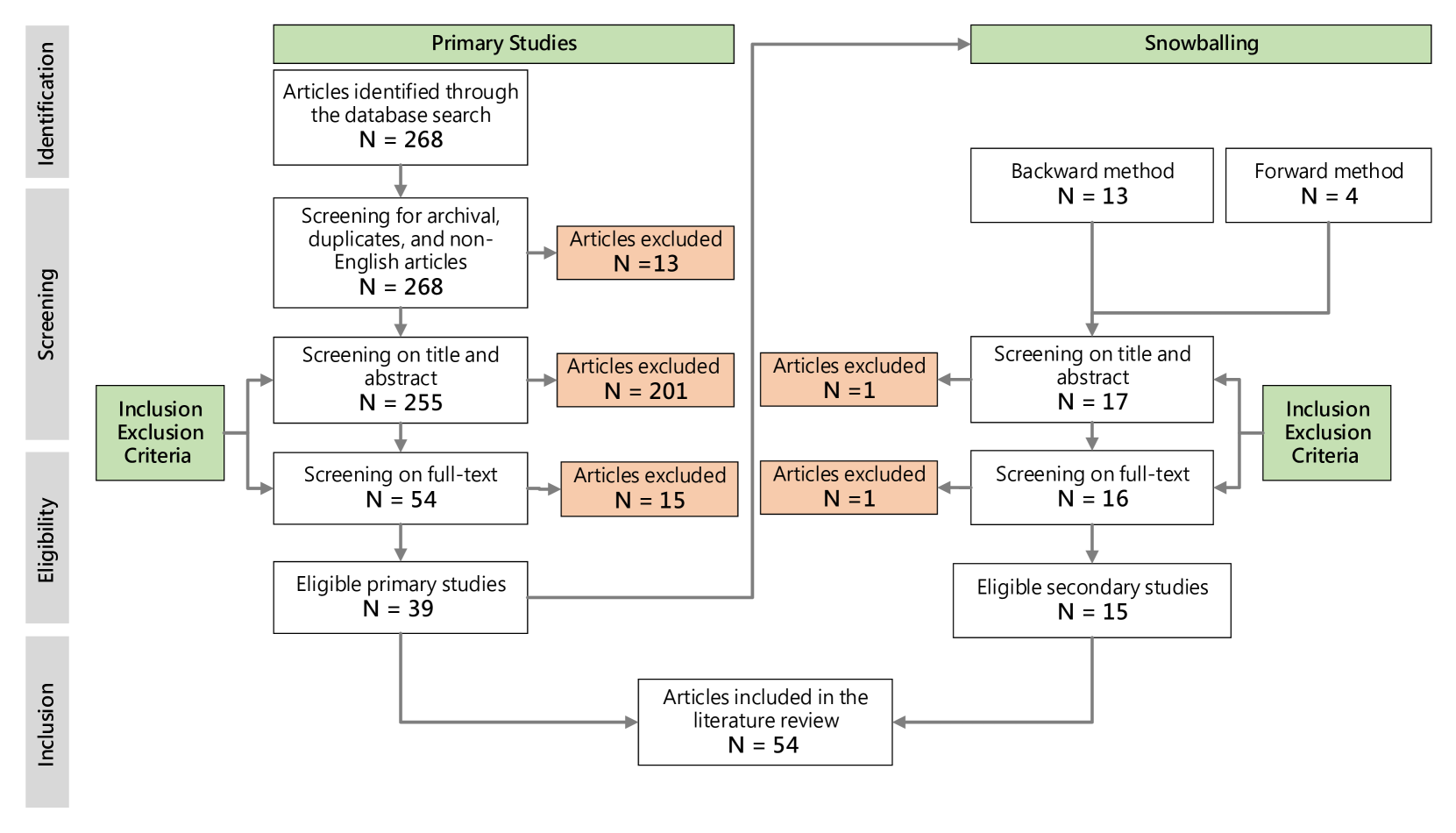
Recent advancements in general-purpose AI have highlighted the importance of guiding AI systems towards the intended goals, ethical principles, and values of individuals and groups, a concept broadly recognized as alignment. However, the lack of clarified definitions and scopes of human-AI alignment poses a significant obstacle, hampering collaborative efforts across research domains to achieve this alignment. In particular, ML- and philosophy-oriented alignment research often views AI alignment as a static, unidirectional process (i.e., aiming to ensure that AI systems' objectives match humans) rather than an ongoing, mutual alignment problem [429]. This perspective largely neglects the long-term interaction and dynamic changes of alignment. To understand these gaps, we introduce a systematic review of over 400 papers published between 2019 and January 2024, spanning multiple domains such as Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and others. We characterize, define and scope human-AI alignment. From this, we present a conceptual framework of Bidirectional Human-AI Alignment to organize the literature from a human-centered perspective. This framework encompasses both 1) conventional studies of aligning AI to humans that ensures AI produces the intended outcomes determined by humans, and 2) a proposed concept of aligning humans to AI, which aims to help individuals and society adjust to AI advancements both cognitively and behaviorally. Additionally, we articulate the key findings derived from literature analysis, including discussions about human values, interaction techniques, and evaluations. To pave the way for future studies, we envision three key challenges for future directions and propose examples of potential future solutions.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a comprehensive review of research on human-AI alignment, which aims to ensure that AI systems behave in ways that are beneficial to humans.
- The authors analyze the current state of the field, identify key challenges, and suggest future research directions to advance the goal of bidirectional human-AI alignment.
- The review covers a wide range of topics, including human-AI interaction, AI explainability and evaluation, and personalized AI systems.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses the challenge of ensuring that AI systems behave in ways that are beneficial to humans, a concept known as human-AI alignment. The authors review the current research in this field, highlighting key issues and suggesting future directions.
One of the main goals is to achieve bidirectional alignment, where not only the AI system behaves in a way that aligns with human preferences, but humans also understand and trust the AI's actions. This is important because as AI systems become more powerful and ubiquitous, it's crucial that humans can effectively communicate with them and have confidence in their behavior.
The paper covers a variety of topics related to human-AI alignment, such as how humans and AI can interact more effectively, how AI systems can be designed to be more transparent and explainable, and how AI systems can be personalized to individual users' needs and preferences. The authors draw insights from research in these areas and propose new ways to address the challenges of ensuring that AI systems are truly aligned with human interests.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a comprehensive literature review on the topic of human-AI alignment, which refers to the goal of ensuring that AI systems behave in ways that are beneficial to humans. The authors analyze the current state of the field, identify key challenges, and suggest future research directions.
The review covers several key aspects of human-AI alignment, including:
- Human-AI interaction: Exploring how humans and AI systems can communicate more effectively and build trust.
- AI explainability and evaluation: Investigating how AI systems can be designed to be more transparent and their behavior can be better understood and evaluated by humans.
- Personalized AI systems: Examining how AI systems can be tailored to individual users' needs and preferences, ensuring a closer alignment between the AI's actions and the user's goals.
The authors also analyze the concept of bidirectional alignment, where not only the AI system behaves in alignment with human preferences, but humans also understand and trust the AI's actions. This is crucial as AI systems become more powerful and ubiquitous, and it's essential that humans can effectively communicate with them and have confidence in their behavior.
The review draws insights from a wide range of research, including studies on quantifying misalignment between agents and beyond-prompts learning from human communication. The authors synthesize these findings to propose new directions for advancing the field of human-AI alignment.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and well-structured review of the current research on human-AI alignment. The authors have done an excellent job of identifying the key challenges and potential solutions in this important and rapidly evolving field.
One of the strengths of the paper is its broad scope, covering a range of topics related to human-AI alignment, from interaction and explainability to personalization. This holistic approach is necessary to address the complex and multifaceted nature of the problem.
However, the paper also acknowledges some of the limitations and caveats of the existing research. For example, the authors note that much of the work on AI explainability has focused on post-hoc explanations, which may not be sufficient to build true understanding and trust between humans and AI systems. They also highlight the need for more research on the long-term effects of personalized AI systems and their potential to exacerbate biases or create echo chambers.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the ethical implications of human-AI alignment in more depth. While the authors discuss the importance of aligning AI systems with human values, they could have delved deeper into the philosophical and moral considerations involved in defining and implementing these values.
Overall, the paper provides a valuable and timely contribution to the field of human-AI alignment. By synthesizing the current research and identifying key areas for future exploration, the authors have laid the groundwork for continued progress towards the goal of ensuring that AI systems truly serve the best interests of humanity.
Conclusion
This comprehensive review paper offers a systematic analysis of the current research on human-AI alignment, a crucial challenge as AI systems become more powerful and ubiquitous. The authors examine key topics such as human-AI interaction, AI explainability and evaluation, and personalized AI systems, ultimately highlighting the importance of bidirectional alignment – where not only the AI system behaves in alignment with human preferences, but humans also understand and trust the AI's actions.
By synthesizing insights from a wide range of studies, the paper provides a valuable framework for advancing the field of human-AI alignment. The authors identify critical challenges and suggest promising future research directions, underscoring the need for continued interdisciplinary collaboration to ensure that AI systems are truly beneficial to humanity.
As AI continues to evolve and become more integrated into our lives, this review paper serves as an important resource for researchers, policymakers, and the general public to better understand the complexities and importance of aligning these powerful technologies with human values and interests.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖
AI Alignment: A Comprehensive Survey
Jiaming Ji, Tianyi Qiu, Boyuan Chen, Borong Zhang, Hantao Lou, Kaile Wang, Yawen Duan, Zhonghao He, Jiayi Zhou, Zhaowei Zhang, Fanzhi Zeng, Kwan Yee Ng, Juntao Dai, Xuehai Pan, Aidan O'Gara, Yingshan Lei, Hua Xu, Brian Tse, Jie Fu, Stephen McAleer, Yaodong Yang, Yizhou Wang, Song-Chun Zhu, Yike Guo, Wen Gao

0
0
AI alignment aims to make AI systems behave in line with human intentions and values. As AI systems grow more capable, so do risks from misalignment. To provide a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of the alignment field, in this survey, we delve into the core concepts, methodology, and practice of alignment. First, we identify four principles as the key objectives of AI alignment: Robustness, Interpretability, Controllability, and Ethicality (RICE). Guided by these four principles, we outline the landscape of current alignment research and decompose them into two key components: forward alignment and backward alignment. The former aims to make AI systems aligned via alignment training, while the latter aims to gain evidence about the systems' alignment and govern them appropriately to avoid exacerbating misalignment risks. On forward alignment, we discuss techniques for learning from feedback and learning under distribution shift. On backward alignment, we discuss assurance techniques and governance practices. We also release and continually update the website (www.alignmentsurvey.com) which features tutorials, collections of papers, blog posts, and other resources.
5/2/2024
Quantifying Misalignment Between Agents
Aidan Kierans, Avijit Ghosh, Hananel Hazan, Shiri Dori-Hacohen

0
0
Growing concerns about the AI alignment problem have emerged in recent years, with previous work focusing mainly on (1) qualitative descriptions of the alignment problem; (2) attempting to align AI actions with human interests by focusing on value specification and learning; and/or (3) focusing on a single agent or on humanity as a singular unit. Recent work in sociotechnical AI alignment has made some progress in defining alignment inclusively, but the field as a whole still lacks a systematic understanding of how to specify, describe, and analyze misalignment among entities, which may include individual humans, AI agents, and complex compositional entities such as corporations, nation-states, and so forth. Previous work on controversy in computational social science offers a mathematical model of contention among populations (of humans). In this paper, we adapt this contention model to the alignment problem, and show how misalignment can vary depending on the population of agents (human or otherwise) being observed, the domain in question, and the agents' probability-weighted preferences between possible outcomes. Our model departs from value specification approaches and focuses instead on the morass of complex, interlocking, sometimes contradictory goals that agents may have in practice. We apply our model by analyzing several case studies ranging from social media moderation to autonomous vehicle behavior. By applying our model with appropriately representative value data, AI engineers can ensure that their systems learn values maximally aligned with diverse human interests.
6/7/2024
🤖
Beyond Prompts: Learning from Human Communication for Enhanced AI Intent Alignment
Yoonsu Kim, Kihoon Son, Seoyoung Kim, Juho Kim

0
0
AI intent alignment, ensuring that AI produces outcomes as intended by users, is a critical challenge in human-AI interaction. The emergence of generative AI, including LLMs, has intensified the significance of this problem, as interactions increasingly involve users specifying desired results for AI systems. In order to support better AI intent alignment, we aim to explore human strategies for intent specification in human-human communication. By studying and comparing human-human and human-LLM communication, we identify key strategies that can be applied to the design of AI systems that are more effective at understanding and aligning with user intent. This study aims to advance toward a human-centered AI system by bringing together human communication strategies for the design of AI systems.
5/10/2024
From Explainable to Interactive AI: A Literature Review on Current Trends in Human-AI Interaction
Muhammad Raees, Inge Meijerink, Ioanna Lykourentzou, Vassilis-Javed Khan, Konstantinos Papangelis

0
0
AI systems are increasingly being adopted across various domains and application areas. With this surge, there is a growing research focus and societal concern for actively involving humans in developing, operating, and adopting these systems. Despite this concern, most existing literature on AI and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) primarily focuses on explaining how AI systems operate and, at times, allowing users to contest AI decisions. Existing studies often overlook more impactful forms of user interaction with AI systems, such as giving users agency beyond contestability and enabling them to adapt and even co-design the AI's internal mechanics. In this survey, we aim to bridge this gap by reviewing the state-of-the-art in Human-Centered AI literature, the domain where AI and HCI studies converge, extending past Explainable and Contestable AI, delving into the Interactive AI and beyond. Our analysis contributes to shaping the trajectory of future Interactive AI design and advocates for a more user-centric approach that provides users with greater agency, fostering not only their understanding of AI's workings but also their active engagement in its development and evolution.
5/27/2024