ToxVidLLM: A Multimodal LLM-based Framework for Toxicity Detection in Code-Mixed Videos

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
ToxVidLLM: A Multimodal LLM-based Framework for Toxicity Detection in Code-Mixed Videos
Krishanu Maity, A. S. Poornash, Sriparna Saha, Pushpak Bhattacharyya
In an era of rapidly evolving internet technology, the surge in multimodal content, including videos, has expanded the horizons of online communication. However, the detection of toxic content in this diverse landscape, particularly in low-resource code-mixed languages, remains a critical challenge. While substantial research has addressed toxic content detection in textual data, the realm of video content, especially in non-English languages, has been relatively underexplored. This paper addresses this research gap by introducing a benchmark dataset, the first of its kind, consisting of 931 videos with 4021 code-mixed Hindi-English utterances collected from YouTube. Each utterance within this dataset has been meticulously annotated for toxicity, severity, and sentiment labels. We have developed an advanced Multimodal Multitask framework built for Toxicity detection in Video Content by leveraging Language Models (LMs), crafted for the primary objective along with the additional tasks of conducting sentiment and severity analysis. ToxVidLM incorporates three key modules - the Encoder module, Cross-Modal Synchronization module, and Multitask module - crafting a generic multimodal LM customized for intricate video classification tasks. Our experiments reveal that incorporating multiple modalities from the videos substantially enhances the performance of toxic content detection by achieving an Accuracy and Weighted F1 score of 94.29% and 94.35%, respectively.
Read more7/16/2024


0
When Video Coding Meets Multimodal Large Language Models: A Unified Paradigm for Video Coding
Pingping Zhang, Jinlong Li, Meng Wang, Nicu Sebe, Sam Kwong, Shiqi Wang
Existing codecs are designed to eliminate intrinsic redundancies to create a compact representation for compression. However, strong external priors from Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have not been explicitly explored in video compression. Herein, we introduce a unified paradigm for Cross-Modality Video Coding (CMVC), which is a pioneering approach to explore multimodality representation and video generative models in video coding. Specifically, on the encoder side, we disentangle a video into spatial content and motion components, which are subsequently transformed into distinct modalities to achieve very compact representation by leveraging MLLMs. During decoding, previously encoded components and video generation models are leveraged to create multiple encoding-decoding modes that optimize video reconstruction quality for specific decoding requirements, including Text-Text-to-Video (TT2V) mode to ensure high-quality semantic information and Image-Text-to-Video (IT2V) mode to achieve superb perceptual consistency. In addition, we propose an efficient frame interpolation model for IT2V mode via Low-Rank Adaption (LoRA) tuning to guarantee perceptual quality, which allows the generated motion cues to behave smoothly. Experiments on benchmarks indicate that TT2V achieves effective semantic reconstruction, while IT2V exhibits competitive perceptual consistency. These results highlight potential directions for future research in video coding.
Read more8/16/2024


0
MM-Soc: Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models in Social Media Platforms
Yiqiao Jin, Minje Choi, Gaurav Verma, Jindong Wang, Srijan Kumar
Social media platforms are hubs for multimodal information exchange, encompassing text, images, and videos, making it challenging for machines to comprehend the information or emotions associated with interactions in online spaces. Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have emerged as a promising solution to these challenges, yet they struggle to accurately interpret human emotions and complex content such as misinformation. This paper introduces MM-Soc, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate MLLMs' understanding of multimodal social media content. MM-Soc compiles prominent multimodal datasets and incorporates a novel large-scale YouTube tagging dataset, targeting a range of tasks from misinformation detection, hate speech detection, and social context generation. Through our exhaustive evaluation on ten size-variants of four open-source MLLMs, we have identified significant performance disparities, highlighting the need for advancements in models' social understanding capabilities. Our analysis reveals that, in a zero-shot setting, various types of MLLMs generally exhibit difficulties in handling social media tasks. However, MLLMs demonstrate performance improvements post fine-tuning, suggesting potential pathways for improvement. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/claws-lab/MMSoc.git.
Read more9/4/2024
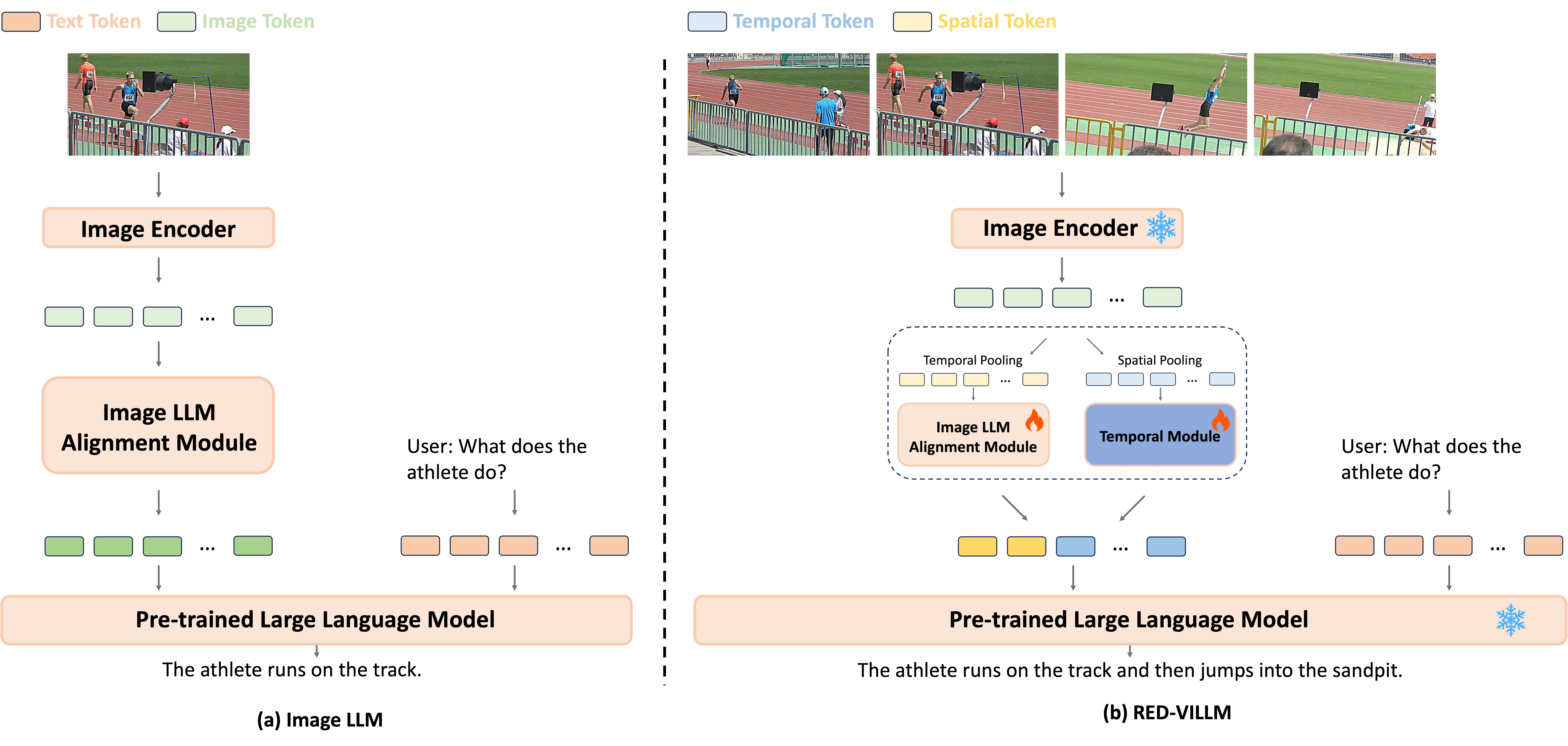

0
From Image to Video, what do we need in multimodal LLMs?
Suyuan Huang, Haoxin Zhang, Yan Gao, Yao Hu, Zengchang Qin
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated profound capabilities in understanding multimodal information, covering from Image LLMs to the more complex Video LLMs. Numerous studies have illustrated their exceptional cross-modal comprehension. Recently, integrating video foundation models with large language models to build a comprehensive video understanding system has been proposed to overcome the limitations of specific pre-defined vision tasks. However, the current advancements in Video LLMs tend to overlook the foundational contributions of Image LLMs, often opting for more complicated structures and a wide variety of multimodal data for pre-training. This approach significantly increases the costs associated with these methods.In response to these challenges, this work introduces an efficient method that strategically leverages the priors of Image LLMs, facilitating a resource-efficient transition from Image to Video LLMs. We propose RED-VILLM, a Resource-Efficient Development pipeline for Video LLMs from Image LLMs, which utilizes a temporal adaptation plug-and-play structure within the image fusion module of Image LLMs. This adaptation extends their understanding capabilities to include temporal information, enabling the development of Video LLMs that not only surpass baseline performances but also do so with minimal instructional data and training resources. Our approach highlights the potential for a more cost-effective and scalable advancement in multimodal models, effectively building upon the foundational work of Image LLMs.
Read more4/19/2024