Towards Secure and Reliable Heterogeneous Real-time Telemetry Communication in Autonomous UAV Swarms

0
👀
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines security vulnerabilities in UAV peer-to-peer telemetry communication
- Explores transitioning to a heterogeneous multi-hop mesh all-to-all communication architecture to improve inter-swarm connectivity and reliability
- Suggests implementing a symmetric key agreement and data encryption mechanism for inter-swarm communication to ensure data integrity and confidentiality without compromising performance
Plain English Explanation
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are becoming increasingly important in solving complex challenges. This paper looks at the security issues with the way UAVs currently communicate their status and data (telemetry) directly with each other.
The researchers propose moving to a new communication system where the UAVs can connect to each other through multiple hops, creating a mesh network. This would make the communication more reliable and allow the UAVs to stay connected, even if some of them are out of direct range.
To keep this communication secure, the paper also suggests using a special encryption method where the UAVs agree on a shared key to encrypt and decrypt their messages. This would protect the data being sent between the UAVs without slowing down the overall system performance.
Technical Explanation
The paper evaluates the security vulnerabilities in the current peer-to-peer telemetry communication used by UAVs. To address these issues, the researchers explore transitioning to a heterogeneous multi-hop mesh all-to-all communication architecture to increase inter-swarm connectivity and reliability.
Additionally, the paper proposes implementing a symmetric key agreement and data encryption mechanism for inter-swarm communication to ensure data integrity and confidentiality without compromising performance. This approach is similar to the techniques discussed in Two-Way Aerial Secure Communications via Distributed and Securing the Skies: IRS-Assisted AOI-Aware Secure for enabling secure communication in UAV networks.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-designed approach to address the security vulnerabilities in UAV peer-to-peer telemetry communication. However, the researchers do not discuss the potential challenges in transitioning existing UAV systems to the proposed multi-hop mesh architecture, such as the compatibility with legacy hardware and software, or the additional computational overhead required.
Additionally, while the symmetric key agreement and encryption mechanism seems promising, the paper does not provide details on the specific algorithms used or evaluate their performance impact on the overall system. Further research may be needed to ensure the proposed security measures can be effectively implemented without compromising the real-time requirements of UAV operations.
Conclusion
This paper presents a promising solution to improve the security of UAV communication by transitioning to a more resilient mesh architecture and implementing robust encryption techniques. If successfully implemented, these advancements could enhance the reliability and trustworthiness of UAV-based systems, paving the way for their wider adoption in various applications, such as ground-to-UAV 140 GHz channel measurement and UAV-enabled collaborative beamforming. However, further research is needed to address the practical challenges and ensure the proposed security measures can be seamlessly integrated into existing UAV infrastructure.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👀

0
Towards Secure and Reliable Heterogeneous Real-time Telemetry Communication in Autonomous UAV Swarms
Pavlo Mykytyn, Marcin Brzozowski, Zoya Dyka, Peter Langendorfer
In the era of cutting-edge autonomous systems, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are becoming an essential part of the solutions for numerous complex challenges. This paper evaluates UAV peer-to-peer telemetry communication, highlighting its security vulnerabilities and explores a transition to a het-erogeneous multi-hop mesh all-to-all communication architecture to increase inter-swarm connectivity and reliability. Additionally, we suggest a symmetric key agreement and data encryption mechanism implementation for inter - swarm communication, to ensure data integrity and confidentiality without compromising performance.
Read more4/12/2024
❗

0
Swarm UAVs Communication
Arindam Majee, Rahul Saha, Snehasish Roy, Srilekha Mandal, Sayan Chatterjee
The advancement in cyber-physical systems has opened a new way in disaster management and rescue operations. The usage of UAVs is very promising in this context. UAVs, mainly quadcopters, are small in size and their payload capacity is limited. A single UAV can not traverse the whole area. Hence multiple UAVs or swarms of UAVs come into the picture managing the entire payload in a modular and equiproportional manner. In this work we have explored a vast topic related to UAVs. Among the UAVs quadcopter is the main focus. We explored the types of quadcopters, their flying strategy,their communication protocols, architecture and controlling techniques, followed by the swarm behaviour in nature and UAVs. Swarm behaviour and a few swarm optimization algorithms has been explored here. Swarm architecture and communication in between swarm UAV networks also got a special attention in our work. In disaster management the UAV swarm network must have to search a large area. And for this proper path planning algorithm is required. We have discussed the existing path planning algorithm, their advantages and disadvantages in great detail. Formation maintenance of the swarm network is an important issue which has been explored through leader-follower technique. The wireless path loss model has been modelled using friis and ground ray reflection model. Using this path loss models we have managed to create the link budget and simulate the variation of communication link performance with the variation of distance.
Read more5/2/2024

0
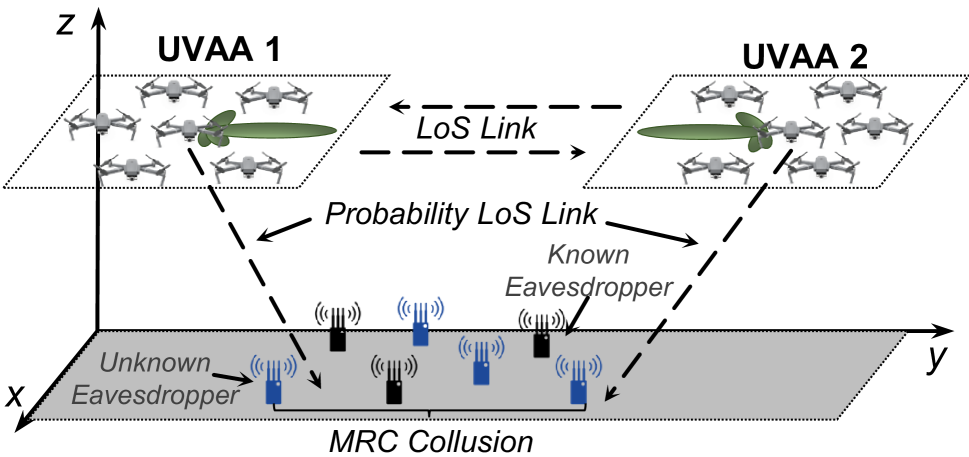
Two-Way Aerial Secure Communications via Distributed Collaborative Beamforming under Eavesdropper Collusion
Jiahui Li, Geng Sun, Qingqing Wu, Shuang Liang, Pengfei Wang, Dusit Niyato
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)-enabled aerial communication provides a flexible, reliable, and cost-effective solution for a range of wireless applications. However, due to the high line-of-sight (LoS) probability, aerial communications between UAVs are vulnerable to eavesdropping attacks, particularly when multiple eavesdroppers collude. In this work, we aim to introduce distributed collaborative beamforming (DCB) into UAV swarms and handle the eavesdropper collusion by controlling the corresponding signal distributions. Specifically, we consider a two-way DCB-enabled aerial communication between two UAV swarms and construct these swarms as two UAV virtual antenna arrays. Then, we minimize the two-way known secrecy capacity and the maximum sidelobe level to avoid information leakage from the known and unknown eavesdroppers, respectively. Simultaneously, we also minimize the energy consumption of UAVs for constructing virtual antenna arrays. Due to the conflicting relationships between secure performance and energy efficiency, we consider these objectives as a multi-objective optimization problem. Following this, we propose an enhanced multi-objective swarm intelligence algorithm via the characterized properties of the problem. Simulation results show that our proposed algorithm can obtain a set of informative solutions and outperform other state-of-the-art baseline algorithms. Experimental tests demonstrate that our method can be deployed in limited computing power platforms of UAVs and is beneficial for saving computational resources.
Read more4/12/2024


0
The Rise of UAV Fleet Technologies for Emergency Wireless Communications in Harsh Environments
Zhuohui Yao, Wenchi Cheng, Wei Zhang, Tao Zhang, Hailin Zhang
For unforeseen emergencies, such as natural disasters and pandemic events, it is highly demanded to cope with the explosive growth of mobile data traffic in extremely critical environments. An Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) fleet is an effective way to facilitate the Emergency wireless COmmunication NETwork (EcoNet). In this article, a MUlti-tier Heterogeneous UAV Network (MuHun), which is with different UAV fleets in different altitudes, is proposed to flexibly serve various emergencies. We refresh the key performance indicators of full coverage, network capacity, low latency, and energy efficiency in harsh environments. Then, we present the special challenges regarding shadowing-dominated complex channel model, energy supply limited short-endurance, various communication mechanisms coexistence, and communication island for underground users in UAV-based EcoNet, followed by the MuHun-based EcoNet architecture and its advantages. Furthermore, some potential solutions such as the new hybrid-channel adapted resource allocation, reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted UAV communications, competitive heterogenous-networks, and magnetic induction based air-to-ground/underground communications are discussed to effectively achieve full coverage, high capacity, high energy efficiency, and diverse qualities of services for EcoNets in harsh environments.
Read more7/25/2024