Codebook-Based Beam Tracking for Conformal ArrayEnabled UAV MmWave Networks
2005.14064

0
0
🚀
Abstract
Millimeter wave (mmWave) communications can potentially meet the high data-rate requirements of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks. However, as the prerequisite of mmWave communications, the narrow directional beam tracking is very challenging because of the three-dimensional (3D) mobility and attitude variation of UAVs. Aiming to address the beam tracking difficulties, we propose to integrate the conformal array (CA) with the surface of each UAV, which enables the full spatial coverage and the agile beam tracking in highly dynamic UAV mmWave networks. More specifically, the key contributions of our work are three-fold. 1) A new mmWave beam tracking framework is established for the CA-enabled UAV mmWave network. 2) A specialized hierarchical codebook is constructed to drive the directional radiating element (DRE)-covered cylindrical conformal array (CCA), which contains both the angular beam pattern and the subarray pattern to fully utilize the potential of the CA. 3) A codebook-based multiuser beam tracking scheme is proposed, where the Gaussian process machine learning enabled UAV position/attitude predication is developed to improve the beam tracking efficiency in conjunction with the tracking-error aware adaptive beamwidth control. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed codebook-based beam tracking scheme in the CA-enabled UAV mmWave network, and demonstrate the advantages of CA over the conventional planner array in terms of spectrum efficiency and outage probability in the highly dynamic scenarios.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Millimeter wave (mmWave) communications can meet the high data-rate requirements of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks.
- Beam tracking, a prerequisite for mmWave communications, is challenging due to the 3D mobility and attitude variation of UAVs.
- The paper proposes integrating conformal arrays (CAs) with UAVs to enable full spatial coverage and agile beam tracking in dynamic UAV mmWave networks.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores a way to improve wireless communication for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which are aircraft that fly without a human pilot on board. UAVs need to be able to transmit and receive large amounts of data quickly, which can be achieved using a type of wireless communication called millimeter wave (mmWave). However, a key challenge with mmWave is that the communication beams need to be precisely aimed, and this is difficult to do with the 3D movement and orientation changes of UAVs.
To address this, the researchers propose integrating a special type of antenna array, called a conformal array (CA), onto the surface of each UAV. This allows the communication beams to be steered more easily to track the rapidly moving UAVs. The paper develops a new beam tracking framework, a specialized codebook to control the CA, and a machine learning-based scheme to predict the UAV's position and orientation to improve beam tracking efficiency.
Overall, the goal is to enable reliable, high-speed wireless links between UAVs using mmWave technology, which could be important for applications like autonomous aerial search and ground-to-UAV communications.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a new mmWave beam tracking framework for UAV networks that integrates conformal antenna arrays (CAs) onto the surface of each UAV. CAs allow for full spatial coverage and agile beam tracking, which is critical given the 3D mobility and attitude variations of UAVs.
Specifically, the key technical contributions are:
- A new mmWave beam tracking framework for CA-enabled UAV networks.
- A specialized hierarchical codebook to control the directional radiating elements (DREs) on a cylindrical conformal array (CCA). This codebook includes both angular beam patterns and subarray patterns to fully leverage the CA's capabilities.
- A codebook-based multiuser beam tracking scheme that uses Gaussian process machine learning to predict UAV position and attitude, improving tracking efficiency. This is combined with an adaptive beamwidth control mechanism that accounts for tracking errors.
The simulations validate the effectiveness of the proposed codebook-based beam tracking approach for CA-enabled UAV mmWave networks. The results demonstrate advantages over conventional planar antenna arrays in terms of spectrum efficiency and outage probability in highly dynamic scenarios.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel solution to the challenging problem of maintaining reliable mmWave links with rapidly moving UAVs. The integration of conformal arrays is a promising approach, as it enables greater beam agility and spatial coverage compared to traditional planar antenna designs.
However, some potential limitations are worth considering. The paper does not address the physical implementation and integration of the conformal arrays onto the UAV platforms, which could introduce additional size, weight, and cost constraints. Additionally, the machine learning-based position/attitude prediction scheme relies on accurate sensor data, which may not always be available, especially in GPS-denied environments.
Further research could explore hybrid beamforming architectures that combine electronic beam steering with mechanical antenna movement to enhance tracking capabilities. Experimental validation of the proposed approach in realistic UAV testbeds would also be valuable to assess its real-world performance and identify any practical implementation challenges.
Conclusion
This paper presents a promising solution to the challenge of maintaining reliable mmWave communications with highly mobile UAVs. By integrating conformal antenna arrays onto the UAVs, the researchers have developed a new beam tracking framework that can better cope with the 3D movement and attitude variations of these aircraft. The specialized codebook and machine learning-based prediction schemes further enhance the system's ability to adaptively track the UAVs and maintain high-speed wireless links. While some implementation details remain to be explored, this work represents an important step towards enabling robust, high-performance mmWave networks for advanced UAV applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

An Accurate Beam-Tracking Algorithm with Adaptive Beam Reconstruction via UAV-BSs for Mobile Users
Jing Zhang, Sheng Gao, Xin Feng, Hongwei Yang, Geng Sun

0
0
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with flexible deployment contribute to enlarging the distance of information transmission to mobile users (MUs) in constrained environment. However, due to the high mobility of both UAVs and MUs, it is challenging to establish an accurate beam towards the target MU with high beam gain in real-time. In this study, UAV base stations (UAV-BSs) consisting of position-known assisted UAVs (A-UAVs) and position-unknown assisted UAVs (U-UAVs) are employed to transmit data to MUs. Specifically, a bi-directional angle-aware beam tracking with adaptive beam reconstruction (BAB-AR) algorithm is proposed to construct an optimal beam that can quickly adapt the movement of the target MU. First, the angle-aware beam tracking is realized within the UAVBSs using a proposed global dynamic crow search algorithm without historical trajectory. Furthermore, the Gaussian process regression model is trained by A-UAVs to predict the azimuth and elevation angles of MUs. Meanwhile, we focus on the beam width and design a time interval adjustment mechanism for adaptive beam reconstruction to track high-speed MUs. Finally, the performance of the BAB-AR algorithm is compared with that of benchmark algorithms, and simulate results verifies that the BAB-AR algorithm can construct an accurate beam capable of covering high-speed MUs with the half power beam width in a timely manner.
4/23/2024

UAV-enabled Collaborative Beamforming via Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning
Saichao Liu, Geng Sun, Jiahui Li, Shuang Liang, Qingqing Wu, Pengfei Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
In this paper, we investigate an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-assistant air-to-ground communication system, where multiple UAVs form a UAV-enabled virtual antenna array (UVAA) to communicate with remote base stations by utilizing collaborative beamforming. To improve the work efficiency of the UVAA, we formulate a UAV-enabled collaborative beamforming multi-objective optimization problem (UCBMOP) to simultaneously maximize the transmission rate of the UVAA and minimize the energy consumption of all UAVs by optimizing the positions and excitation current weights of all UAVs. This problem is challenging because these two optimization objectives conflict with each other, and they are non-concave to the optimization variables. Moreover, the system is dynamic, and the cooperation among UAVs is complex, making traditional methods take much time to compute the optimization solution for a single task. In addition, as the task changes, the previously obtained solution will become obsolete and invalid. To handle these issues, we leverage the multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MADRL) to address the UCBMOP. Specifically, we use the heterogeneous-agent trust region policy optimization (HATRPO) as the basic framework, and then propose an improved HATRPO algorithm, namely HATRPO-UCB, where three techniques are introduced to enhance the performance. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can learn a better strategy compared with other methods. Moreover, extensive experiments also demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed techniques.
4/12/2024

Wideband Beamforming for Near-Field Communications with Circular Arrays
Yunhui Guo, Yang Zhang, Zhaolin Wang, Yuanwei Liu

0
0
The beamforming performance of the uniform circular array (UCA) in near-field wideband communication systems is investigated. Compared to uniform linear array (ULA), UCA exhibits uniform effective array aperture in all directions, thus enabling more users to benefit from near-field communications. In this paper, the unique beam squint effect in near-field wideband UCA systems is comprehensively analyzed in both the distance and angular domains. It is rigorously demonstrated that the beam focal point only exists at a specific frequency in wideband UCA systems, resulting in significant beamforming loss. To alleviate this unique beam squint effect, the true-time delay (TTD)-based beamforming architecture is exploited. In particular, two wideband beamforming optimization approaches leveraging TTD units are proposed. 1) Analytical approach: In this approach, the phase shifters (PSs) and the time delay of TTD units are designed based on the analytical formula for beamforming gain. Following this design, the minimum number of TTD units required to achieve a predetermined beamforming gain is quantified. 2) Joint-optimization approach: In this method, the PSs and the TTD units are jointly optimized under practical maximum delay constraints to approximate the optimal unconstrained analog beamformer. Specifically, an efficient alternating optimization algorithm is proposed, where the PSs and the TTD units are alternately updated using either the closed-form solution or the low-complexity linear search approach. Extensive numerical results demonstrate that 1) the proposed beamforming schemes effectively mitigate the beam squint effect, and 2) the joint-optimization approach outperforms the analytical approach in terms of array gain and achievable spectral efficiency.
4/4/2024
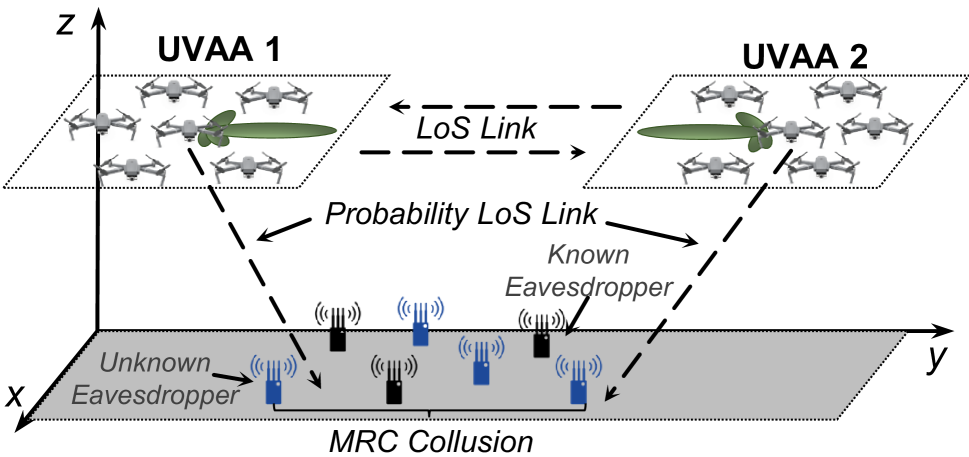
Two-Way Aerial Secure Communications via Distributed Collaborative Beamforming under Eavesdropper Collusion
Jiahui Li, Geng Sun, Qingqing Wu, Shuang Liang, Pengfei Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)-enabled aerial communication provides a flexible, reliable, and cost-effective solution for a range of wireless applications. However, due to the high line-of-sight (LoS) probability, aerial communications between UAVs are vulnerable to eavesdropping attacks, particularly when multiple eavesdroppers collude. In this work, we aim to introduce distributed collaborative beamforming (DCB) into UAV swarms and handle the eavesdropper collusion by controlling the corresponding signal distributions. Specifically, we consider a two-way DCB-enabled aerial communication between two UAV swarms and construct these swarms as two UAV virtual antenna arrays. Then, we minimize the two-way known secrecy capacity and the maximum sidelobe level to avoid information leakage from the known and unknown eavesdroppers, respectively. Simultaneously, we also minimize the energy consumption of UAVs for constructing virtual antenna arrays. Due to the conflicting relationships between secure performance and energy efficiency, we consider these objectives as a multi-objective optimization problem. Following this, we propose an enhanced multi-objective swarm intelligence algorithm via the characterized properties of the problem. Simulation results show that our proposed algorithm can obtain a set of informative solutions and outperform other state-of-the-art baseline algorithms. Experimental tests demonstrate that our method can be deployed in limited computing power platforms of UAVs and is beneficial for saving computational resources.
4/12/2024