User-Access Point Association for High Density MIMO Wireless LANs

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines user-access point (AP) association in dense MIMO wireless LANs
- Focuses on uplink (UL) MIMO to improve network performance
- Proposes an optimization framework to jointly optimize user-AP association and UL MIMO precoding
- Aims to maximize the total UL throughput while maintaining fairness among users
Plain English Explanation
This research paper looks at how users in a dense wireless network should connect to access points (APs) in order to get the best performance. The key idea is to use uplink (UL) MIMO, which allows multiple users to transmit data to an AP at the same time using multiple antennas.
The researchers develop an optimization framework to determine the best way to associate users with APs and how to optimize the MIMO precoding at the same time. The goal is to maximize the total uplink throughput while also ensuring fairness between users.
Technical Explanation
The paper first presents the system and network models, including the MIMO capabilities of the APs and users, the channel conditions, and the optimization objectives.
The key technical contribution is the proposed optimization framework, which jointly optimizes the user-AP associations and the UL MIMO precoding. This is formulated as a mixed-integer nonlinear program that aims to maximize the total UL throughput while maintaining fairness constraints.
The authors develop an efficient algorithm to solve this optimization problem, using techniques like sequential convex approximation and Lagrangian relaxation.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive optimization framework for user-AP association and UL MIMO precoding in dense MIMO wireless LANs. The joint optimization approach is a key strength, as it allows the system to be tuned for maximal performance.
However, the optimization problem is quite complex, and the authors' algorithm may not scale well to very large networks. Additionally, the paper does not consider practical implementation issues, such as the overhead of frequently updating user-AP associations.
Further research could explore more distributed or heuristic approaches to make the solution more practical for real-world deployment. The impact of imperfect channel state information or user mobility could also be investigated.
Conclusion
This research presents an important step forward in addressing the challenges of user-AP association in dense MIMO wireless LANs. By jointly optimizing both the user-AP associations and the UL MIMO precoding, the proposed framework can significantly improve the overall network performance and user fairness. While there are some practical limitations, this work offers valuable insights and a solid foundation for future research in this area.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
User-Access Point Association for High Density MIMO Wireless LANs
Phillip B. Oni, Steven D. Blostein
Wireless local area network (WLAN) access points (APs) are being deployed in high density to improve coverage and throughput. The emerging multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) implementation for uplink (UL) transmissions promises high per-user throughput and improved aggregate network throughput. However, the high throughput potential of dense UL-MIMO WLAN is impaired by multiple access channel interference and high contention among densely distributed user stations (STAs). We investigate the problem of actualizing the throughput potential of UL-MIMO in high density WLANs via user-AP association. Since user-AP association influences interference and STA contention, a method to optimally distribute STAs among APs is proposed to maximize aggregate users' throughput utility. This problem is transformed into a graph matching problem with the throughput utility function as the graph edge weights. The graph matching problem is solved as a combinatorial problem using a modified classical Kuhn-Munkres algorithm. A dynamic implementation of the proposed algorithm is used to periodically update user-AP associations when there are changes in the network due to new entrants and/or user mobility. Simulated dense UL-MIMO WLAN scenarios reveal that the proposed scheme achieves an average of $36.9 %$, $33.5 %$, $20.4 %$ and $11.3 %$ gains over the default strongest signal first (SSF) association scheme used in conventional WLAN, Greedy [14], SmartAssoc [13] and best performance first (BPF) [5] algorithms, respectively.
Read more8/27/2024

0
Joint AP-UE Association and Power Factor Optimization for Distributed Massive MIMO
Mohd Saif Ali Khan, Samar Agnihotri, Karthik R. M
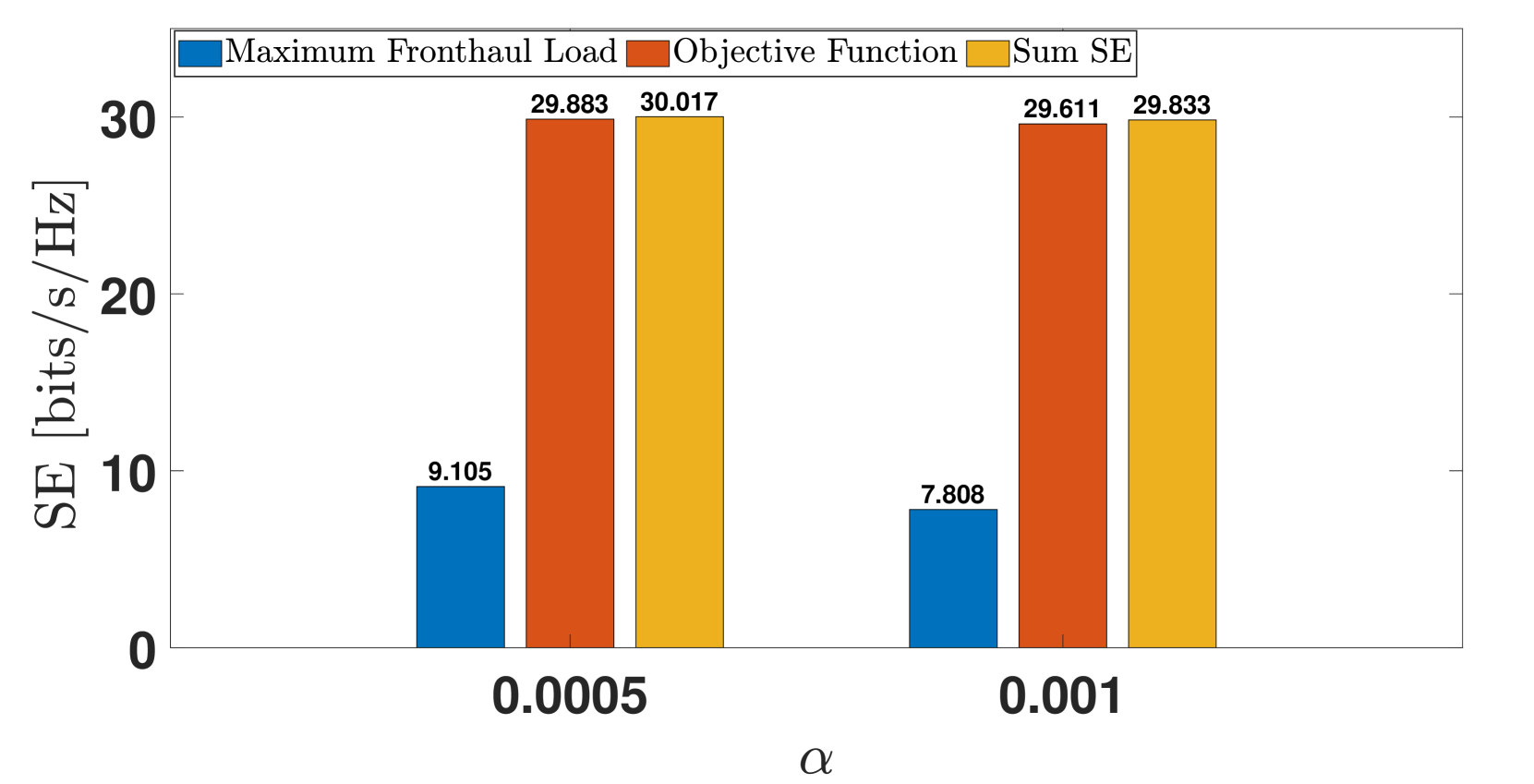
The uplink sum-throughput of distributed massive multiple-input-multiple-output (mMIMO) networks depends majorly on Access point (AP)-User Equipment (UE) association and power control. The AP-UE association and power control both are important problems in their own right in distributed mMIMO networks to improve scalability and reduce front-haul load of the network, and to enhance the system performance by mitigating the interference and boosting the desired signals, respectively. Unlike previous studies, which focused primarily on addressing these two problems separately, this work addresses the uplink sum-throughput maximization problem in distributed mMIMO networks by solving the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, while maintaining Quality-of-Service (QoS) requirements for each UE. To improve scalability, we present an l1-penalty function that delicately balances the trade-off between spectral efficiency (SE) and front-haul signaling load. Our proposed methodology leverages fractional programming, Lagrangian dual formation, and penalty functions to provide an elegant and effective iterative solution with guaranteed convergence. Extensive numerical simulations validate the efficacy of the proposed technique for maximizing sum-throughput while considering the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, demonstrating its superiority over approaches that address these problems individually. Furthermore, the results show that the introduced penalty function can help us effectively control the maximum front-haul load.
Read more5/14/2024

0
IEEE 802.11be Network Throughput Optimization with Multi-Link Operation and AP Coordination
Lyutianyang Zhang, Hao Yin, Sumit Roy, Liu Cao, Xiangyu Gao, Vanlin Sathya
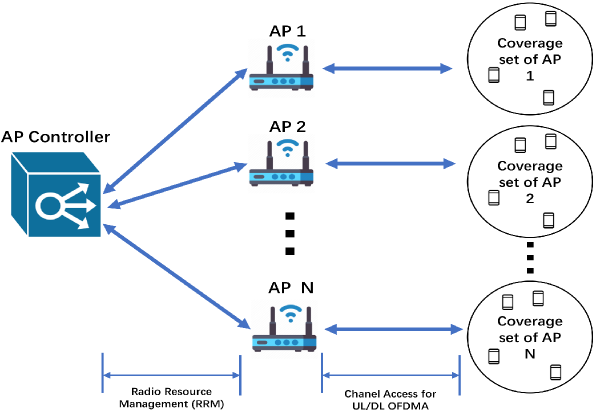
IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) introduces a new concept called multi-link operation (MLO), which allows multiple Wi-Fi interfaces in different bands (2.4, 5, and 6 GHz) to work together to increase network throughput, reduce latency, and improve spectrum reuse efficiency in dense overlapping networks. To make the most of MLO, this paper proposes a new data-driven resource allocation algorithm for the 11be network with the aid of an access point (AP) controller. To maximize network throughput, a network topology optimization problem is formulated for 11be network, which is solved by exploiting the totally unimodular property of the bipartite graph formed by the connection between AP and station (STA) in Wi-Fi networks. Subsequently, a proportional fairness algorithm is applied for radio link allocation, network throughput optimization considering the channel condition, and the fairness of the multi-link device (MLD) data rate. The performance of the proposed algorithm on two main MLO implementations - multi-link multi-radio (MLMR) with simultaneous transmission and reception (STR), and the interplay between multiple nodes employing them are evaluated through cross-layer (PHY-MAC) data rate simulation with PHY abstraction.
Read more4/9/2024


0
Spatial Reuse in IEEE 802.11bn Coordinated Multi-AP WLANs: A Throughput Analysis
David Nunez, Francesc Wilhelmi, Lorenzo Galati-Giordano, Giovanni Geraci, Boris Bellalta
IEEE 802.11 networks continuously adapt to meet the stringent requirements of emerging applications like cloud gaming, eXtended Reality (XR), and video streaming services, which require high throughput, low latency, and high reliability. To address these challenges, Coordinated Spatial Reuse (C-SR) can potentially contribute to optimizing spectrum resource utilization. This mechanism is expected to enable a higher number of simultaneous transmissions, thereby boosting spectral efficiency in dense environments and increasing the overall network performance. In this paper, we focus on the performance analysis of C-SR in Wi-Fi 8 networks. In particular, we consider an implementation of C-SR where channel access and inter-Access Point (AP) communication are performed over-the-air using the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF). For such a purpose, we leverage the well-known Bianchi's throughput model and extend it to support multi-AP transmissions via C-SR. Numerical results in a WLAN network that consists of four APs show C-SR throughput gains ranging from 54% to 280% depending on the inter-AP distance and the position of the stations in the area.
Read more7/24/2024