YuLan: An Open-source Large Language Model
2406.19853

0
0

Abstract
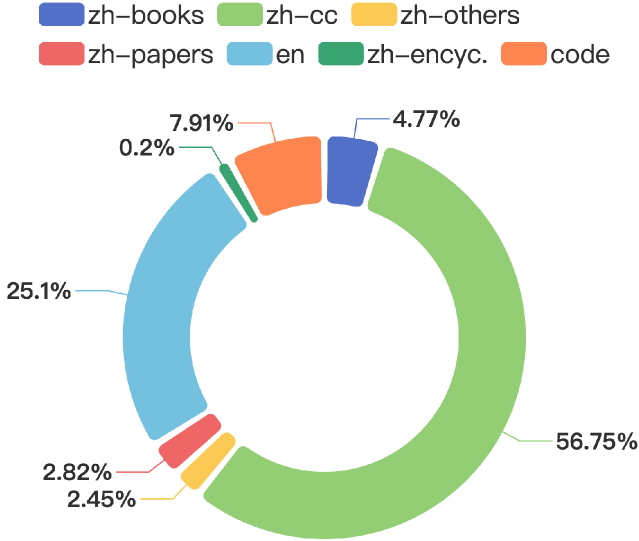
Large language models (LLMs) have become the foundation of many applications, leveraging their extensive capabilities in processing and understanding natural language. While many open-source LLMs have been released with technical reports, the lack of training details hinders further research and development. This paper presents the development of YuLan, a series of open-source LLMs with $12$ billion parameters. The base model of YuLan is pre-trained on approximately $1.7$T tokens derived from a diverse corpus, including massive English, Chinese, and multilingual texts. We design a three-stage pre-training method to enhance YuLan's overall capabilities. Subsequent phases of training incorporate instruction-tuning and human alignment, employing a substantial volume of high-quality synthesized data. To facilitate the learning of complex and long-tail knowledge, we devise a curriculum-learning framework throughout across these stages, which helps LLMs learn knowledge in an easy-to-hard manner. YuLan's training is finished on Jan, 2024 and has achieved performance on par with state-of-the-art LLMs across various English and Chinese benchmarks. This paper outlines a comprehensive technical roadmap for developing LLMs from scratch. Our model and codes are available at https://github.com/RUC-GSAI/YuLan-Chat.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper describes the development of an open-source large language model called YuLan.
- YuLan is a state-of-the-art language model trained on a massive amount of text data, with the goal of being a powerful and versatile tool for natural language processing tasks.
- The paper provides details on the model architecture, training process, and evaluation results, highlighting its performance and capabilities.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have created a new large language model called YuLan, which is a powerful artificial intelligence (AI) system that can understand and generate human-like text. Large language models are trained on huge amounts of text data, allowing them to learn the patterns and structure of language.
YuLan is designed to be an open-source tool that can be used for a wide range of natural language processing tasks, such as answering questions, summarizing text, and generating coherent and meaningful text. The researchers have described the model's architecture, how it was trained, and how well it performs on various benchmarks.
The key idea behind YuLan is to create a highly capable and versatile language model that can be used by researchers, developers, and anyone interested in working with natural language data. By making it open-source, the researchers hope that others can build upon their work and further advance the field of natural language processing.
Technical Explanation
The YuLan model is built using a Transformer architecture, which is a type of neural network that has been highly successful in natural language processing tasks. The model consists of a tokenizer that converts text into a sequence of numerical tokens, an encoder that processes the input text, and a decoder that generates the output text.
The model was trained on a massive corpus of text data, including web pages, books, and other online sources. The researchers used self-supervised learning techniques, where the model learns to predict the next word in a sequence of text, to train the model. This allows the model to learn the underlying patterns and structure of language without being explicitly told what to do.
The researchers evaluated the performance of YuLan on a variety of benchmark tasks, such as language understanding, text generation, and question answering. The results showed that YuLan outperforms many existing language models and can be used for a wide range of natural language processing applications.
Critical Analysis
The researchers have provided a thorough technical explanation of the YuLan model and its capabilities. However, they have not addressed some potential limitations or concerns that may arise from the use of such a powerful language model.
One potential issue is the potential for bias and misinformation in the model's outputs, as it is trained on a vast and diverse corpus of text data that may contain inaccuracies or biases. The researchers should have addressed how they plan to mitigate these risks and ensure the model's outputs are reliable and trustworthy.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss the energy and computational costs associated with training and running the YuLan model, which can be a significant concern for real-world applications. The researchers should have provided more information on the model's resource requirements and how they plan to address the environmental impact of large language models.
Overall, the paper provides a strong technical foundation for the YuLan model, but could have benefited from a more comprehensive discussion of potential limitations and areas for further research.
Conclusion
The YuLan model represents a significant advancement in the field of large language models, offering a powerful and versatile tool for a wide range of natural language processing tasks. By making the model open-source, the researchers are enabling others to build upon their work and further push the boundaries of what is possible with artificial intelligence.
While the technical details and evaluation results are impressive, the paper could have done more to address potential concerns and limitations of the model. Nonetheless, the development of YuLan is an important step forward in the quest to create AI systems that can truly understand and engage with human language.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Chinese Tiny LLM: Pretraining a Chinese-Centric Large Language Model
Xinrun Du, Zhouliang Yu, Songyang Gao, Ding Pan, Yuyang Cheng, Ziyang Ma, Ruibin Yuan, Xingwei Qu, Jiaheng Liu, Tianyu Zheng, Xinchen Luo, Guorui Zhou, Binhang Yuan, Wenhu Chen, Jie Fu, Ge Zhang

0
0
In this study, we introduce CT-LLM, a 2B large language model (LLM) that illustrates a pivotal shift towards prioritizing the Chinese language in developing LLMs. Uniquely initiated from scratch, CT-LLM diverges from the conventional methodology by primarily incorporating Chinese textual data, utilizing an extensive corpus of 1,200 billion tokens, including 800 billion Chinese tokens, 300 billion English tokens, and 100 billion code tokens. This strategic composition facilitates the model's exceptional proficiency in understanding and processing Chinese, a capability further enhanced through alignment techniques. Demonstrating remarkable performance on the CHC-Bench, CT-LLM excels in Chinese language tasks, and showcases its adeptness in English through SFT. This research challenges the prevailing paradigm of training LLMs predominantly on English corpora and then adapting them to other languages, broadening the horizons for LLM training methodologies. By open-sourcing the full process of training a Chinese LLM, including a detailed data processing procedure with the obtained Massive Appropriate Pretraining Chinese Corpus (MAP-CC), a well-chosen multidisciplinary Chinese Hard Case Benchmark (CHC-Bench), and the 2B-size Chinese Tiny LLM (CT-LLM), we aim to foster further exploration and innovation in both academia and industry, paving the way for more inclusive and versatile language models.
4/10/2024

Xmodel-LM Technical Report
Yichuan Wang, Yang Liu, Yu Yan, Qun Wang, Xucheng Huang, Ling Jiang

0
0
We introduce Xmodel-LM, a compact and efficient 1.1B language model pre-trained on around 2 trillion tokens. Trained on our self-built dataset (Xdata), which balances Chinese and English corpora based on downstream task optimization, Xmodel-LM exhibits remarkable performance despite its smaller size. It notably surpasses existing open-source language models of similar scale. Our model checkpoints and code are publicly accessible on GitHub at https://github.com/XiaoduoAILab/XmodelLM.
6/27/2024
🎯
ChuXin: 1.6B Technical Report
Xiaomin Zhuang, Yufan Jiang, Qiaozhi He, Zhihua Wu

0
0
In this report, we present ChuXin, an entirely open-source language model with a size of 1.6 billion parameters. Unlike the majority of works that only open-sourced the model weights and architecture, we have made everything needed to train a model available, including the training data, the training process, and the evaluation code. Our goal is to empower and strengthen the open research community, fostering transparency and enabling a new wave of innovation in the field of language modeling. Furthermore, we extend the context length to 1M tokens through lightweight continual pretraining and demonstrate strong needle-in-a-haystack retrieval performance. The weights for both models are available at Hugging Face to download and use.
5/9/2024
🐍
Tele-FLM Technical Report
Xiang Li, Yiqun Yao, Xin Jiang, Xuezhi Fang, Chao Wang, Xinzhang Liu, Zihan Wang, Yu Zhao, Xin Wang, Yuyao Huang, Shuangyong Song, Yongxiang Li, Zheng Zhang, Bo Zhao, Aixin Sun, Yequan Wang, Zhongjiang He, Zhongyuan Wang, Xuelong Li, Tiejun Huang

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) have showcased profound capabilities in language understanding and generation, facilitating a wide array of applications. However, there is a notable paucity of detailed, open-sourced methodologies on efficiently scaling LLMs beyond 50 billion parameters with minimum trial-and-error cost and computational resources. In this report, we introduce Tele-FLM (aka FLM-2), a 52B open-sourced multilingual large language model that features a stable, efficient pre-training paradigm and enhanced factual judgment capabilities. Tele-FLM demonstrates superior multilingual language modeling abilities, measured by BPB on textual corpus. Besides, in both English and Chinese foundation model evaluation, it is comparable to strong open-sourced models that involve larger pre-training FLOPs, such as Llama2-70B and DeepSeek-67B. In addition to the model weights, we share the core designs, engineering practices, and training details, which we expect to benefit both the academic and industrial communities.
4/26/2024