Adapting General Disentanglement-Based Speaker Anonymization for Enhanced Emotion Preservation

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Focuses on adapting a general disentanglement-based speaker anonymization approach to enhance emotion preservation
- Proposes a modified system to better maintain emotional characteristics during the anonymization process
- Evaluates the emotional similarity and anonymization performance of the proposed method
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a technique for anonymizing speakers' voices while trying to preserve the emotional content of the speech. Typically, voice anonymization can remove the unique identifying characteristics of a speaker's voice, but this may also end up distorting the emotional expression.
The researchers adapted a general disentanglement-based approach, which aims to separate different aspects of the voice, such as speaker identity, emotion, and linguistic content. By modifying this method, they were able to maintain the emotional characteristics of the speech while still anonymizing the speaker's identity.
The key idea is to carefully balance the competing goals of preserving emotion and obscuring the speaker's identity. The proposed system was evaluated on its ability to preserve emotional similarity and anonymize the speaker effectively.
Technical Explanation
The paper builds upon a general disentanglement-based speaker anonymization approach, which aims to separate the speaker's identity, emotion, and linguistic content into distinct latent representations.
The researchers modified this framework to better preserve the emotional characteristics of the speech during the anonymization process. This involved introducing additional constraints and losses to the model, encouraging it to maintain the emotional content while still effectively anonymizing the speaker.
The experimental evaluation focused on assessing the emotional similarity and anonymization performance of the proposed method, comparing it to the original disentanglement-based approach and other baselines. The results demonstrate the ability of the modified system to preserve emotional expression while still successfully anonymizing the speaker's identity.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a thoughtful approach to addressing the challenge of balancing speaker anonymization and emotion preservation. By building upon an existing disentanglement-based framework, the researchers were able to leverage insights from prior work while introducing novel modifications to better suit their goal of enhanced emotion preservation.
However, the paper does not delve into potential limitations or caveats of the proposed method. It would be valuable to understand any trade-offs or challenges encountered, such as the impact on other voice characteristics or the computational complexity of the modified system.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the broader implications of this research, such as its potential applications in sensitive domains like healthcare or the ethical considerations around preserving emotional expression in anonymized voices.
Conclusion
The paper presents an innovative approach to speaker anonymization that aims to preserve emotional characteristics, a crucial aspect often overlooked in prior work. By adapting a general disentanglement-based framework, the researchers demonstrate the feasibility of maintaining emotional similarity while effectively anonymizing speaker identity.
This research has the potential to advance the field of voice anonymization, particularly in scenarios where preserving emotional expression is important, such as in healthcare applications or accessibility services. The findings could also inspire further exploration of the delicate balance between privacy and emotional fidelity in voice-based technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Adapting General Disentanglement-Based Speaker Anonymization for Enhanced Emotion Preservation
Xiaoxiao Miao, Yuxiang Zhang, Xin Wang, Natalia Tomashenko, Donny Cheng Lock Soh, Ian Mcloughlin
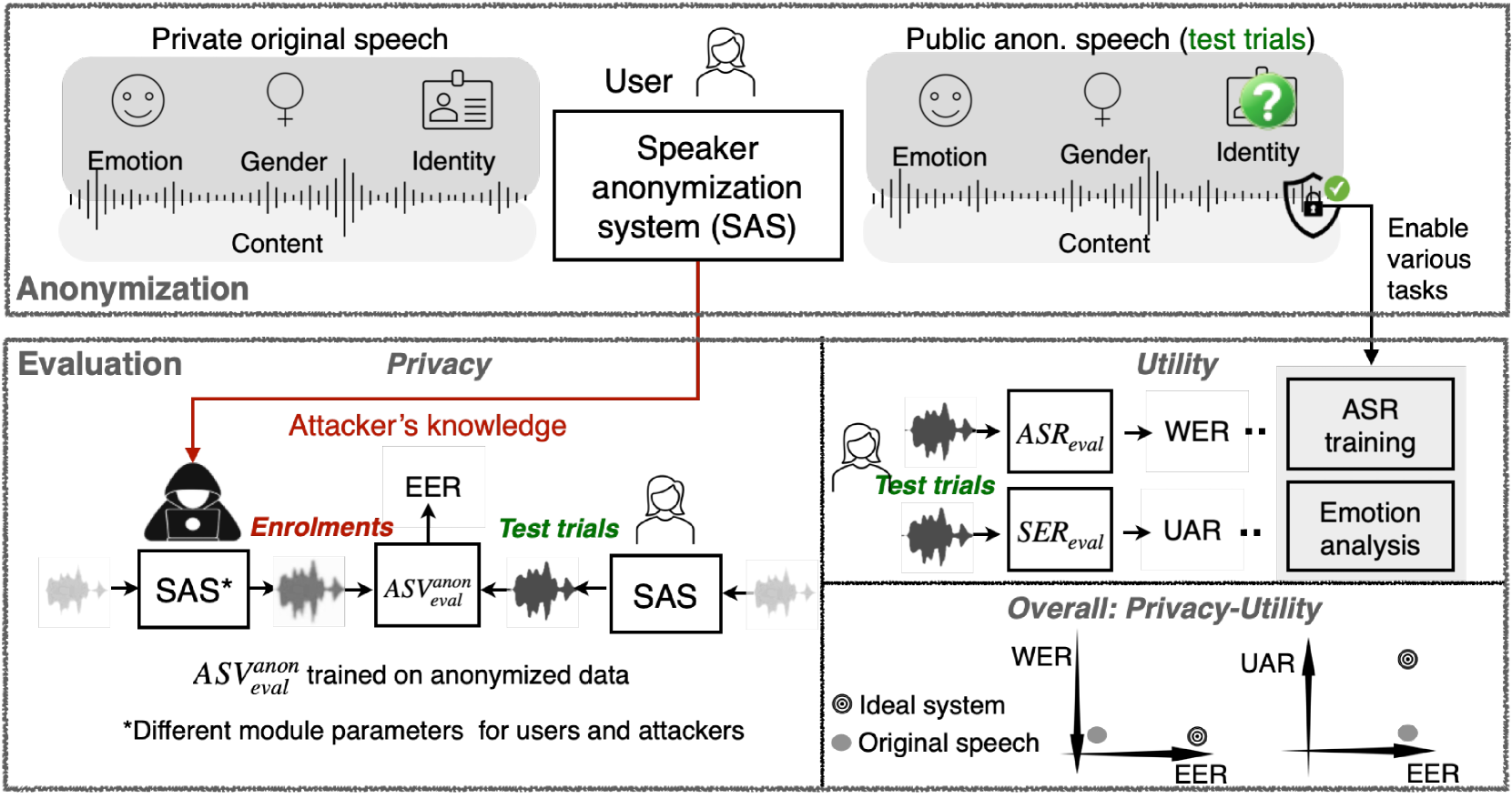
A general disentanglement-based speaker anonymization system typically separates speech into content, speaker, and prosody features using individual encoders. This paper explores how to adapt such a system when a new speech attribute, for example, emotion, needs to be preserved to a greater extent. While existing systems are good at anonymizing speaker embeddings, they are not designed to preserve emotion. Two strategies for this are examined. First, we show that integrating emotion embeddings from a pre-trained emotion encoder can help preserve emotional cues, even though this approach slightly compromises privacy protection. Alternatively, we propose an emotion compensation strategy as a post-processing step applied to anonymized speaker embeddings. This conceals the original speaker's identity and reintroduces the emotional traits lost during speaker embedding anonymization. Specifically, we model the emotion attribute using support vector machines to learn separate boundaries for each emotion. During inference, the original speaker embedding is processed in two ways: one, by an emotion indicator to predict emotion and select the emotion-matched SVM accurately; and two, by a speaker anonymizer to conceal speaker characteristics. The anonymized speaker embedding is then modified along the corresponding SVM boundary towards an enhanced emotional direction to save the emotional cues. The proposed strategies are also expected to be useful for adapting a general disentanglement-based speaker anonymization system to preserve other target paralinguistic attributes, with potential for a range of downstream tasks.
Read more8/13/2024


0
Privacy versus Emotion Preservation Trade-offs in Emotion-Preserving Speaker Anonymization
Zexin Cai, Henry Li Xinyuan, Ashi Garg, Leibny Paola Garc'ia-Perera, Kevin Duh, Sanjeev Khudanpur, Nicholas Andrews, Matthew Wiesner
Advances in speech technology now allow unprecedented access to personally identifiable information through speech. To protect such information, the differential privacy field has explored ways to anonymize speech while preserving its utility, including linguistic and paralinguistic aspects. However, anonymizing speech while maintaining emotional state remains challenging. We explore this problem in the context of the VoicePrivacy 2024 challenge. Specifically, we developed various speaker anonymization pipelines and find that approaches either excel at anonymization or preserving emotion state, but not both simultaneously. Achieving both would require an in-domain emotion recognizer. Additionally, we found that it is feasible to train a semi-effective speaker verification system using only emotion representations, demonstrating the challenge of separating these two modalities.
Read more9/6/2024


0
Asynchronous Voice Anonymization Using Adversarial Perturbation On Speaker Embedding
Rui Wang, Liping Chen, Kong AiK Lee, Zhen-Hua Ling
Voice anonymization has been developed as a technique for preserving privacy by replacing the speaker's voice in a speech signal with that of a pseudo-speaker, thereby obscuring the original voice attributes from machine recognition and human perception. In this paper, we focus on altering the voice attributes against machine recognition while retaining human perception. We referred to this as the asynchronous voice anonymization. To this end, a speech generation framework incorporating a speaker disentanglement mechanism is employed to generate the anonymized speech. The speaker attributes are altered through adversarial perturbation applied on the speaker embedding, while human perception is preserved by controlling the intensity of perturbation. Experiments conducted on the LibriSpeech dataset showed that the speaker attributes were obscured with their human perception preserved for 60.71% of the processed utterances.
Read more6/14/2024


0
NPU-NTU System for Voice Privacy 2024 Challenge
Jixun Yao, Nikita Kuzmin, Qing Wang, Pengcheng Guo, Ziqian Ning, Dake Guo, Kong Aik Lee, Eng-Siong Chng, Lei Xie
Speaker anonymization is an effective privacy protection solution that conceals the speaker's identity while preserving the linguistic content and paralinguistic information of the original speech. To establish a fair benchmark and facilitate comparison of speaker anonymization systems, the VoicePrivacy Challenge (VPC) was held in 2020 and 2022, with a new edition planned for 2024. In this paper, we describe our proposed speaker anonymization system for VPC 2024. Our system employs a disentangled neural codec architecture and a serial disentanglement strategy to gradually disentangle the global speaker identity and time-variant linguistic content and paralinguistic information. We introduce multiple distillation methods to disentangle linguistic content, speaker identity, and emotion. These methods include semantic distillation, supervised speaker distillation, and frame-level emotion distillation. Based on these distillations, we anonymize the original speaker identity using a weighted sum of a set of candidate speaker identities and a randomly generated speaker identity. Our system achieves the best trade-off of privacy protection and emotion preservation in VPC 2024.
Read more9/9/2024