Advancements in UWB: Paving the Way for Sovereign Data Networks in Healthcare Facilities

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Advancements in ultra-wideband (UWB) technology are paving the way for secure and reliable data networks in healthcare facilities
- Key focus areas include security enhancements, localization capabilities, and integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart city infrastructure
- Research explores how UWB can enable sovereign data networks that protect patient privacy and support critical healthcare applications
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses how recent advancements in UWB technology are opening up new possibilities for data networks in healthcare settings. UWB is a wireless communication standard that offers high-precision localization capabilities and robust security features.
By leveraging UWB, healthcare facilities can build sovereign data networks that keep sensitive patient information secure and enable critical applications like asset tracking and patient monitoring. UWB's ability to accurately pinpoint the location of connected devices is particularly valuable in healthcare, allowing facilities to closely monitor the movements of staff, patients, and medical equipment.
Additionally, UWB-enabled IoT systems can integrate with broader smart city infrastructure, creating a holistic ecosystem to support healthcare delivery. This could lead to improved emergency response, more efficient resource allocation, and better coordination between healthcare facilities and other community services.
Technical Explanation
The paper examines how UWB technology can be leveraged to enhance security and localization capabilities in healthcare environments. UWB's high-bandwidth, low-power, and precise ranging characteristics make it well-suited for applications requiring accurate tracking and secure communications.
The researchers outline several key security enhancements enabled by UWB, including device authentication, encryption, and anti-jamming measures. These features help protect against unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of sensitive patient data transmitted across the network.
The paper also explores UWB's localization capabilities, which can track the position of connected devices with centimeter-level accuracy. This allows healthcare facilities to monitor the movements of staff, patients, and medical equipment in real-time, improving asset management and supporting critical applications like emergency response.
By integrating UWB-enabled IoT systems with broader smart city infrastructure, the researchers envision a holistic ecosystem that can enhance healthcare delivery. This includes improved coordination between healthcare facilities and community services, more efficient resource allocation, and enhanced emergency response capabilities.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a compelling vision for how UWB technology can transform data networks in healthcare facilities, addressing key challenges around security, localization, and integration with smart city systems. However, the researchers acknowledge several potential limitations and areas for further research.
One concern is the scalability of UWB-based networks, as the high-precision localization capabilities may become more challenging to maintain in large-scale deployments with many connected devices. The researchers suggest exploring hybrid approaches that combine UWB with other wireless technologies to address this issue.
The paper also highlights the need for further research on the privacy implications of UWB-enabled tracking and monitoring systems, particularly regarding patient consent and data ownership. Addressing these ethical considerations will be crucial as healthcare facilities look to adopt these technologies.
Additionally, the researchers note that the integration of UWB-based healthcare systems with broader smart city infrastructure remains a complex challenge, requiring careful coordination and standardization across different stakeholders and domains.
Conclusion
The advancements in UWB technology outlined in this paper hold significant promise for enhancing data networks in healthcare facilities. By leveraging UWB's security features and precise localization capabilities, healthcare organizations can build sovereign data networks that protect patient privacy and enable critical applications like asset tracking and patient monitoring.
Furthermore, the integration of UWB-enabled IoT systems with smart city infrastructure has the potential to improve emergency response, resource allocation, and coordination between healthcare facilities and community services. However, the researchers highlight the need to address scalability, privacy, and cross-domain integration challenges to fully realize the potential of UWB in healthcare settings.
As UWB technology continues to evolve, the insights and recommendations provided in this paper can help guide healthcare organizations and policymakers in shaping the future of secure and intelligent data networks in the healthcare sector.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Advancements in UWB: Paving the Way for Sovereign Data Networks in Healthcare Facilities
Khan Reaz, Thibaud Ardoin, Lea Muth, Marian Margraf, Gerhard Wunder, Mahsa Kholghi, Kai Jansen, Christian Zenger, Julian Schmidt, Enrico Koppe, Zoran Utkovski, Igor Bjelakovic, Mathis Schmieder, Olaf Dressel
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology re-emerges as a groundbreaking ranging technology with its precise micro-location capabilities and robustness. This paper highlights the security dimensions of UWB technology, focusing in particular on the intricacies of device fingerprinting for authentication, examined through the lens of state-of-the-art deep learning techniques. Furthermore, we explore various potential enhancements to the UWB standard that could realize a sovereign UWB data network. We argue that UWB data communication holds significant potential in healthcare and ultra-secure environments, where the use of the common unlicensed 2.4~GHz band-centric wireless technology is limited or prohibited. A sovereign UWB network could serve as an alternative, providing secure localization and short-range data communication in such environments.
Read more8/26/2024
🔎

0
Securing Hybrid Wireless Body Area Networks (HyWBAN): Advancements in Semantic Communications and Jamming Techniques
Simone Soderi, Mariella Sarestoniemi, Syifaul Fuada, Matti Hamalainen, Marcos Katz, Jari Iinatti
This paper explores novel strategies to strengthen the security of Hybrid Wireless Body Area Networks (HyWBANs), essential in smart healthcare and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Recognizing the vulnerability of HyWBAN to sophisticated cyber-attacks, we propose an innovative combination of semantic communications and jamming receivers. This dual-layered security mechanism protects against unauthorized access and data breaches, particularly in scenarios involving in-body to on-body communication channels. We conduct comprehensive laboratory measurements to understand hybrid (radio and optical) communication propagation through biological tissues and utilize these insights to refine a dataset for training a Deep Learning (DL) model. These models, in turn, generate semantic concepts linked to cryptographic keys for enhanced data confidentiality and integrity using a jamming receiver. The proposed model demonstrates a significant reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional cryptographic methods, like Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH), especially when supplemented with jamming. Our approach addresses the primary security concerns and sets the baseline for future secure biomedical communication systems advancements.
Read more4/26/2024


0
Semi-Supervised Novelty Detection for Precise Ultra-Wideband Error Signal Prediction
Umberto Albertin, Alessandro Navone, Mauro Martini, Marcello Chiaberge
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology is an emerging low-cost solution for localization in a generic environment. However, UWB signal can be affected by signal reflections and non-line-of-sight (NLoS) conditions between anchors; hence, in a broader sense, the specific geometry of the environment and the disposition of obstructing elements in the map may drastically hinder the reliability of UWB for precise robot localization. This work aims to mitigate this problem by learning a map-specific characterization of the UWB quality signal with a fingerprint semi-supervised novelty detection methodology. An unsupervised autoencoder neural network is trained on nominal UWB map conditions, and then it is used to predict errors derived from the introduction of perturbing novelties in the environment. This work poses a step change in the understanding of UWB localization and its reliability in evolving environmental conditions. The resulting performance of the proposed method is proved by fine-grained experiments obtained with a visual tracking ground truth.
Read more4/9/2024

0
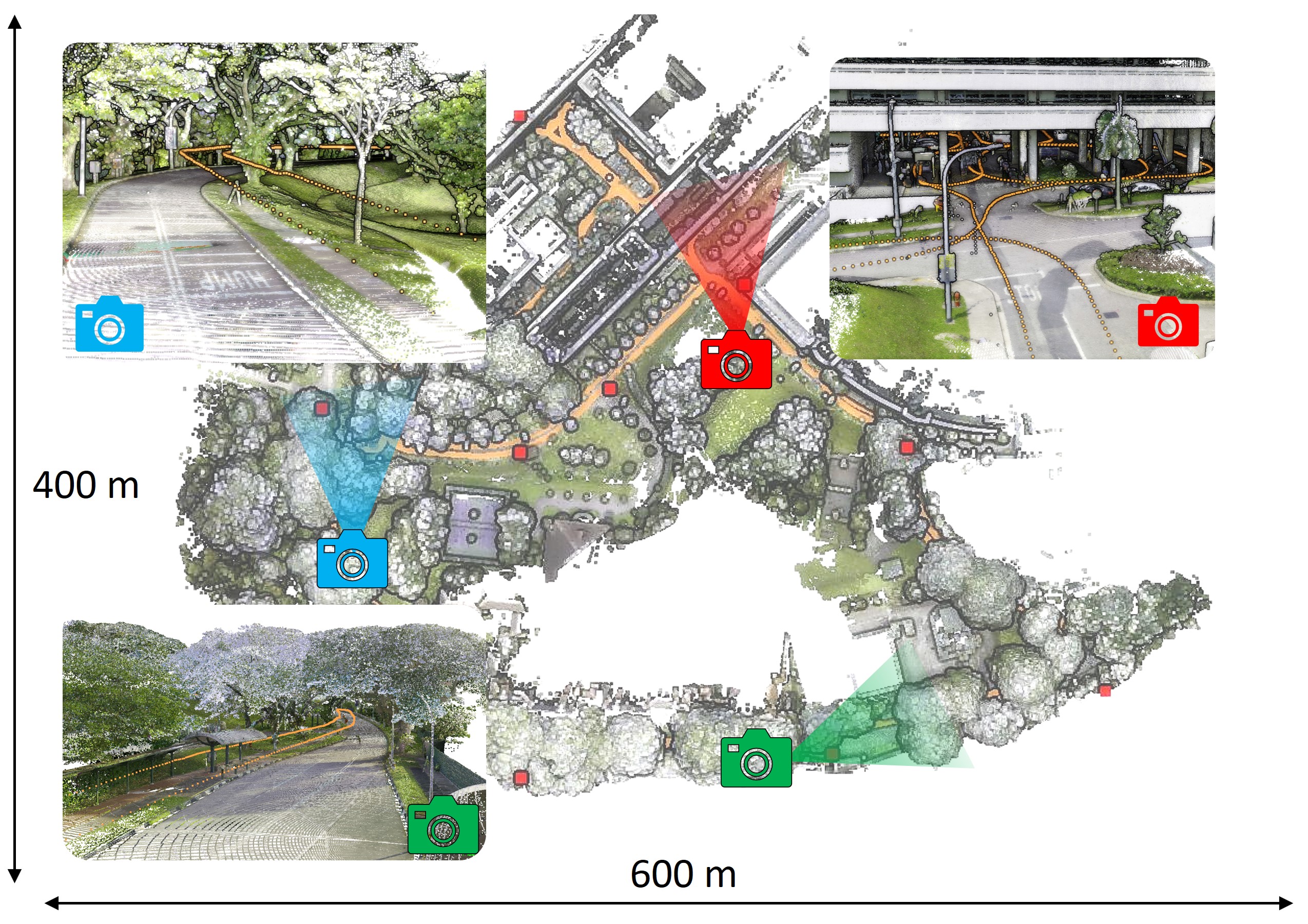
ULOC: Learning to Localize in Complex Large-Scale Environments with Ultra-Wideband Ranges
Thien-Minh Nguyen, Yizhuo Yang, Tien-Dat Nguyen, Shenghai Yuan, Lihua Xie
While UWB-based methods can achieve high localization accuracy in small-scale areas, their accuracy and reliability are significantly challenged in large-scale environments. In this paper, we propose a learning-based framework named ULOC for Ultra-Wideband (UWB) based localization in such complex large-scale environments. First, anchors are deployed in the environment without knowledge of their actual position. Then, UWB observations are collected when the vehicle travels in the environment. At the same time, map-consistent pose estimates are developed from registering (onboard self-localization) data with the prior map to provide the training labels. We then propose a network based on MAMBA that learns the ranging patterns of UWBs over a complex large-scale environment. The experiment demonstrates that our solution can ensure high localization accuracy on a large scale compared to the state-of-the-art. We release our source code to benefit the community at https://github.com/brytsknguyen/uloc.
Read more9/18/2024