Bi-Directional Transformers vs. word2vec: Discovering Vulnerabilities in Lifted Compiled Code

0
📶
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📶

0
Bi-Directional Transformers vs. word2vec: Discovering Vulnerabilities in Lifted Compiled Code
Gary A. McCully, John D. Hastings, Shengjie Xu, Adam Fortier
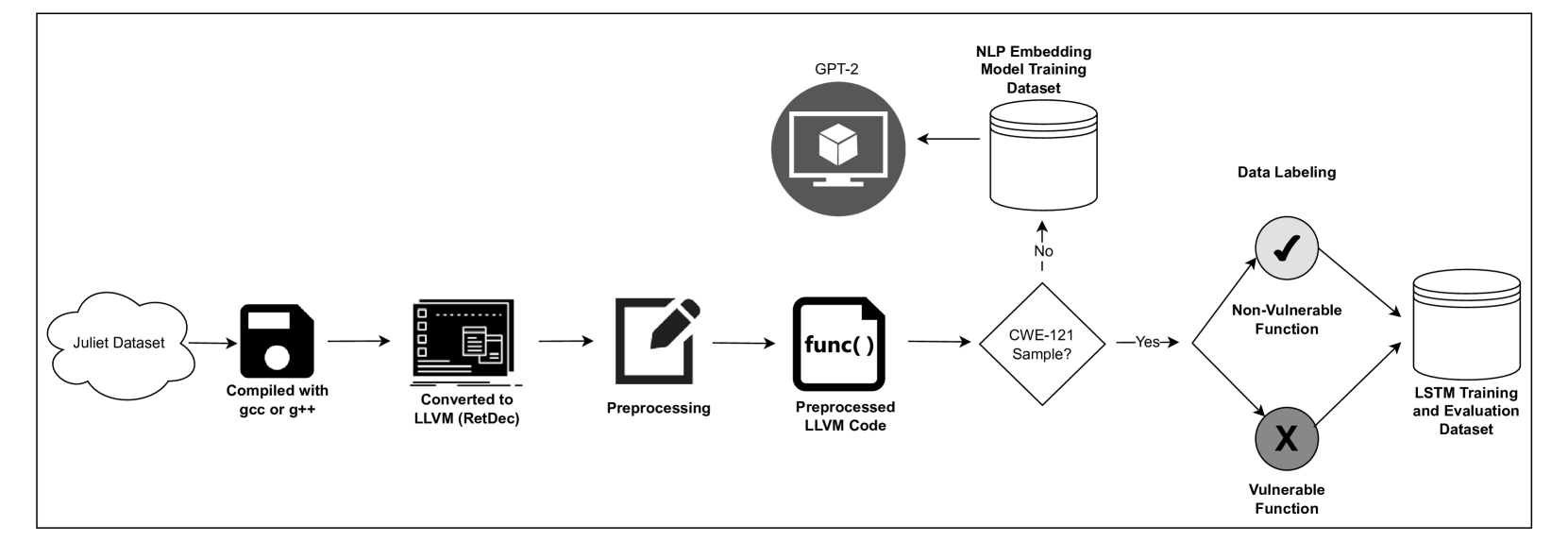
Detecting vulnerabilities within compiled binaries is challenging due to lost high-level code structures and other factors such as architectural dependencies, compilers, and optimization options. To address these obstacles, this research explores vulnerability detection using natural language processing (NLP) embedding techniques with word2vec, BERT, and RoBERTa to learn semantics from intermediate representation (LLVM IR) code. Long short-term memory (LSTM) neural networks were trained on embeddings from encoders created using approximately 48k LLVM functions from the Juliet dataset. This study is pioneering in its comparison of word2vec models with multiple bidirectional transformer (BERT, RoBERTa) embeddings built using LLVM code to train neural networks to detect vulnerabilities in compiled binaries. word2vec Skip-Gram models achieved 92% validation accuracy in detecting vulnerabilities, outperforming word2vec Continuous Bag of Words (CBOW), BERT, and RoBERTa. This suggests that complex contextual embeddings may not provide advantages over simpler word2vec models for this task when a limited number (e.g. 48K) of data samples are used to train the bidirectional transformer-based models. The comparative results provide novel insights into selecting optimal embeddings for learning compiler-independent semantic code representations to advance machine learning detection of vulnerabilities in compiled binaries.
Read more9/10/2024

0
New!Comparing Unidirectional, Bidirectional, and Word2vec Models for Discovering Vulnerabilities in Compiled Lifted Code
Gary A. McCully, John D. Hastings, Shengjie Xu, Adam Fortier
Ransomware and other forms of malware cause significant financial and operational damage to organizations by exploiting long-standing and often difficult-to-detect software vulnerabilities. To detect vulnerabilities such as buffer overflows in compiled code, this research investigates the application of unidirectional transformer-based embeddings, specifically GPT-2. Using a dataset of LLVM functions, we trained a GPT-2 model to generate embeddings, which were subsequently used to build LSTM neural networks to differentiate between vulnerable and non-vulnerable code. Our study reveals that embeddings from the GPT-2 model significantly outperform those from bidirectional models of BERT and RoBERTa, achieving an accuracy of 92.5% and an F1-score of 89.7%. LSTM neural networks were developed with both frozen and unfrozen embedding model layers. The model with the highest performance was achieved when the embedding layers were unfrozen. Further, the research finds that, in exploring the impact of different optimizers within this domain, the SGD optimizer demonstrates superior performance over Adam. Overall, these findings reveal important insights into the potential of unidirectional transformer-based approaches in enhancing cybersecurity defenses.
Read more9/27/2024
💬

0
Harnessing Large Language Models for Software Vulnerability Detection: A Comprehensive Benchmarking Study
Karl Tamberg, Hayretdin Bahsi
Despite various approaches being employed to detect vulnerabilities, the number of reported vulnerabilities shows an upward trend over the years. This suggests the problems are not caught before the code is released, which could be caused by many factors, like lack of awareness, limited efficacy of the existing vulnerability detection tools or the tools not being user-friendly. To help combat some issues with traditional vulnerability detection tools, we propose using large language models (LLMs) to assist in finding vulnerabilities in source code. LLMs have shown a remarkable ability to understand and generate code, underlining their potential in code-related tasks. The aim is to test multiple state-of-the-art LLMs and identify the best prompting strategies, allowing extraction of the best value from the LLMs. We provide an overview of the strengths and weaknesses of the LLM-based approach and compare the results to those of traditional static analysis tools. We find that LLMs can pinpoint many more issues than traditional static analysis tools, outperforming traditional tools in terms of recall and F1 scores. The results should benefit software developers and security analysts responsible for ensuring that the code is free of vulnerabilities.
Read more5/27/2024

0
VulDetectBench: Evaluating the Deep Capability of Vulnerability Detection with Large Language Models
Yu Liu, Lang Gao, Mingxin Yang, Yu Xie, Ping Chen, Xiaojin Zhang, Wei Chen
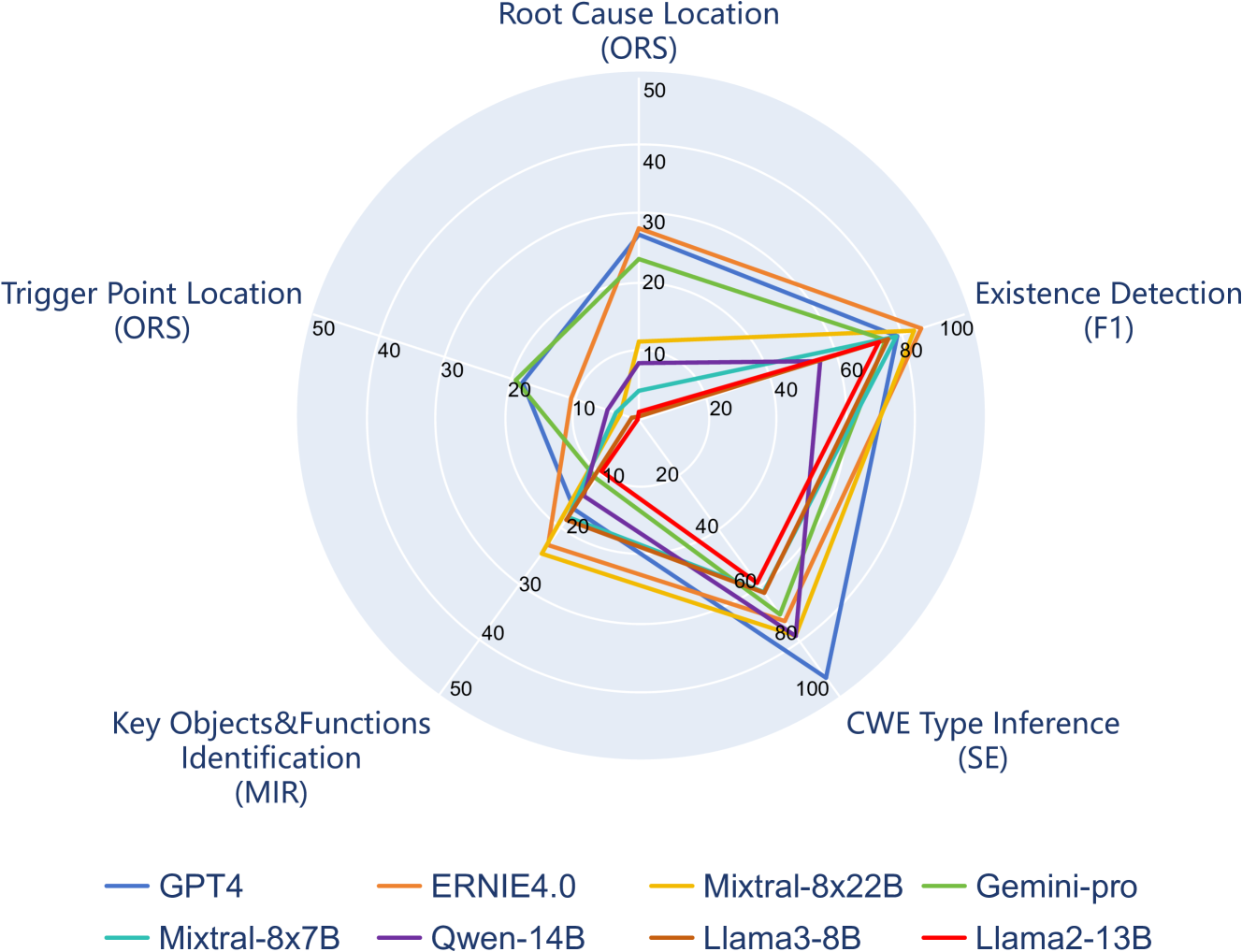
Large Language Models (LLMs) have training corpora containing large amounts of program code, greatly improving the model's code comprehension and generation capabilities. However, sound comprehensive research on detecting program vulnerabilities, a more specific task related to code, and evaluating the performance of LLMs in this more specialized scenario is still lacking. To address common challenges in vulnerability analysis, our study introduces a new benchmark, VulDetectBench, specifically designed to assess the vulnerability detection capabilities of LLMs. The benchmark comprehensively evaluates LLM's ability to identify, classify, and locate vulnerabilities through five tasks of increasing difficulty. We evaluate the performance of 17 models (both open- and closed-source) and find that while existing models can achieve over 80% accuracy on tasks related to vulnerability identification and classification, they still fall short on specific, more detailed vulnerability analysis tasks, with less than 30% accuracy, making it difficult to provide valuable auxiliary information for professional vulnerability mining. Our benchmark effectively evaluates the capabilities of various LLMs at different levels in the specific task of vulnerability detection, providing a foundation for future research and improvements in this critical area of code security. VulDetectBench is publicly available at https://github.com/Sweetaroo/VulDetectBench.
Read more8/22/2024