A Comprehensive Sustainable Framework for Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Proposes a comprehensive sustainable framework for machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI)
- Discusses the importance of sustainability in the development and deployment of ML and AI systems
- Covers key aspects of sustainability, including environmental, social, and economic considerations
Plain English Explanation
This paper presents a detailed framework for ensuring the sustainable development and use of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) systems. The researchers recognize that as ML and AI become more widespread, it's crucial to consider their long-term impact on the environment, society, and the economy.
The paper on balancing progress and responsibility highlights the need to weigh the benefits of AI and ML against their potential negative consequences. This research builds on that by providing a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices to make AI and ML more sustainable.
The framework covers a wide range of sustainability factors, such as energy efficiency and resource usage, the ethical and social implications of these technologies, and their economic sustainability. The goal is to help organizations and researchers develop AI and ML systems that are not only powerful and innovative, but also environmentally friendly, socially responsible, and economically viable in the long run.
By taking a holistic approach to sustainability, the authors aim to ensure that the rapid advancements in AI and ML can be harnessed in a way that benefits humanity and the planet, rather than causing harm. This framework can serve as a valuable guide for anyone involved in the development and deployment of these transformative technologies.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a comprehensive sustainable framework for machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) that considers environmental, social, and economic factors. It builds on previous research, such as the work on balancing progress and responsibility, to provide a more holistic approach to sustainability in the field of AI and ML.
The framework covers several key aspects of sustainability:
-
Environmental Sustainability: This includes considerations around energy efficiency and resource usage, as well as the environmental impact of data collection, model training, and deployment.
-
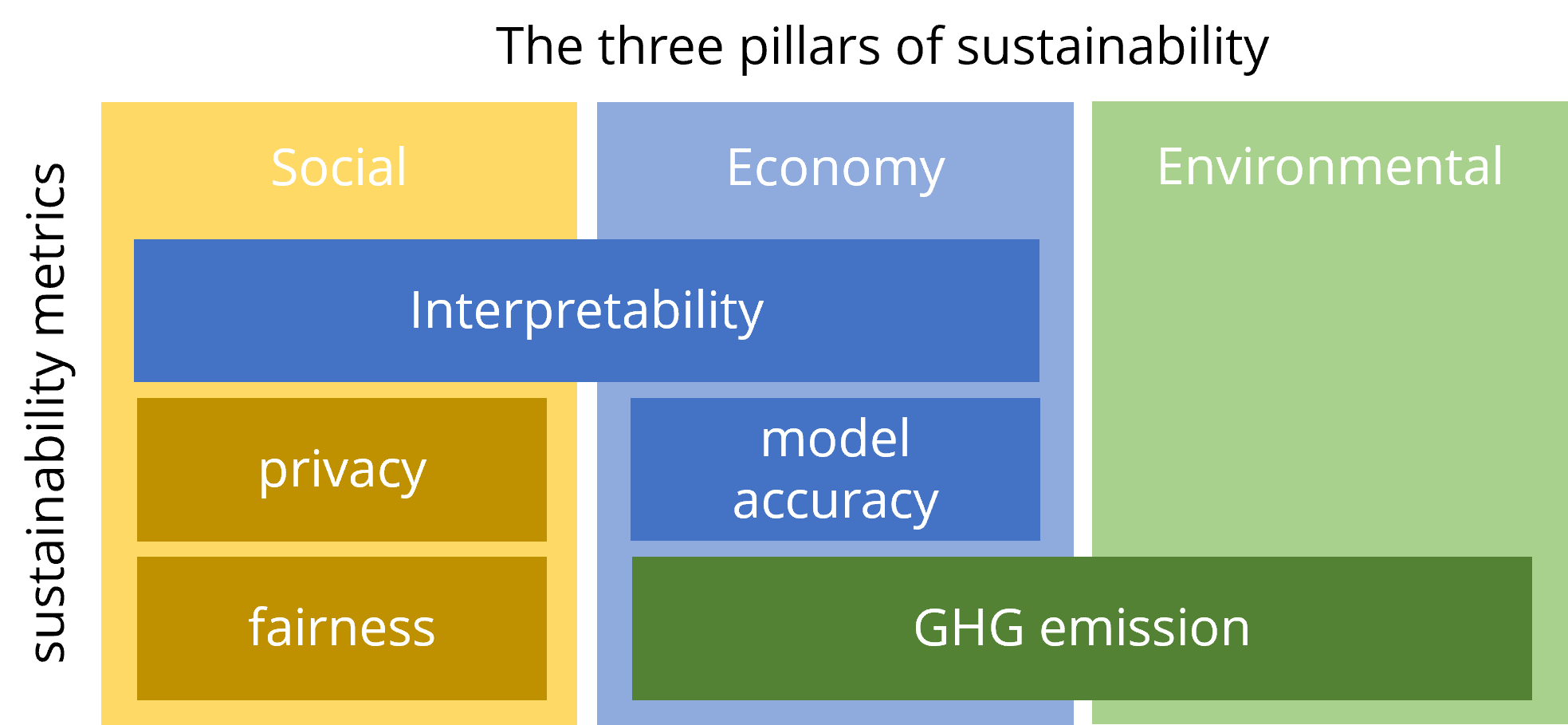
Social Sustainability: The framework addresses the ethical and social implications of AI and ML, such as fairness, privacy, and the potential for societal disruption.
-
Economic Sustainability: The authors also consider the economic sustainability of AI and ML systems, including their impact on jobs, the cost of deployment, and their long-term viability.
The paper provides a detailed set of guidelines and best practices for each of these sustainability pillars, drawing on existing research and industry examples. The goal is to help organizations and researchers develop AI and ML systems that are not only powerful and innovative, but also environmentally friendly, socially responsible, and economically viable in the long run.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive and well-researched framework for sustainable AI and ML development, addressing a critical gap in the field. By considering environmental, social, and economic factors, the authors provide a holistic approach that goes beyond simple efficiency or cost-cutting measures.
One of the strengths of the framework is its flexibility, as it can be adapted to a wide range of AI and ML applications and industries. The authors also acknowledge the need for ongoing research and collaboration to further refine and improve the framework as the field of AI and ML continues to evolve.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into some of the more complex and challenging aspects of sustainability, such as the difficulty of measuring and quantifying environmental and social impacts. Additionally, the framework may require significant resources and expertise to implement, which could be a barrier for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets.
Despite these potential limitations, the proposed framework is a valuable contribution to the field of AI and ML, as it highlights the importance of sustainability and provides a practical roadmap for addressing it. As the world grapples with the growing influence of these transformative technologies, this research can help ensure that their development and deployment are aligned with the long-term well-being of the planet and society.
Conclusion
This paper presents a comprehensive sustainable framework for the development and deployment of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) systems. The framework covers environmental, social, and economic factors, providing a holistic approach to sustainability in the field of AI and ML.
By addressing a wide range of sustainability considerations, the proposed framework can help organizations and researchers ensure that the rapid advancements in AI and ML are harnessed in a way that benefits humanity and the planet, rather than causing harm. This research is a valuable contribution to the ongoing efforts to make AI and ML more sustainable and responsible.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges and opportunities presented by these transformative technologies, the insights and guidelines provided in this paper can serve as a crucial guide for ensuring that their development and deployment are aligned with the long-term well-being of our society and the environment.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
A Comprehensive Sustainable Framework for Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Roberto Pagliari, Peter Hill, Po-Yu Chen, Maciej Dabrowny, Tingsheng Tan, Francois Buet-Golfouse
In financial applications, regulations or best practices often lead to specific requirements in machine learning relating to four key pillars: fairness, privacy, interpretability and greenhouse gas emissions. These all sit in the broader context of sustainability in AI, an emerging practical AI topic. However, although these pillars have been individually addressed by past literature, none of these works have considered all the pillars. There are inherent trade-offs between each of the pillars (for example, accuracy vs fairness or accuracy vs privacy), making it even more important to consider them together. This paper outlines a new framework for Sustainable Machine Learning and proposes FPIG, a general AI pipeline that allows for these critical topics to be considered simultaneously to learn the trade-offs between the pillars better. Based on the FPIG framework, we propose a meta-learning algorithm to estimate the four key pillars given a dataset summary, model architecture, and hyperparameters before model training. This algorithm allows users to select the optimal model architecture for a given dataset and a given set of user requirements on the pillars. We illustrate the trade-offs under the FPIG model on three classical datasets and demonstrate the meta-learning approach with an example of real-world datasets and models with different interpretability, showcasing how it can aid model selection.
Read more7/18/2024


0
New!Green Federated Learning: A new era of Green Aware AI
Dipanwita Thakur, Antonella Guzzo, Giancarlo Fortino
The development of AI applications, especially in large-scale wireless networks, is growing exponentially, alongside the size and complexity of the architectures used. Particularly, machine learning is acknowledged as one of today's most energy-intensive computational applications, posing a significant challenge to the environmental sustainability of next-generation intelligent systems. Achieving environmental sustainability entails ensuring that every AI algorithm is designed with sustainability in mind, integrating green considerations from the architectural phase onwards. Recently, Federated Learning (FL), with its distributed nature, presents new opportunities to address this need. Hence, it's imperative to elucidate the potential and challenges stemming from recent FL advancements and their implications for sustainability. Moreover, it's crucial to furnish researchers, stakeholders, and interested parties with a roadmap to navigate and understand existing efforts and gaps in green-aware AI algorithms. This survey primarily aims to achieve this objective by identifying and analyzing over a hundred FL works, assessing their contributions to green-aware artificial intelligence for sustainable environments, with a specific focus on IoT research. It delves into current issues in green federated learning from an energy-efficient standpoint, discussing potential challenges and future prospects for green IoT application research.
Read more9/20/2024


0
Integrating ESG and AI: A Comprehensive Responsible AI Assessment Framework
Sung Une Lee, Harsha Perera, Yue Liu, Boming Xia, Qinghua Lu, Liming Zhu, Jessica Cairns, Moana Nottage
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a widely developed and adopted technology across entire industry sectors. Integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations with AI investments is crucial for ensuring ethical and sustainable technological advancement. Particularly from an investor perspective, this integration not only mitigates risks but also enhances long-term value creation by aligning AI initiatives with broader societal goals. Yet, this area has been less explored in both academia and industry. To bridge the gap, we introduce a novel ESG-AI framework, which is developed based on insights from engagements with 28 companies and comprises three key components. The framework provides a structured approach to this integration, developed in collaboration with industry practitioners. The ESG-AI framework provides an overview of the environmental and social impacts of AI applications, helping users such as investors assess the materiality of AI use. Moreover, it enables investors to evaluate a company's commitment to responsible AI through structured engagements and thorough assessment of specific risk areas. We have publicly released the framework and toolkit in April 2024, which has received significant attention and positive feedback from the investment community. This paper details each component of the framework, demonstrating its applicability in real-world contexts and its potential to guide ethical AI investments.
Read more8/7/2024

0
Balancing Progress and Responsibility: A Synthesis of Sustainability Trade-Offs of AI-Based Systems
Apoorva Nalini Pradeep Kumar, Justus Bogner, Markus Funke, Patricia Lago
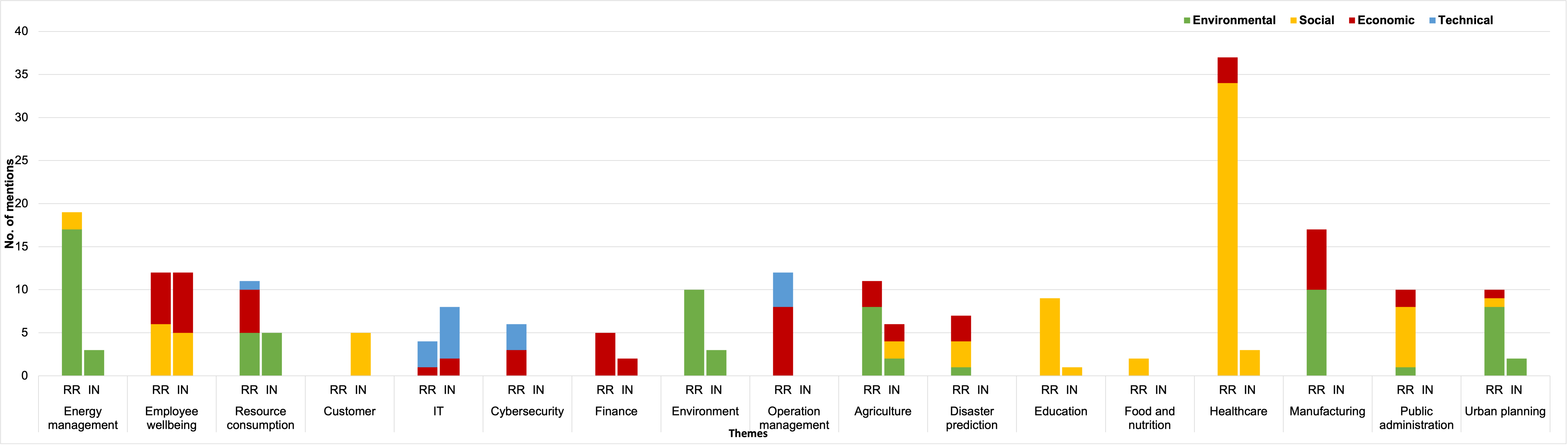
Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities have increased the eagerness of companies to integrate AI into software systems. While AI can be used to have a positive impact on several dimensions of sustainability, this is often overshadowed by its potential negative influence. While many studies have explored sustainability factors in isolation, there is insufficient holistic coverage of potential sustainability benefits or costs that practitioners need to consider during decision-making for AI adoption. We therefore aim to synthesize trade-offs related to sustainability in the context of integrating AI into software systems. We want to make the sustainability benefits and costs of integrating AI more transparent and accessible for practitioners. The study was conducted in collaboration with a Dutch financial organization. We first performed a rapid review that led to the inclusion of 151 research papers. Afterward, we conducted six semi-structured interviews to enrich the data with industry perspectives. The combined results showcase the potential sustainability benefits and costs of integrating AI. The labels synthesized from the review regarding potential sustainability benefits were clustered into 16 themes, with energy management being the most frequently mentioned one. 11 themes were identified in the interviews, with the top mentioned theme being employee wellbeing. Regarding sustainability costs, the review discovered seven themes, with deployment issues being the most popular one, followed by ethics & society. Environmental issues was the top theme from the interviews. Our results provide valuable insights to organizations and practitioners for understanding the potential sustainability implications of adopting AI.
Read more4/8/2024