Controllable Text Summarization: Unraveling Challenges, Approaches, and Prospects -- A Survey

0
🏅
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper highlights the limitations of generic text summarization approaches and the growing need for summarization methods that are tailored to specific user needs and objectives.
- It formalizes the Controllable Text Summarization (CTS) task, categorizes different controllable attributes, and presents a comprehensive review of existing datasets and methods in this context.
- The paper also uncovers research limitations and gaps, and explores potential solutions and future directions for CTS.
Plain English Explanation
Summarizing text is a common task, but generic text summarization approaches often fail to address the unique needs and goals of individual users. Recently, researchers have been developing more customizable summarization methods that can be tailored to specific objectives.
The paper in question defines the Controllable Text Summarization (CTS) task and categorizes different ways that summarization can be controlled, such as by topic, query focus, or specific attributes. It reviews the existing research in each of these areas, highlighting the progress made and the challenges that remain.
The key idea is to make text summarization more flexible and user-centered, so that the summary produced aligns better with what the individual user is looking for. This could be especially useful in applications like news, research, or customer support, where the same content may need to be summarized differently for different audiences or purposes.
Technical Explanation
The paper formalizes the Controllable Text Summarization (CTS) task, which aims to generate text summaries that align with specific user objectives and preferences. It categorizes the various controllable attributes used in CTS research, including topic, topic-aware evaluation, query focus, specific attributes, and others.
For each category of controllable attributes, the paper presents a thorough review of the existing datasets and methods. It examines how the summarization models are designed to incorporate the desired control signals, the evaluation approaches used, and the key insights and findings from the research.
The paper also identifies limitations and research gaps in the current CTS landscape. For example, it notes the need for more comprehensive and diverse datasets, the challenge of defining appropriate evaluation metrics, and the difficulty of scaling CTS methods to work with large language models.
Based on their analysis, the authors explore potential solutions and future directions for CTS, such as leveraging instruction-tuning techniques, developing more robust evaluation frameworks, and investigating the integration of CTS with other text generation tasks.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable and comprehensive survey of the emerging field of Controllable Text Summarization (CTS), highlighting the importance of developing summarization methods that are tailored to individual user needs and objectives.
One of the key strengths of the paper is its thorough categorization of the various controllable attributes used in CTS research. This taxonomic approach helps to organize the existing work and clearly illustrate the diversity of control signals that can be incorporated into summarization models.
However, the paper also acknowledges the significant limitations and challenges that remain in this field. For example, the authors note the need for more comprehensive and diverse CTS datasets, as well as the difficulty of defining appropriate evaluation metrics that can effectively capture the nuanced aspects of controlled summarization.
Additionally, while the paper explores potential solutions and future directions, such as the use of instruction-tuning techniques, it does not provide a deep dive into the feasibility or practical implementation of these approaches. Further research and experimentation may be needed to fully assess the viability of the proposed solutions.
Overall, the paper serves as an excellent starting point for researchers and practitioners interested in the field of Controllable Text Summarization. By highlighting the current state of the art, the limitations, and the promising avenues for future work, it sets the stage for continued advancements in this important area of natural language processing.
Conclusion
The paper presents a comprehensive survey of the emerging field of Controllable Text Summarization (CTS), which aims to develop summarization methods that are more closely tailored to individual user needs and objectives.
By formalizing the CTS task, categorizing the various controllable attributes, and thoroughly reviewing the existing datasets and methods, the authors have provided a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in this domain. The paper also uncovers key limitations and research gaps, and explores potential solutions and future directions, such as the use of instruction-tuning techniques and the development of more robust evaluation frameworks.
Overall, the paper underscores the importance of moving beyond generic text summarization approaches and towards more personalized and user-centric summarization solutions. As the field of CTS continues to evolve, the insights and findings presented in this survey are likely to play a crucial role in guiding future research and driving practical applications of this technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🏅

0
Controllable Text Summarization: Unraveling Challenges, Approaches, and Prospects -- A Survey
Ashok Urlana, Pruthwik Mishra, Tathagato Roy, Rahul Mishra
Generic text summarization approaches often fail to address the specific intent and needs of individual users. Recently, scholarly attention has turned to the development of summarization methods that are more closely tailored and controlled to align with specific objectives and user needs. Despite a growing corpus of controllable summarization research, there is no comprehensive survey available that thoroughly explores the diverse controllable attributes employed in this context, delves into the associated challenges, and investigates the existing solutions. In this survey, we formalize the Controllable Text Summarization (CTS) task, categorize controllable attributes according to their shared characteristics and objectives, and present a thorough examination of existing datasets and methods within each category. Moreover, based on our findings, we uncover limitations and research gaps, while also exploring potential solutions and future directions for CTS. We release our detailed analysis of CTS papers at https://github.com/ashokurlana/controllable_text_summarization_survey.
Read more5/29/2024
🧪

0
Topic-Controllable Summarization: Topic-Aware Evaluation and Transformer Methods
Tatiana Passali, Grigorios Tsoumakas
Topic-controllable summarization is an emerging research area with a wide range of potential applications. However, existing approaches suffer from significant limitations. For example, the majority of existing methods built upon recurrent architectures, which can significantly limit their performance compared to more recent Transformer-based architectures, while they also require modifications to the model's architecture for controlling the topic. At the same time, there is currently no established evaluation metric designed specifically for topic-controllable summarization. This work proposes a new topic-oriented evaluation measure to automatically evaluate the generated summaries based on the topic affinity between the generated summary and the desired topic. The reliability of the proposed measure is demonstrated through appropriately designed human evaluation. In addition, we adapt topic embeddings to work with powerful Transformer architectures and propose a novel and efficient approach for guiding the summary generation through control tokens. Experimental results reveal that control tokens can achieve better performance compared to more complicated embedding-based approaches while also being significantly faster.
Read more4/15/2024

0
Abstractive Text Summarization: State of the Art, Challenges, and Improvements
Hassan Shakil, Ahmad Farooq, Jugal Kalita
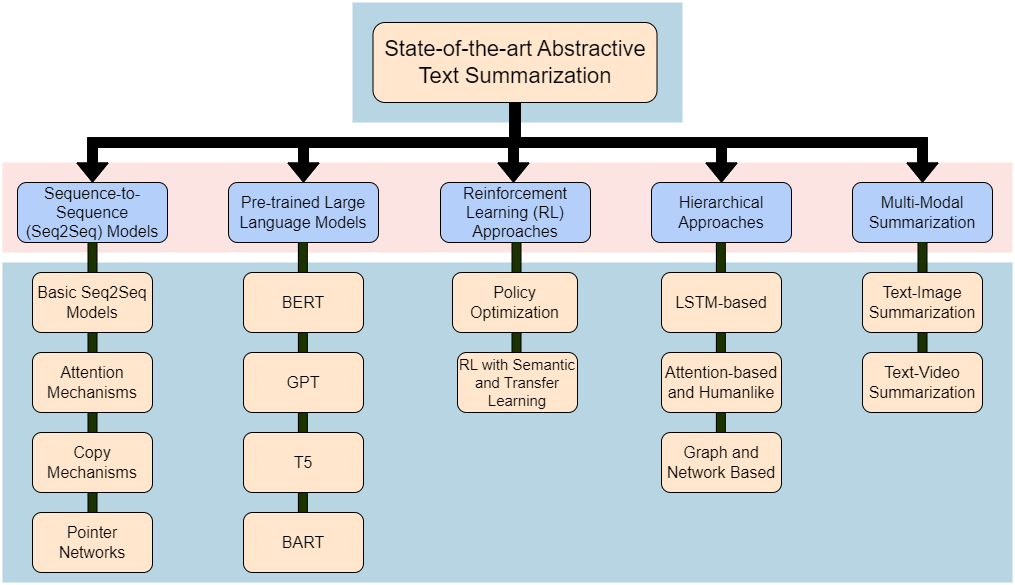
Specifically focusing on the landscape of abstractive text summarization, as opposed to extractive techniques, this survey presents a comprehensive overview, delving into state-of-the-art techniques, prevailing challenges, and prospective research directions. We categorize the techniques into traditional sequence-to-sequence models, pre-trained large language models, reinforcement learning, hierarchical methods, and multi-modal summarization. Unlike prior works that did not examine complexities, scalability and comparisons of techniques in detail, this review takes a comprehensive approach encompassing state-of-the-art methods, challenges, solutions, comparisons, limitations and charts out future improvements - providing researchers an extensive overview to advance abstractive summarization research. We provide vital comparison tables across techniques categorized - offering insights into model complexity, scalability and appropriate applications. The paper highlights challenges such as inadequate meaning representation, factual consistency, controllable text summarization, cross-lingual summarization, and evaluation metrics, among others. Solutions leveraging knowledge incorporation and other innovative strategies are proposed to address these challenges. The paper concludes by highlighting emerging research areas like factual inconsistency, domain-specific, cross-lingual, multilingual, and long-document summarization, as well as handling noisy data. Our objective is to provide researchers and practitioners with a structured overview of the domain, enabling them to better understand the current landscape and identify potential areas for further research and improvement.
Read more9/5/2024


0
ATLAS: Improving Lay Summarisation with Attribute-based Control
Zhihao Zhang, Tomas Goldsack, Carolina Scarton, Chenghua Lin
Lay summarisation aims to produce summaries of scientific articles that are comprehensible to non-expert audiences. However, previous work assumes a one-size-fits-all approach, where the content and style of the produced summary are entirely dependent on the data used to train the model. In practice, audiences with different levels of expertise will have specific needs, impacting what content should appear in a lay summary and how it should be presented. Aiming to address this, we propose ATLAS, a novel abstractive summarisation approach that can control various properties that contribute to the overall layness of the generated summary using targeted control attributes. We evaluate ATLAS on a combination of biomedical lay summarisation datasets, where it outperforms state-of-the-art baselines using mainstream summarisation metrics. Additional analyses provided on the discriminatory power and emergent influence of our selected controllable attributes further attest to the effectiveness of our approach.
Read more6/11/2024