Cooperative Visual-LiDAR Extrinsic Calibration Technology for Intersection Vehicle-Infrastructure: A review

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This review paper discusses the use of cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration technology for intersection vehicle-infrastructure applications.
- The paper examines the current state of research in this area, highlighting the key challenges and opportunities.
- The review covers topics such as camera-LiDAR calibration, road-side infrastructure, autonomous vehicles, multi-sensor fusion, and joint external parameter calibration.
Plain English Explanation
Autonomous vehicles rely on a variety of sensors, including cameras and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems, to perceive their surroundings and navigate safely. However, for these sensors to work together effectively, they need to be properly calibrated, meaning their relative positions and orientations must be precisely known.
This paper reviews research on a technique called "cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration" that can help solve this problem, particularly in the context of autonomous vehicles operating at intersections. The key idea is to leverage infrastructure installed at intersections, such as cameras and LiDAR units, to help calibrate the sensors on the vehicles themselves.
By having the infrastructure and the vehicles work together, the calibration process can be made more robust and reliable. This is important because accurate calibration is crucial for effective sensor fusion, which is the process of combining data from multiple sensors to get a more complete and accurate understanding of the vehicle's surroundings.
The review covers the various approaches researchers have taken to tackle this problem, including linking to relevant papers, multi-sensor fusion techniques, and calibration algorithms. It also discusses the potential benefits of this technology, such as improved safety and efficiency for autonomous vehicles navigating intersections.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides a comprehensive review of the current state of research on cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration for intersection vehicle-infrastructure applications. The authors highlight the importance of accurate sensor calibration in the context of autonomous vehicles, as it is a critical component for effective multi-sensor fusion and reliable perception of the vehicle's surroundings.
The review discusses various approaches to camera-LiDAR calibration, including methods that leverage infrastructure-based sensors and techniques that involve joint calibration of multiple sensors. The authors also cover research on calibration algorithms that can handle the unique challenges of intersection environments, such as the presence of dynamic obstacles and the need for real-time, online calibration.
The review highlights the potential benefits of cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration, including improved safety and efficiency for autonomous vehicles navigating intersections. The authors also discuss the implications of this technology for end-to-end autonomous driving systems and online, target-free calibration approaches.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-researched review of the current state of the art in cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration for intersection vehicle-infrastructure applications. The authors have done an excellent job of synthesizing the relevant literature and highlighting the key challenges and opportunities in this field.
One potential limitation of the review is that it does not delve deeply into the specific technical details of the various calibration algorithms and sensor fusion techniques discussed. While this is understandable given the breadth of the topic, some readers may wish for a more in-depth technical analysis of the underlying methods.
Additionally, the review does not address the potential scalability and deployment challenges of this technology, such as the need for widespread adoption of compatible infrastructure and the integration of cooperative calibration systems into existing autonomous vehicle architectures. These are important practical considerations that could impact the real-world implementation of this technology.
Overall, this review provides a valuable and informative overview of the state of research in cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration for intersection vehicle-infrastructure applications. It serves as a useful starting point for researchers and practitioners interested in exploring this important area of autonomous vehicle technology.
Conclusion
This review paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration technology for intersection vehicle-infrastructure applications. The authors highlight the key challenges and opportunities in this field, including the importance of accurate sensor calibration for effective multi-sensor fusion and reliable perception in autonomous vehicles.
The review covers a range of topics, including camera-LiDAR calibration, the use of road-side infrastructure, multi-sensor fusion techniques, and joint external parameter calibration algorithms. The authors also discuss the potential benefits of this technology, such as improved safety and efficiency for autonomous vehicles navigating intersections.
While the review does not delve deeply into the technical details of the various methods discussed, it provides a valuable synthesis of the current research landscape and serves as a solid foundation for further exploration in this rapidly evolving field of autonomous vehicle technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Cooperative Visual-LiDAR Extrinsic Calibration Technology for Intersection Vehicle-Infrastructure: A review
Xinyu Zhang, Yijin Xiong, Qianxin Qu, Renjie Wang, Xin Gao, Jing Liu, Shichun Guo, Jun Li
In the typical urban intersection scenario, both vehicles and infrastructures are equipped with visual and LiDAR sensors. By successfully integrating the data from vehicle-side and road monitoring devices, a more comprehensive and accurate environmental perception and information acquisition can be achieved. The Calibration of sensors, as an essential component of autonomous driving technology, has consistently drawn significant attention. Particularly in scenarios involving multiple sensors collaboratively perceiving and addressing localization challenges, the requirement for inter-sensor calibration becomes crucial. Recent years have witnessed the emergence of the concept of multi-end cooperation, where infrastructure captures and transmits surrounding environment information to vehicles, bolstering their perception capabilities while mitigating costs. However, this also poses technical complexities, underscoring the pressing need for diverse end calibration. Camera and LiDAR, the bedrock sensors in autonomous driving, exhibit expansive applicability. This paper comprehensively examines and analyzes the calibration of multi-end camera-LiDAR setups from vehicle, roadside, and vehicle-road cooperation perspectives, outlining their relevant applications and profound significance. Concluding with a summary, we present our future-oriented ideas and hypotheses.
Read more5/17/2024


0
V2I-Calib: A Novel Calibration Approach for Collaborative Vehicle and Infrastructure LiDAR Systems
Qianxin Qu, Yijin Xiong, Guipeng Zhang, Xin Wu, Xiaohan Gao, Xin Gao, Hanyu Li, Shichun Guo, Guoying Zhang
Cooperative LiDAR systems integrating vehicles and road infrastructure, termed V2I calibration, exhibit substantial potential, yet their deployment encounters numerous challenges. A pivotal aspect of ensuring data accuracy and consistency across such systems involves the calibration of LiDAR units across heterogeneous vehicular and infrastructural endpoints. This necessitates the development of calibration methods that are both real-time and robust, particularly those that can ensure robust performance in urban canyon scenarios without relying on initial positioning values. Accordingly, this paper introduces a novel approach to V2I calibration, leveraging spatial association information among perceived objects. Central to this method is the innovative Overall Intersection over Union (oIoU) metric, which quantifies the correlation between targets identified by vehicle and infrastructure systems, thereby facilitating the real-time monitoring of calibration results. Our approach involves identifying common targets within the perception results of vehicle and infrastructure LiDAR systems through the construction of an affinity matrix. These common targets then form the basis for the calculation and optimization of extrinsic parameters. Comparative and ablation studies conducted using the DAIR-V2X dataset substantiate the superiority of our approach. For further insights and resources, our project repository is accessible at https://github.com/MassimoQu/v2i-calib.
Read more9/19/2024
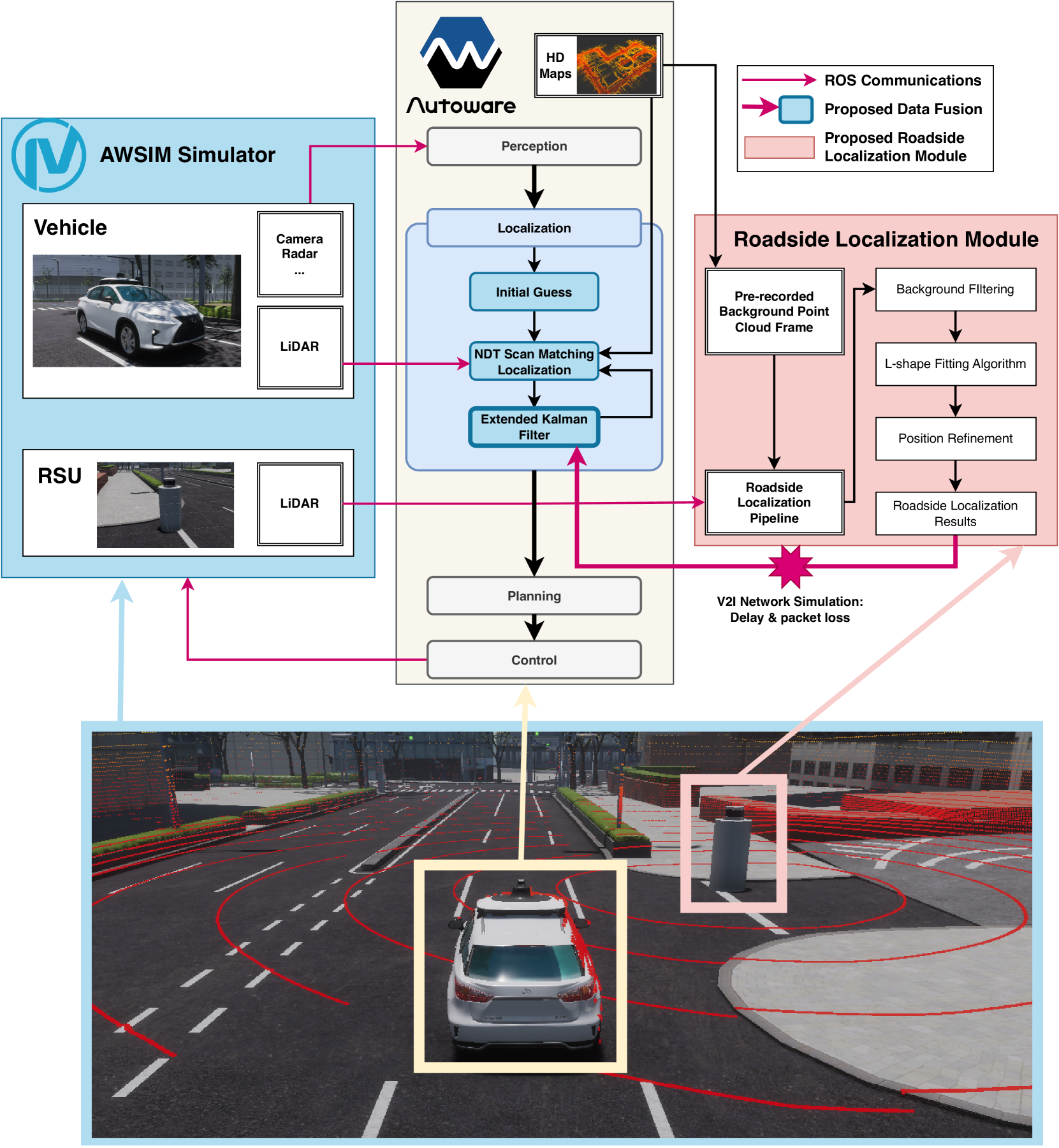

0
Accurate Cooperative Localization Utilizing LiDAR-equipped Roadside Infrastructure for Autonomous Driving
Yuze Jiang, Ehsan Javanmardi, Manabu Tsukada, Hiroshi Esaki
Recent advancements in LiDAR technology have significantly lowered costs and improved both its precision and resolution, thereby solidifying its role as a critical component in autonomous vehicle localization. Using sophisticated 3D registration algorithms, LiDAR now facilitates vehicle localization with centimeter-level accuracy. However, these high-precision techniques often face reliability challenges in environments devoid of identifiable map features. To address this limitation, we propose a novel approach that utilizes road side units (RSU) with vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications to assist vehicle self-localization. By using RSUs as stationary reference points and processing real-time LiDAR data, our method enhances localization accuracy through a cooperative localization framework. By placing RSUs in critical areas, our proposed method can improve the reliability and precision of vehicle localization when the traditional vehicle self-localization technique falls short. Evaluation results in an end-to-end autonomous driving simulator AWSIM show that the proposed method can improve localization accuracy by up to 80% under vulnerable environments compared to traditional localization methods. Additionally, our method also demonstrates robust resistance to network delays and packet loss in heterogeneous network environments.
Read more7/12/2024
🔎

0
Roadside LiDAR Assisted Cooperative Localization for Connected Autonomous Vehicles
Yuze Jiang, Ehsan Javanmardi, Jin Nakazato, Manabu Tsukada, Hiroshi Esaki
Advancements in LiDAR technology have led to more cost-effective production while simultaneously improving precision and resolution. As a result, LiDAR has become integral to vehicle localization, achieving centimeter-level accuracy through techniques like Normal Distributions Transform (NDT) and other advanced 3D registration algorithms. Nonetheless, these approaches are reliant on high-definition 3D point cloud maps, the creation of which involves significant expenditure. When such maps are unavailable or lack sufficient features for 3D registration algorithms, localization accuracy diminishes, posing a risk to road safety. To address this, we proposed to use LiDAR-equipped roadside unit and Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication to accurately estimate the connected autonomous vehicle's position and help the vehicle when its self-localization is not accurate enough. Our simulation results indicate that this method outperforms traditional NDT scan matching-based approaches in terms of localization accuracy.
Read more7/12/2024