V2I-Calib: A Novel Calibration Approach for Collaborative Vehicle and Infrastructure LiDAR Systems

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a novel approach called V2I-Calib for calibrating collaborative vehicle and infrastructure LiDAR systems.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser light to measure distances, often used in autonomous vehicles and smart infrastructure.
- Calibrating LiDAR systems is crucial for accurately fusing data from multiple sensors, which is essential for applications like cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration, roadside LiDAR-assisted cooperative localization, and accurate cooperative localization.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new method for calibrating LiDAR sensors that are used in both vehicles and road infrastructure, such as traffic lights or signs. Calibration is the process of aligning and adjusting the sensors so that they can accurately measure distances and positions of objects in the environment.
This is important for systems that combine data from multiple LiDAR sensors, like those used in LiDAR-vision tightly coupled collaborative perception or re-calibration methods for object detection. By calibrating the sensors properly, the system can better understand the locations of things like other vehicles, pedestrians, and road features.
The new calibration method, called V2I-Calib, uses a special calibration target that is placed in the environment. Sensors on both the vehicle and infrastructure can detect this target, and the system can then figure out how the different sensors are oriented relative to each other. This allows the sensors to be properly aligned and calibrated, improving the overall performance of the collaborative perception system.
Technical Explanation
The V2I-Calib approach leverages a calibration target that is detected by both vehicle-mounted and infrastructure-mounted LiDAR sensors. By analyzing the relative positioning and orientation of the target as observed by the different sensors, the system can determine the extrinsic calibration parameters between the vehicle and infrastructure LiDAR setups.
The key steps of the V2I-Calib method are:
- Placement of a calibration target in the environment that is observable by both vehicle and infrastructure LiDAR sensors.
- Acquisition of LiDAR point cloud data from the vehicle and infrastructure sensors observing the calibration target.
- Segmentation and extraction of the calibration target from the point cloud data.
- Estimation of the 6-DoF (degrees of freedom) pose of the calibration target relative to each sensor.
- Optimization of the extrinsic calibration parameters between the vehicle and infrastructure LiDAR systems based on the relative target poses.
This calibration method does not require any specialized hardware or infrastructure and can be performed autonomously, making it well-suited for practical deployment in real-world cooperative perception systems.
Critical Analysis
The V2I-Calib approach addresses an important challenge in collaborative LiDAR-based perception systems. By providing a robust and automated calibration method, it can help ensure the accurate fusion of data from vehicle and infrastructure sensors, which is crucial for applications like cooperative visual-LiDAR extrinsic calibration, roadside LiDAR-assisted cooperative localization, and accurate cooperative localization.
However, the paper does not address potential limitations, such as the sensitivity of the calibration to the placement and visibility of the calibration target, or the impact of environmental factors like weather and lighting conditions on the performance of the method. Additionally, the authors do not provide a comparison to other calibration approaches or discuss the computational complexity and scalability of the V2I-Calib algorithm.
Conclusion
The V2I-Calib method presented in this paper offers a novel approach to calibrating collaborative vehicle and infrastructure LiDAR systems. By leveraging a shared calibration target, the system can automatically determine the extrinsic parameters between the sensors, enabling the accurate fusion of data from multiple sources. This is a critical capability for advanced cooperative perception systems, such as those used in LiDAR-vision tightly coupled collaborative perception and re-calibration methods for object detection. Further research is needed to address potential limitations and validate the method's performance in real-world conditions, but the V2I-Calib approach shows promise as a practical solution for calibrating collaborative LiDAR systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
V2I-Calib: A Novel Calibration Approach for Collaborative Vehicle and Infrastructure LiDAR Systems
Qianxin Qu, Yijin Xiong, Xin Wu, Hanyu Li, Shichun Guo
Cooperative vehicle and infrastructure LiDAR systems hold great potential, yet their implementation faces numerous challenges. Calibration of LiDAR systems across heterogeneous vehicle and infrastructure endpoints is a critical step to ensure the accuracy and consistency of perception system data, necessitating calibration methods that are real-time and stable. To this end, this paper introduces a novel calibration method for cooperative vehicle and road infrastructure LiDAR systems, which exploits spatial association information between detection boxes. The method centers around a novel Overall IoU metric that reflects the correlation of targets between vehicle and infrastructure, enabling real-time monitoring of calibration results. We search for common matching boxes between vehicle and infrastructure nodes by constructing an affinity matrix. Subsequently, these matching boxes undergo extrinsic parameter computation and optimization. Comparative and ablation experiments on the DAIR-V2X dataset confirm the superiority of our method. To better reflect the differences in calibration results, we have categorized the calibration tasks on the DAIR-V2X dataset based on their level of difficulty, enriching the dataset's utility for future research. Our project is available at https://github.com/MassimoQu/v2i-calib .
Read more7/16/2024


0
Cooperative Visual-LiDAR Extrinsic Calibration Technology for Intersection Vehicle-Infrastructure: A review
Xinyu Zhang, Yijin Xiong, Qianxin Qu, Renjie Wang, Xin Gao, Jing Liu, Shichun Guo, Jun Li
In the typical urban intersection scenario, both vehicles and infrastructures are equipped with visual and LiDAR sensors. By successfully integrating the data from vehicle-side and road monitoring devices, a more comprehensive and accurate environmental perception and information acquisition can be achieved. The Calibration of sensors, as an essential component of autonomous driving technology, has consistently drawn significant attention. Particularly in scenarios involving multiple sensors collaboratively perceiving and addressing localization challenges, the requirement for inter-sensor calibration becomes crucial. Recent years have witnessed the emergence of the concept of multi-end cooperation, where infrastructure captures and transmits surrounding environment information to vehicles, bolstering their perception capabilities while mitigating costs. However, this also poses technical complexities, underscoring the pressing need for diverse end calibration. Camera and LiDAR, the bedrock sensors in autonomous driving, exhibit expansive applicability. This paper comprehensively examines and analyzes the calibration of multi-end camera-LiDAR setups from vehicle, roadside, and vehicle-road cooperation perspectives, outlining their relevant applications and profound significance. Concluding with a summary, we present our future-oriented ideas and hypotheses.
Read more5/17/2024
🔎

0
Roadside LiDAR Assisted Cooperative Localization for Connected Autonomous Vehicles
Yuze Jiang, Ehsan Javanmardi, Jin Nakazato, Manabu Tsukada, Hiroshi Esaki
Advancements in LiDAR technology have led to more cost-effective production while simultaneously improving precision and resolution. As a result, LiDAR has become integral to vehicle localization, achieving centimeter-level accuracy through techniques like Normal Distributions Transform (NDT) and other advanced 3D registration algorithms. Nonetheless, these approaches are reliant on high-definition 3D point cloud maps, the creation of which involves significant expenditure. When such maps are unavailable or lack sufficient features for 3D registration algorithms, localization accuracy diminishes, posing a risk to road safety. To address this, we proposed to use LiDAR-equipped roadside unit and Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication to accurately estimate the connected autonomous vehicle's position and help the vehicle when its self-localization is not accurate enough. Our simulation results indicate that this method outperforms traditional NDT scan matching-based approaches in terms of localization accuracy.
Read more7/12/2024
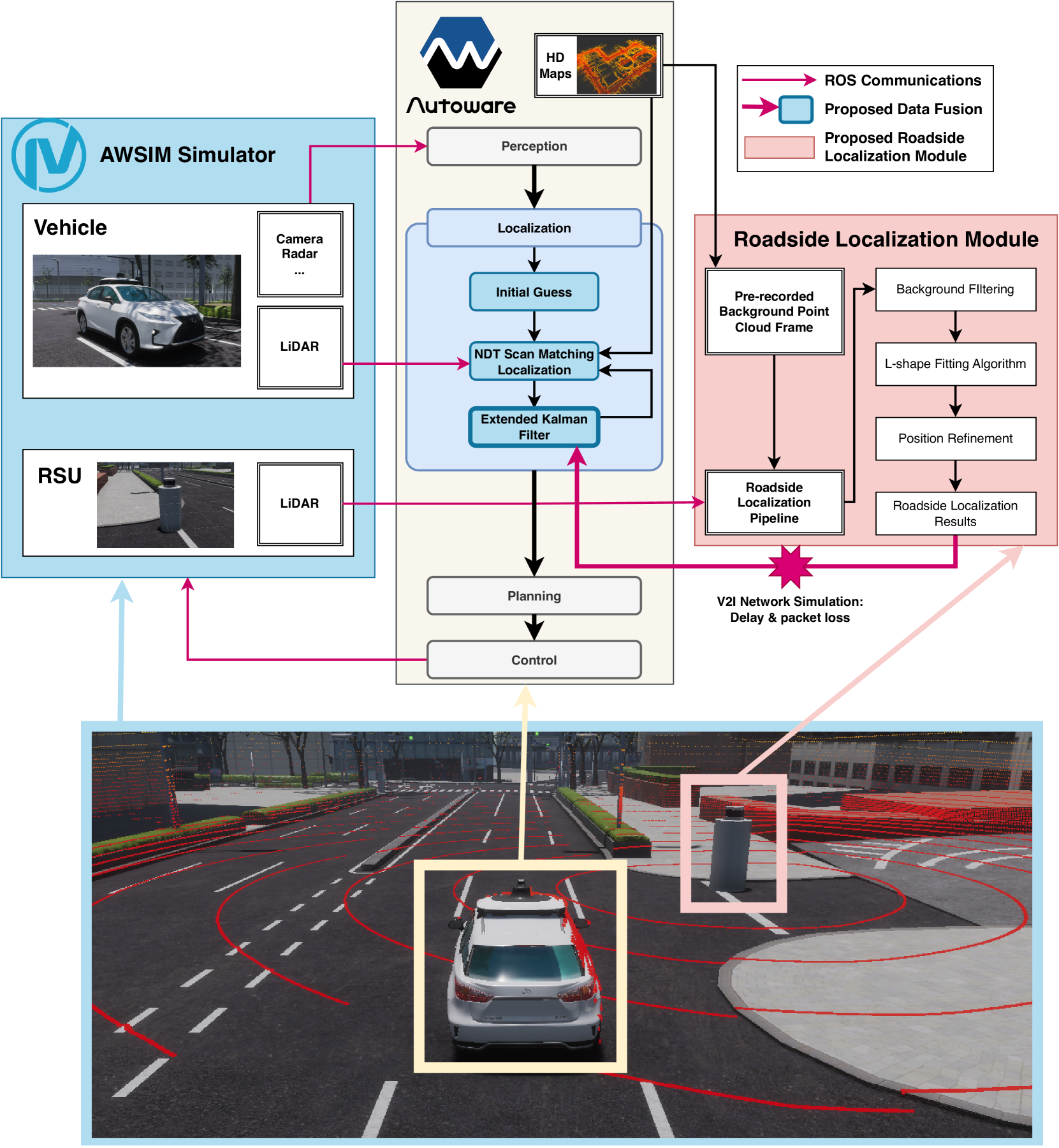

0
Accurate Cooperative Localization Utilizing LiDAR-equipped Roadside Infrastructure for Autonomous Driving
Yuze Jiang, Ehsan Javanmardi, Manabu Tsukada, Hiroshi Esaki
Recent advancements in LiDAR technology have significantly lowered costs and improved both its precision and resolution, thereby solidifying its role as a critical component in autonomous vehicle localization. Using sophisticated 3D registration algorithms, LiDAR now facilitates vehicle localization with centimeter-level accuracy. However, these high-precision techniques often face reliability challenges in environments devoid of identifiable map features. To address this limitation, we propose a novel approach that utilizes road side units (RSU) with vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications to assist vehicle self-localization. By using RSUs as stationary reference points and processing real-time LiDAR data, our method enhances localization accuracy through a cooperative localization framework. By placing RSUs in critical areas, our proposed method can improve the reliability and precision of vehicle localization when the traditional vehicle self-localization technique falls short. Evaluation results in an end-to-end autonomous driving simulator AWSIM show that the proposed method can improve localization accuracy by up to 80% under vulnerable environments compared to traditional localization methods. Additionally, our method also demonstrates robust resistance to network delays and packet loss in heterogeneous network environments.
Read more7/12/2024