CoSTA: Code-Switched Speech Translation using Aligned Speech-Text Interleaving
2406.10993

0
0
Abstract
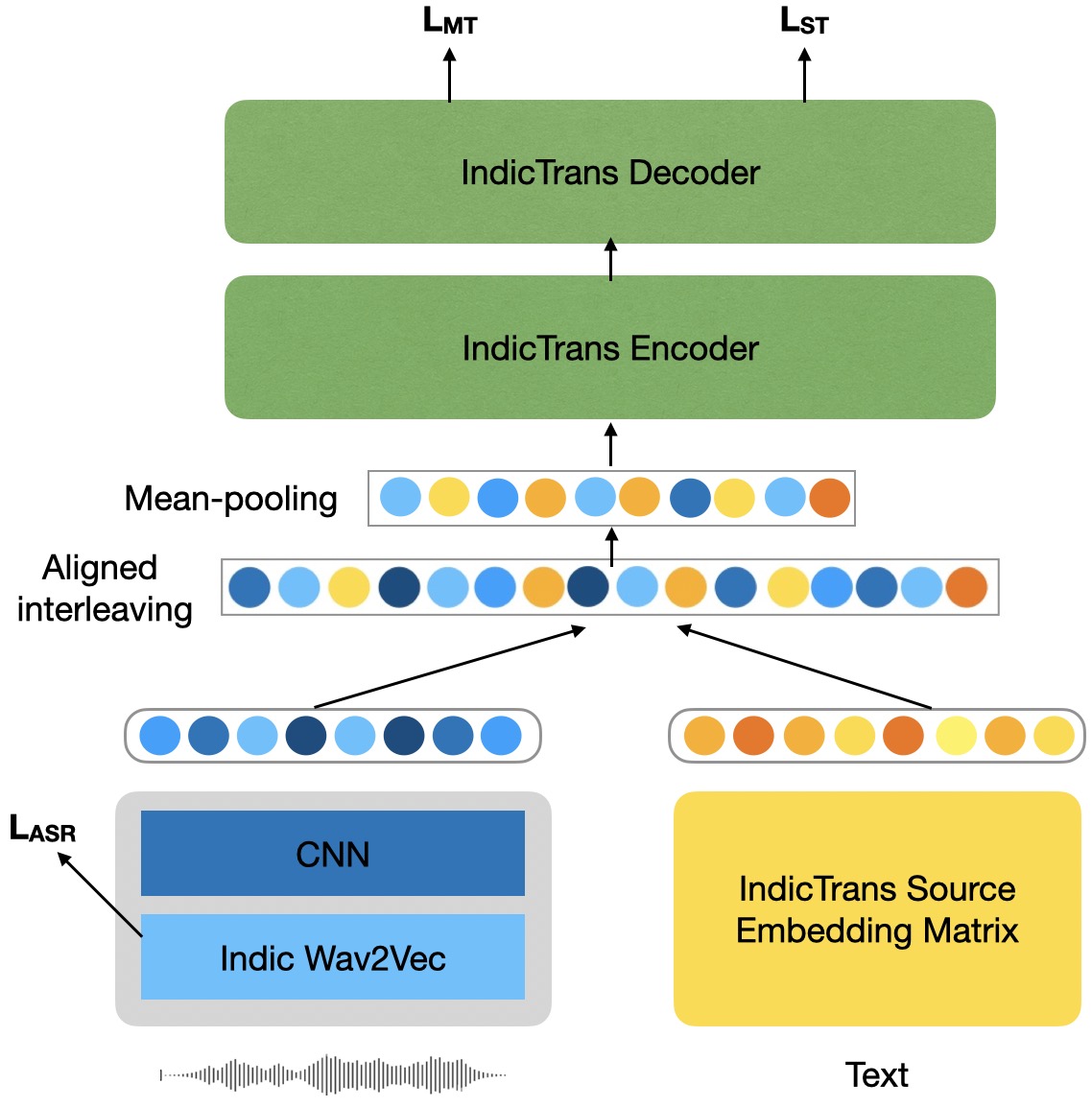
Code-switching is a widely prevalent linguistic phenomenon in multilingual societies like India. Building speech-to-text models for code-switched speech is challenging due to limited availability of datasets. In this work, we focus on the problem of spoken translation (ST) of code-switched speech in Indian languages to English text. We present a new end-to-end model architecture COSTA that scaffolds on pretrained automatic speech recognition (ASR) and machine translation (MT) modules (that are more widely available for many languages). Speech and ASR text representations are fused using an aligned interleaving scheme and are fed further as input to a pretrained MT module; the whole pipeline is then trained end-to-end for spoken translation using synthetically created ST data. We also release a new evaluation benchmark for code-switched Bengali-English, Hindi-English, Marathi-English and Telugu- English speech to English text. COSTA significantly outperforms many competitive cascaded and end-to-end multimodal baselines by up to 3.5 BLEU points.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces CoSTA, a method for translating code-switched speech (speech that mixes multiple languages) into a target language.
- The key innovation is "aligned speech-text interleaving," which aligns the code-switched speech with corresponding text segments in multiple languages.
- This allows the model to learn cross-lingual representations and handle code-switching more effectively than previous approaches.
Plain English Explanation
Code-switched speech, where people mix multiple languages in the same conversation, is common in many multilingual settings. However, translating this type of speech into a single target language is challenging for traditional speech translation systems.
The researchers behind CoSTA propose a new approach that aims to address this problem. Their key idea is to align the code-switched speech with corresponding text segments in multiple languages. This "aligned speech-text interleaving" allows the model to learn rich cross-lingual representations, which helps it handle the code-switching more effectively.
For example, if the input speech is "I want to go to the [Spanish] parque [English] park," the model would learn to associate the Spanish word "parque" with the English word "park," enabling it to correctly translate the full utterance.
This approach builds on recent advances in end-to-end speech translation and code-switching modeling, combining them in a novel way to tackle the challenge of translating code-switched speech.
Technical Explanation
The core of the CoSTA approach is the "aligned speech-text interleaving" technique. The model takes as input code-switched speech and corresponding text segments in multiple languages. It then learns to align the speech and text, allowing it to build cross-lingual representations that capture the relationships between words and sounds across languages.
This is implemented using a transformer-based architecture with three key components:
- Speech Encoder: Encodes the input code-switched speech.
- Text Encoder: Encodes the corresponding text segments in multiple languages.
- Interleaving Decoder: Generates the translation in the target language, attending to both the speech and text encodings.
The key innovation is the way the speech and text encodings are combined in the interleaving decoder. This allows the model to learn robust cross-lingual representations that enable it to handle code-switching more effectively than previous cascade-based approaches.
Critical Analysis
The authors acknowledge several limitations of their approach. First, the model requires aligned speech and text data, which may not be readily available for all language pairs and domains. Second, the performance of CoSTA is still lower than that of human translators, suggesting room for further improvements.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the model's robustness to noisy or spontaneous speech, which is a common challenge in real-world speech translation scenarios. Further research is needed to understand how CoSTA would perform in more realistic settings.
That said, the core idea of aligned speech-text interleaving is a promising direction for improving code-switched speech translation. By leveraging cross-lingual representations, the approach represents an important step towards more accurate and versatile speech translation systems.
Conclusion
The CoSTA paper presents a novel approach to translating code-switched speech, a common phenomenon in multilingual settings. By aligning the input speech with corresponding text segments in multiple languages, the model can learn rich cross-lingual representations that enable it to handle code-switching more effectively than previous methods.
While the current implementation has some limitations, the underlying principles of CoSTA offer a compelling path forward for advancing the state-of-the-art in speech translation. As the field continues to evolve, techniques like aligned speech-text interleaving may play a key role in developing translation systems that can seamlessly navigate the complexities of real-world, multilingual communication.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
End-to-End Speech-to-Text Translation: A Survey
Nivedita Sethiya, Chandresh Kumar Maurya

0
0
Speech-to-text translation pertains to the task of converting speech signals in a language to text in another language. It finds its application in various domains, such as hands-free communication, dictation, video lecture transcription, and translation, to name a few. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), as well as Machine Translation(MT) models, play crucial roles in traditional ST translation, enabling the conversion of spoken language in its original form to written text and facilitating seamless cross-lingual communication. ASR recognizes spoken words, while MT translates the transcribed text into the target language. Such disintegrated models suffer from cascaded error propagation and high resource and training costs. As a result, researchers have been exploring end-to-end (E2E) models for ST translation. However, to our knowledge, there is no comprehensive review of existing works on E2E ST. The present survey, therefore, discusses the work in this direction. Our attempt has been to provide a comprehensive review of models employed, metrics, and datasets used for ST tasks, providing challenges and future research direction with new insights. We believe this review will be helpful to researchers working on various applications of ST models.
6/11/2024
ArzEn-LLM: Code-Switched Egyptian Arabic-English Translation and Speech Recognition Using LLMs
Ahmed Heakl, Youssef Zaghloul, Mennatullah Ali, Rania Hossam, Walid Gomaa

0
0
Motivated by the widespread increase in the phenomenon of code-switching between Egyptian Arabic and English in recent times, this paper explores the intricacies of machine translation (MT) and automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, focusing on translating code-switched Egyptian Arabic-English to either English or Egyptian Arabic. Our goal is to present the methodologies employed in developing these systems, utilizing large language models such as LLama and Gemma. In the field of ASR, we explore the utilization of the Whisper model for code-switched Egyptian Arabic recognition, detailing our experimental procedures including data preprocessing and training techniques. Through the implementation of a consecutive speech-to-text translation system that integrates ASR with MT, we aim to overcome challenges posed by limited resources and the unique characteristics of the Egyptian Arabic dialect. Evaluation against established metrics showcases promising results, with our methodologies yielding a significant improvement of $56%$ in English translation over the state-of-the-art and $9.3%$ in Arabic translation. Since code-switching is deeply inherent in spoken languages, it is crucial that ASR systems can effectively handle this phenomenon. This capability is crucial for enabling seamless interaction in various domains, including business negotiations, cultural exchanges, and academic discourse. Our models and code are available as open-source resources. Code: url{http://github.com/ahmedheakl/arazn-llm}}, Models: url{http://huggingface.co/collections/ahmedheakl/arazn-llm-662ceaf12777656607b9524e}.
6/27/2024
CrossVoice: Crosslingual Prosody Preserving Cascade-S2ST using Transfer Learning
Medha Hira, Arnav Goel, Anubha Gupta

0
0
This paper presents CrossVoice, a novel cascade-based Speech-to-Speech Translation (S2ST) system employing advanced ASR, MT, and TTS technologies with cross-lingual prosody preservation through transfer learning. We conducted comprehensive experiments comparing CrossVoice with direct-S2ST systems, showing improved BLEU scores on tasks such as Fisher Es-En, VoxPopuli Fr-En and prosody preservation on benchmark datasets CVSS-T and IndicTTS. With an average mean opinion score of 3.75 out of 4, speech synthesized by CrossVoice closely rivals human speech on the benchmark, highlighting the efficacy of cascade-based systems and transfer learning in multilingual S2ST with prosody transfer.
6/19/2024
Improving Zero-Shot Chinese-English Code-Switching ASR with kNN-CTC and Gated Monolingual Datastores
Jiaming Zhou, Shiwan Zhao, Hui Wang, Tian-Hao Zhang, Haoqin Sun, Xuechen Wang, Yong Qin

0
0
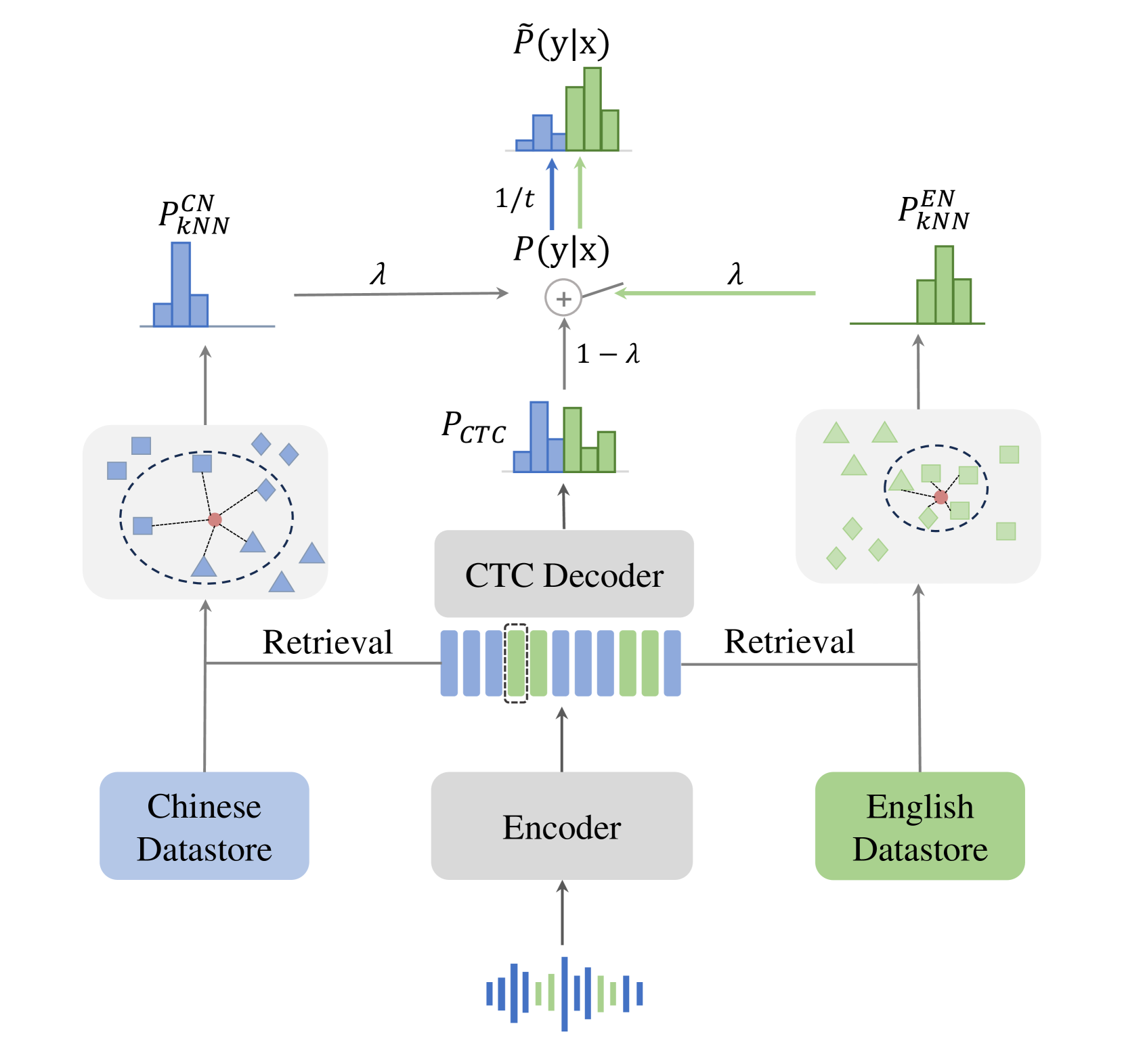
The kNN-CTC model has proven to be effective for monolingual automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, its direct application to multilingual scenarios like code-switching, presents challenges. Although there is potential for performance improvement, a kNN-CTC model utilizing a single bilingual datastore can inadvertently introduce undesirable noise from the alternative language. To address this, we propose a novel kNN-CTC-based code-switching ASR (CS-ASR) framework that employs dual monolingual datastores and a gated datastore selection mechanism to reduce noise interference. Our method selects the appropriate datastore for decoding each frame, ensuring the injection of language-specific information into the ASR process. We apply this framework to cutting-edge CTC-based models, developing an advanced CS-ASR system. Extensive experiments demonstrate the remarkable effectiveness of our gated datastore mechanism in enhancing the performance of zero-shot Chinese-English CS-ASR.
6/17/2024