The Critical Role of Effective Communication in Human-Robot Collaborative Assembly

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This research paper examines the critical role of effective communication in human-robot collaborative assembly.
- It proposes a natural collaborative assembly framework that enables seamless interaction between humans and robots.
- The framework focuses on enhancing communication and coordination to improve the efficiency and safety of collaborative assembly tasks.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how important good communication is when humans and robots work together on assembly tasks. It describes a new framework that aims to make this collaboration smoother and more natural. The key idea is to improve the way the human and robot communicate and coordinate their actions, which can make the assembly process more efficient and safer.
For example, the robot could use clear verbal instructions or visual cues to let the human know what it's about to do next. And the human could provide feedback to the robot, so they're both aware of each other's intentions and can adjust their behavior accordingly. By enhancing this back-and-forth communication, the human and robot can work together more harmoniously on the assembly tasks.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a Natural Collaborative Assembly Framework that aims to enable seamless interaction between humans and robots during collaborative assembly tasks. The framework focuses on improving communication and coordination between the human and robot partners.
Some key elements of the framework include:
- Multimodal communication channels that allow the human and robot to exchange information through speech, gestures, and visual displays.
- Intention recognition to help the robot understand the human's goals and planned actions.
- Legibility enhancement to make the robot's own actions and intentions more clear and interpretable to the human.
- Conflict resolution mechanisms to handle any discrepancies or misalignments between the human and robot during the collaborative assembly process.
By incorporating these communication-focused capabilities, the framework aims to improve the efficiency, safety, and overall fluency of human-robot collaboration in assembly tasks.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the key challenges and design considerations involved in enabling effective communication between humans and robots during collaborative assembly.
One potential limitation highlighted is the need for further research to develop robust intention recognition and legibility enhancement capabilities, which are critical for the framework to work effectively in real-world scenarios.
Additionally, the paper acknowledges the importance of trust and transparency in human-robot collaboration, an area that may require more in-depth exploration to ensure the framework is adopted and used safely by human workers.
Overall, the proposed framework presents a promising approach to enhancing communication and coordination in human-robot collaborative assembly, but continued research and development will be needed to fully realize its potential benefits.
Conclusion
This research paper highlights the critical role of effective communication in enabling successful human-robot collaboration during assembly tasks. By proposing a comprehensive framework that focuses on improving the exchange of information, intentions, and feedback between human and robot partners, the authors aim to enhance the efficiency, safety, and overall fluency of these collaborative interactions.
While the framework presents a compelling vision, the authors acknowledge the need for further advancements in key enabling technologies, as well as the importance of addressing trust and transparency concerns. Nonetheless, this work represents an important step forward in the ongoing effort to integrate robots seamlessly into human-centric manufacturing and assembly processes.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
The Critical Role of Effective Communication in Human-Robot Collaborative Assembly
Davide Ferrari, Cristian Secchi
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC), effective communication between humans and robots is crucial for complex task execution. Traditional request-response systems often lack naturalness and may hinder efficiency. This study emphasizes the importance of adopting human-like communication interactions to enable fluent vocal communication between human operators and robots simulating a collaborative human-robot industrial assembly. We propose a novel approach that employs human-like interactions through natural dialogue, enabling human operators to engage in vocal conversations with robots. Through a comparative experiment, we demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in enhancing task performance and collaboration efficiency. The robot's ability to engage in meaningful vocal conversations enables it to seek clarification, provide status updates, and ask for assistance when required, leading to improved coordination and a smoother workflow. The results indicate that the adoption of human-like conversational interactions positively influences the human-robot collaborative dynamic. Human operators find it easier to convey complex instructions and preferences, resulting in a more productive and satisfying collaboration experience.
Read more9/12/2024


0
Collaborative Conversation in Safe Multimodal Human-Robot Collaboration
Davide Ferrari, Andrea Pupa, Cristian Secchi
In the context of Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC), it is crucial that the two actors are able to communicate with each other in a natural and efficient manner. The absence of a communication interface is often a cause of undesired slowdowns. On one hand, this is because unforeseen events may occur, leading to errors. On the other hand, due to the close contact between humans and robots, the speed must be reduced significantly to comply with safety standard ISO/TS 15066. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture that enables operators and robots to communicate efficiently, emulating human-to-human dialogue, while addressing safety concerns. This approach aims to establish a communication framework that not only facilitates collaboration but also reduces undesired speed reduction. Through the use of a predictive simulator, we can anticipate safety-related limitations, ensuring smoother workflows, minimizing risks, and optimizing efficiency. The overall architecture has been validated with a UR10e and compared with a state of the art technique. The results show a significant improvement in user experience, with a corresponding 23% reduction in execution times and a 50% decrease in robot downtime.
Read more9/12/2024
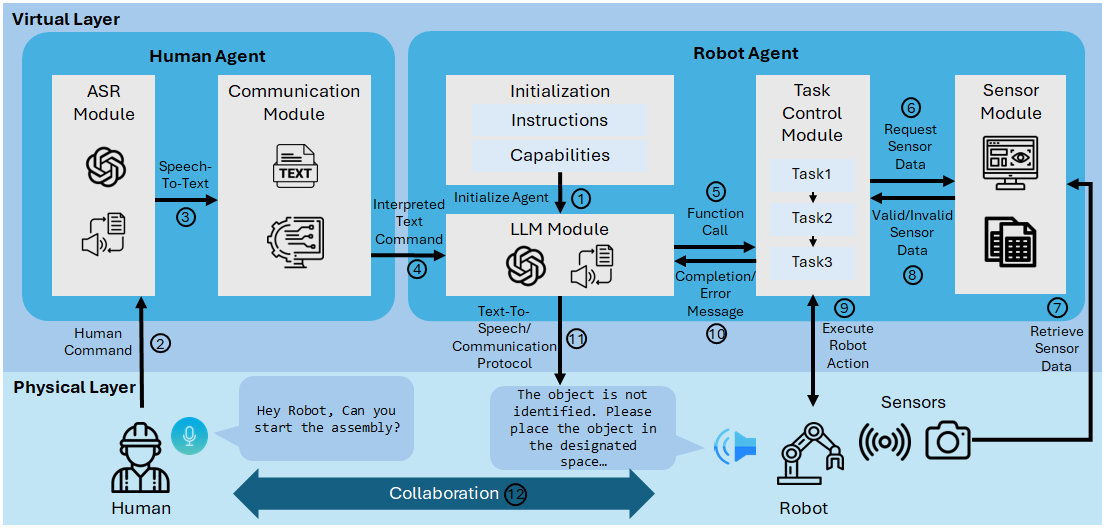

0
Enhancing Human-Robot Collaborative Assembly in Manufacturing Systems Using Large Language Models
Jonghan Lim, Sujani Patel, Alex Evans, John Pimley, Yifei Li, Ilya Kovalenko
The development of human-robot collaboration has the ability to improve manufacturing system performance by leveraging the unique strengths of both humans and robots. On the shop floor, human operators contribute with their adaptability and flexibility in dynamic situations, while robots provide precision and the ability to perform repetitive tasks. However, the communication gap between human operators and robots limits the collaboration and coordination of human-robot teams in manufacturing systems. Our research presents a human-robot collaborative assembly framework that utilizes a large language model for enhancing communication in manufacturing environments. The framework facilitates human-robot communication by integrating voice commands through natural language for task management. A case study for an assembly task demonstrates the framework's ability to process natural language inputs and address real-time assembly challenges, emphasizing adaptability to language variation and efficiency in error resolution. The results suggest that large language models have the potential to improve human-robot interaction for collaborative manufacturing assembly applications.
Read more6/24/2024


0
Model-free Legibility: Enhancing Human-Robot Interactions through Implicit Communication and Influence Modulation
Haoyang Jiang, Elizabeth A. Croft, Michael G. Burke
Communication is essential for successful interaction. In human-robot interaction, implicit communication enhances robots' understanding of human needs, emotions, and intentions. This paper introduces a method to foster implicit communication in HRI without explicitly modeling human intentions or relying on pre-existing knowledge. Leveraging Transfer Entropy, we modulate influence between agents in social interactions in scenarios involving either collaboration or competition. By integrating influence into agents' rewards within a partially observable Markov decision process, we demonstrate that boosting influence enhances collaboration or competition performance, while resisting influence diminishes performance. Our findings are validated through simulations and real-world experiments with human participants.
Read more6/19/2024