DiagGPT: An LLM-based and Multi-agent Dialogue System with Automatic Topic Management for Flexible Task-Oriented Dialogue
2308.08043

0
0
✨
Abstract
A significant application of Large Language Models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, is their deployment as chat agents, which respond to human inquiries across a variety of domains. While current LLMs proficiently answer general questions, they often fall short in complex diagnostic scenarios such as legal, medical, or other specialized consultations. These scenarios typically require Task-Oriented Dialogue (TOD), where an AI chat agent must proactively pose questions and guide users toward specific goals or task completion. Previous fine-tuning models have underperformed in TOD and the full potential of conversational capability in current LLMs has not yet been fully explored. In this paper, we introduce DiagGPT (Dialogue in Diagnosis GPT), an innovative approach that extends LLMs to more TOD scenarios. In addition to guiding users to complete tasks, DiagGPT can effectively manage the status of all topics throughout the dialogue development. This feature enhances user experience and offers a more flexible interaction in TOD. Our experiments demonstrate that DiagGPT exhibits outstanding performance in conducting TOD with users, showing its potential for practical applications in various fields.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores an innovative approach called DiagGPT that extends large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT to handle more complex task-oriented dialogues (TOD).
- Current LLMs are proficient at answering general questions but struggle in specialized scenarios like legal, medical, or other consultations that require guiding users to specific goals.
- DiagGPT aims to enhance the conversational capabilities of LLMs by enabling them to proactively manage the status of discussion topics and guide users more effectively in TOD scenarios.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are very good at answering general questions. However, they often struggle when it comes to more complex, specialized tasks that require guiding a user through a specific process or goal. This is known as "task-oriented dialogue" (TOD).
The paper introduces an approach called DiagGPT that tries to address this limitation. DiagGPT builds on top of existing LLMs to make them better at TOD scenarios. The key idea is that DiagGPT can actively manage the status of different topics throughout a conversation, helping to guide the user towards their goal.
For example, imagine you're trying to get medical advice from an AI chatbot. A regular LLM might be able to answer basic questions, but it wouldn't be able to actively probe for more information, ask follow-up questions, and guide you towards a diagnosis. DiagGPT, on the other hand, would be designed to do just that - to have a more natural, back-and-forth conversation to understand your symptoms and ultimately provide a more helpful recommendation.
The paper demonstrates that DiagGPT can achieve outstanding performance in these types of TOD scenarios, suggesting it could be very useful for practical applications in fields like healthcare, law, and other specialized domains.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces an innovative approach called DiagGPT that extends large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT to handle more complex task-oriented dialogues (TOD).
While current LLMs are proficient at answering general questions, they often fall short in specialized scenarios such as legal, medical, or other consultations that require an AI chatbot to proactively guide users towards specific goals or task completion. Previous fine-tuning models have underperformed in TOD, and the full potential of conversational capability in current LLMs has not been fully explored.
The key innovation in DiagGPT is its ability to effectively manage the status of all topics throughout the dialogue development. This feature enhances the user experience and offers more flexible interaction in TOD scenarios. The paper demonstrates that DiagGPT exhibits outstanding performance in conducting TOD with users, suggesting its potential for practical applications in various fields.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to enhancing the conversational capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for task-oriented dialogues (TOD). By introducing the DiagGPT model, the researchers have shown that LLMs can be extended to handle more complex, specialized scenarios that require proactive user guidance.
However, the paper does not delve into the specific architectural details or training process of DiagGPT, which would be helpful for understanding its inner workings and potential limitations. Additionally, the paper does not provide a comprehensive comparison of DiagGPT's performance against other state-of-the-art TOD models, which would help contextualize its relative strengths and weaknesses.
Furthermore, the paper acknowledges that the full potential of conversational capability in current LLMs has not been fully explored, suggesting that there may be room for further advancements in this area. It would be interesting to see how DiagGPT could be combined with other techniques, such as enhancing general agent capabilities with low-parameter LLMs or dynamic generation of personalities in LLMs, to further improve its performance and versatility.
Conclusion
The paper presents an innovative approach called DiagGPT that aims to extend the conversational capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to handle more complex, task-oriented dialogue (TOD) scenarios. By enabling LLMs to proactively manage the status of discussion topics, DiagGPT can guide users more effectively towards specific goals or task completion.
The results suggest that DiagGPT has the potential to significantly improve the user experience and practical applications of LLMs in specialized domains, such as healthcare, law, and other consultative services. This research represents an important step towards unlocking the full potential of conversational AI systems and could have far-reaching implications for the field of natural language processing and dialogue systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
Transforming Dental Diagnostics with Artificial Intelligence: Advanced Integration of ChatGPT and Large Language Models for Patient Care
Masoumeh Farhadi Nia, Mohsen Ahmadi, Elyas Irankhah

0
0
Artificial intelligence has dramatically reshaped our interaction with digital technologies, ushering in an era where advancements in AI algorithms and Large Language Models (LLMs) have natural language processing (NLP) systems like ChatGPT. This study delves into the impact of cutting-edge LLMs, notably OpenAI's ChatGPT, on medical diagnostics, with a keen focus on the dental sector. Leveraging publicly accessible datasets, these models augment the diagnostic capabilities of medical professionals, streamline communication between patients and healthcare providers, and enhance the efficiency of clinical procedures. The advent of ChatGPT-4 is poised to make substantial inroads into dental practices, especially in the realm of oral surgery. This paper sheds light on the current landscape and explores potential future research directions in the burgeoning field of LLMs, offering valuable insights for both practitioners and developers. Furthermore, it critically assesses the broad implications and challenges within various sectors, including academia and healthcare, thus mapping out an overview of AI's role in transforming dental diagnostics for enhanced patient care.
6/12/2024
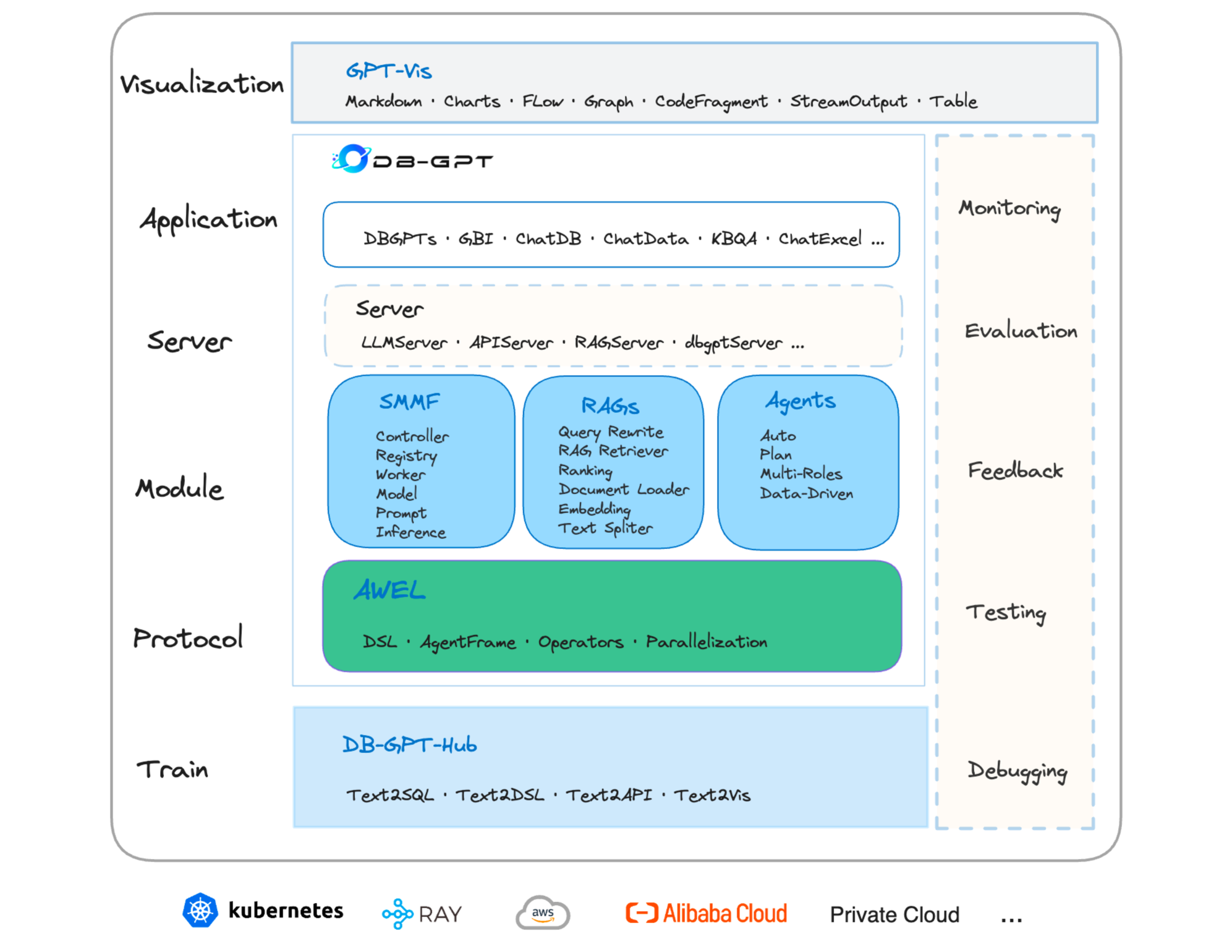
Demonstration of DB-GPT: Next Generation Data Interaction System Empowered by Large Language Models
Siqiao Xue, Danrui Qi, Caigao Jiang, Wenhui Shi, Fangyin Cheng, Keting Chen, Hongjun Yang, Zhiping Zhang, Jianshan He, Hongyang Zhang, Ganglin Wei, Wang Zhao, Fan Zhou, Hong Yi, Shaodong Liu, Hongjun Yang, Faqiang Chen

0
0
The recent breakthroughs in large language models (LLMs) are positioned to transition many areas of software. The technologies of interacting with data particularly have an important entanglement with LLMs as efficient and intuitive data interactions are paramount. In this paper, we present DB-GPT, a revolutionary and product-ready Python library that integrates LLMs into traditional data interaction tasks to enhance user experience and accessibility. DB-GPT is designed to understand data interaction tasks described by natural language and provide context-aware responses powered by LLMs, making it an indispensable tool for users ranging from novice to expert. Its system design supports deployment across local, distributed, and cloud environments. Beyond handling basic data interaction tasks like Text-to-SQL with LLMs, it can handle complex tasks like generative data analysis through a Multi-Agents framework and the Agentic Workflow Expression Language (AWEL). The Service-oriented Multi-model Management Framework (SMMF) ensures data privacy and security, enabling users to employ DB-GPT with private LLMs. Additionally, DB-GPT offers a series of product-ready features designed to enable users to integrate DB-GPT within their product environments easily. The code of DB-GPT is available at Github(https://github.com/eosphoros-ai/DB-GPT) which already has over 10.7k stars. Please install DB-GPT for your own usage with the instructions(https://github.com/eosphoros-ai/DB-GPT#install) and watch a 5-minute introduction video on Youtube(https://youtu.be/n_8RI1ENyl4) to further investigate DB-GPT.
4/26/2024

The Battle of LLMs: A Comparative Study in Conversational QA Tasks
Aryan Rangapur, Aman Rangapur

0
0
Large language models have gained considerable interest for their impressive performance on various tasks. Within this domain, ChatGPT and GPT-4, developed by OpenAI, and the Gemini, developed by Google, have emerged as particularly popular among early adopters. Additionally, Mixtral by Mistral AI and Claude by Anthropic are newly released, further expanding the landscape of advanced language models. These models are viewed as disruptive technologies with applications spanning customer service, education, healthcare, and finance. More recently, Mistral has entered the scene, captivating users with its unique ability to generate creative content. Understanding the perspectives of these users is crucial, as they can offer valuable insights into the potential strengths, weaknesses, and overall success or failure of these technologies in various domains. This research delves into the responses generated by ChatGPT, GPT-4, Gemini, Mixtral and Claude across different Conversational QA corpora. Evaluation scores were meticulously computed and subsequently compared to ascertain the overall performance of these models. Our study pinpointed instances where these models provided inaccurate answers to questions, offering insights into potential areas where they might be susceptible to errors. In essence, this research provides a comprehensive comparison and evaluation of these state of-the-art language models, shedding light on their capabilities while also highlighting potential areas for improvement
5/29/2024
💬
Digital Diagnostics: The Potential Of Large Language Models In Recognizing Symptoms Of Common Illnesses
Gaurav Kumar Gupta, Aditi Singh, Sijo Valayakkad Manikandan, Abul Ehtesham

0
0
The recent swift development of LLMs like GPT-4, Gemini, and GPT-3.5 offers a transformative opportunity in medicine and healthcare, especially in digital diagnostics. This study evaluates each model diagnostic abilities by interpreting a user symptoms and determining diagnoses that fit well with common illnesses, and it demonstrates how each of these models could significantly increase diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Through a series of diagnostic prompts based on symptoms from medical databases, GPT-4 demonstrates higher diagnostic accuracy from its deep and complete history of training on medical data. Meanwhile, Gemini performs with high precision as a critical tool in disease triage, demonstrating its potential to be a reliable model when physicians are trying to make high-risk diagnoses. GPT-3.5, though slightly less advanced, is a good tool for medical diagnostics. This study highlights the need to study LLMs for healthcare and clinical practices with more care and attention, ensuring that any system utilizing LLMs promotes patient privacy and complies with health information privacy laws such as HIPAA compliance, as well as the social consequences that affect the varied individuals in complex healthcare contexts. This study marks the start of a larger future effort to study the various ways in which assigning ethical concerns to LLMs task of learning from human biases could unearth new ways to apply AI in complex medical settings.
5/14/2024