EDA Corpus: A Large Language Model Dataset for Enhanced Interaction with OpenROAD
2405.06676

0
0
💬
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) serve as powerful tools for design, providing capabilities for both task automation and design assistance. Recent advancements have shown tremendous potential for facilitating LLM integration into the chip design process; however, many of these works rely on data that are not publicly available and/or not permissively licensed for use in LLM training and distribution. In this paper, we present a solution aimed at bridging this gap by introducing an open-source dataset tailored for OpenROAD, a widely adopted open-source EDA toolchain. The dataset features over 1000 data points and is structured in two formats: (i) a pairwise set comprised of question prompts with prose answers, and (ii) a pairwise set comprised of code prompts and their corresponding OpenROAD scripts. By providing this dataset, we aim to facilitate LLM-focused research within the EDA domain. The dataset is available at https://github.com/OpenROAD-Assistant/EDA-Corpus.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Researchers present an open-source dataset tailored for the OpenROAD EDA (Electronic Design Automation) toolchain, aimed at facilitating LLM (Large Language Model) integration into chip design processes.
- The dataset features over 1000 data points in two formats: (i) question prompts with prose answers, and (ii) code prompts with corresponding OpenROAD scripts.
- This dataset aims to bridge the gap between LLM research and the EDA domain, where much of the existing data is not publicly available or permissively licensed.
Plain English Explanation
Designing computer chips is a complex process, and large language models can be powerful tools to help automate certain tasks and assist designers. However, much of the data used in recent research on integrating language models into chip design is not publicly available or not licensed for use in training and distributing language models.
To address this, the researchers have created an open-source dataset specifically tailored for the OpenROAD EDA toolchain. This dataset includes over 1000 data points, with two different formats: one set of question prompts and their corresponding prose answers, and another set of code prompts and the matching OpenROAD scripts. By making this dataset available, the researchers hope to enable more research into using language models to improve chip design, similar to how datasets like LibrisQA and KazQAD have advanced research in other domains.
Technical Explanation
The researchers have created an open-source dataset that is designed to facilitate the integration of LLMs into the chip design process, specifically targeting the OpenROAD EDA toolchain. The dataset consists of over 1000 data points structured in two formats:
-
Pairwise question prompts and prose answers: This set of data pairs question prompts with prose-based answers, similar to the LUCID dataset for generating interesting dialogues.
-
Pairwise code prompts and OpenROAD scripts: This set of data pairs code prompts with their corresponding OpenROAD scripts, which are used to automate various tasks in the chip design process.
By providing this dataset, the researchers aim to enable more LLM-focused research within the EDA domain, where much of the existing data is not publicly available or permissively licensed for use in LLM training and distribution.
Critical Analysis
The researchers have acknowledged the limitations of existing data sources in the EDA domain and have taken a proactive step to address this gap by creating an open-source dataset. This is a commendable effort, as it can facilitate broader research and development in the integration of LLMs into chip design processes.
However, the paper does not provide detailed information about the process used to curate and structure the dataset. It would be helpful to know more about the sources of the data, the criteria used for selection, and the quality assurance measures taken to ensure the dataset's reliability and consistency.
Additionally, while the dataset covers a significant number of data points, it would be valuable to understand the breadth and depth of the topics and use cases represented. Providing more information about the diversity and comprehensiveness of the dataset could help potential users assess its suitability for their research or applications.
Conclusion
The researchers have developed an open-source dataset tailored for the OpenROAD EDA toolchain, with the goal of enabling more LLM-focused research in the chip design domain. By making this dataset available, they aim to bridge the gap between LLM research and the specific needs of the EDA community, where much of the existing data is not publicly accessible or permissively licensed.
This effort can have significant implications for the development of more efficient and intelligent chip design processes, potentially leading to advancements in areas like medical question answering or conversational AI. The availability of this dataset can encourage further research and innovation in the integration of LLMs into the chip design workflow, ultimately benefiting the broader EDA community and the technology industry as a whole.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Zyda: A 1.3T Dataset for Open Language Modeling
Yury Tokpanov, Beren Millidge, Paolo Glorioso, Jonathan Pilault, Adam Ibrahim, James Whittington, Quentin Anthony

0
0
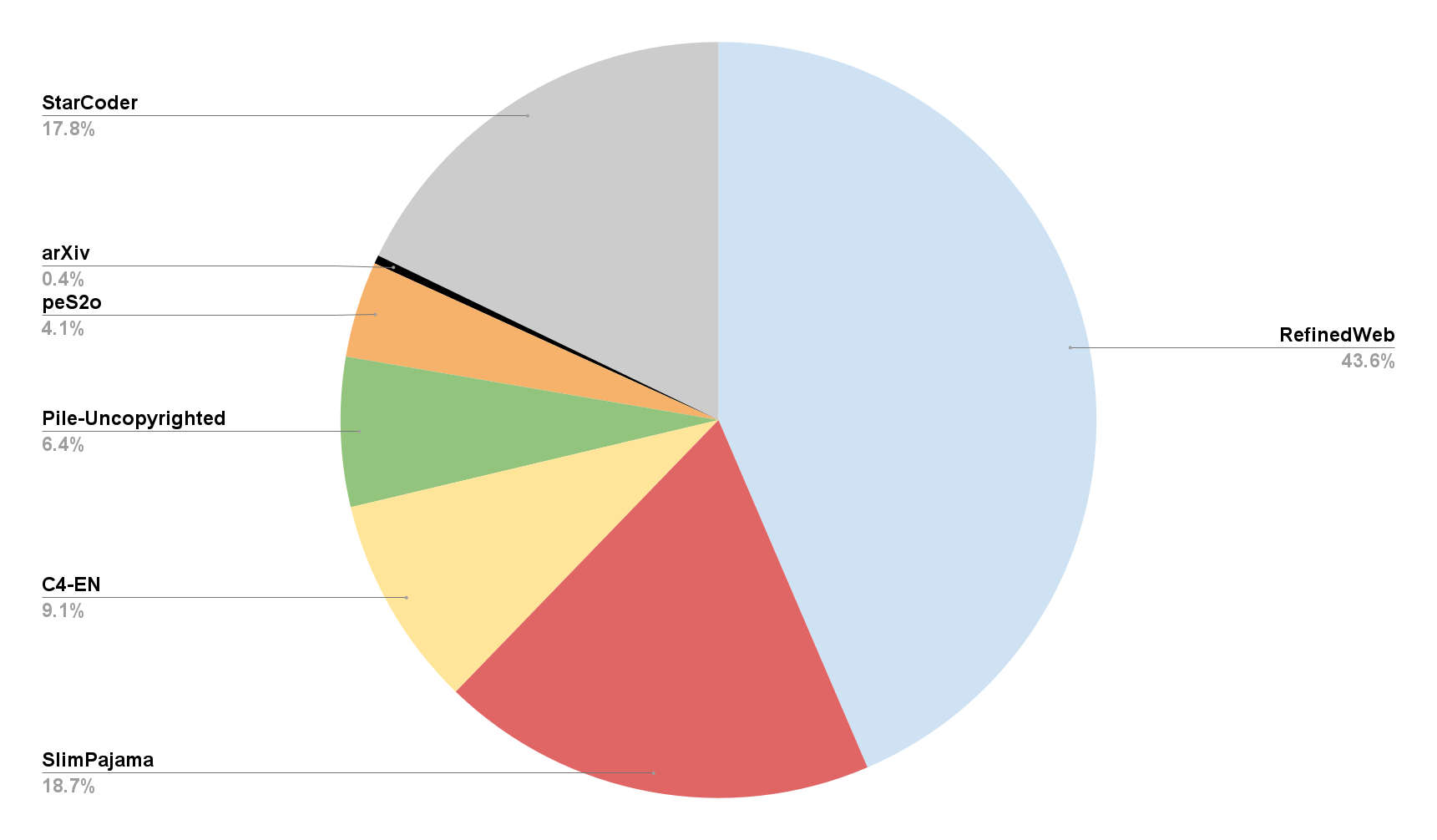
The size of large language models (LLMs) has scaled dramatically in recent years and their computational and data requirements have surged correspondingly. State-of-the-art language models, even at relatively smaller sizes, typically require training on at least a trillion tokens. This rapid advancement has eclipsed the growth of open-source datasets available for large-scale LLM pretraining. In this paper, we introduce Zyda (Zyphra Dataset), a dataset under a permissive license comprising 1.3 trillion tokens, assembled by integrating several major respected open-source datasets into a single, high-quality corpus. We apply rigorous filtering and deduplication processes, both within and across datasets, to maintain and enhance the quality derived from the original datasets. Our evaluations show that Zyda not only competes favorably with other open datasets like Dolma, FineWeb, and RefinedWeb, but also substantially improves the performance of comparable models from the Pythia suite. Our rigorous data processing methods significantly enhance Zyda's effectiveness, outperforming even the best of its constituent datasets when used independently.
6/5/2024
🖼️
Tagengo: A Multilingual Chat Dataset
Peter Devine

0
0
Open source large language models (LLMs) have shown great improvements in recent times. However, many of these models are focused solely on popular spoken languages. We present a high quality dataset of more than 70k prompt-response pairs in 74 languages which consist of human generated prompts and synthetic responses. We use this dataset to train a state-of-the-art open source English LLM to chat multilingually. We evaluate our model on MT-Bench chat benchmarks in 6 languages, finding that our multilingual model outperforms previous state-of-the-art open source LLMs across each language. We further find that training on more multilingual data is beneficial to the performance in a chosen target language (Japanese) compared to simply training on only data in that language. These results indicate the necessity of training on large amounts of high quality multilingual data to make a more accessible LLM.
5/22/2024
🔍
The Evolution of Darija Open Dataset: Introducing Version 2
Aissam Outchakoucht, Hamza Es-Samaali

0
0
Darija Open Dataset (DODa) represents an open-source project aimed at enhancing Natural Language Processing capabilities for the Moroccan dialect, Darija. With approximately 100,000 entries, DODa stands as the largest collaborative project of its kind for Darija-English translation. The dataset features semantic and syntactic categorizations, variations in spelling, verb conjugations across multiple tenses, as well as tens of thousands of translated sentences. The dataset includes entries written in both Latin and Arabic alphabets, reflecting the linguistic variations and preferences found in different sources and applications. The availability of such dataset is critical for developing applications that can accurately understand and generate Darija, thus supporting the linguistic needs of the Moroccan community and potentially extending to similar dialects in neighboring regions. This paper explores the strategic importance of DODa, its current achievements, and the envisioned future enhancements that will continue to promote its use and expansion in the global NLP landscape.
5/24/2024
Audio Dialogues: Dialogues dataset for audio and music understanding
Arushi Goel, Zhifeng Kong, Rafael Valle, Bryan Catanzaro

0
0
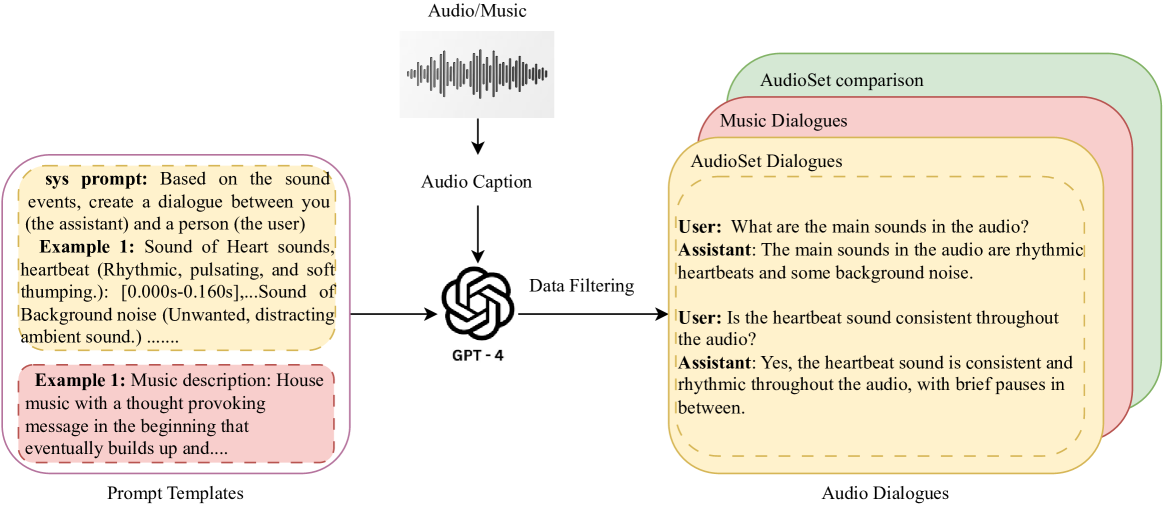
Existing datasets for audio understanding primarily focus on single-turn interactions (i.e. audio captioning, audio question answering) for describing audio in natural language, thus limiting understanding audio via interactive dialogue. To address this gap, we introduce Audio Dialogues: a multi-turn dialogue dataset containing 163.8k samples for general audio sounds and music. In addition to dialogues, Audio Dialogues also has question-answer pairs to understand and compare multiple input audios together. Audio Dialogues leverages a prompting-based approach and caption annotations from existing datasets to generate multi-turn dialogues using a Large Language Model (LLM). We evaluate existing audio-augmented large language models on our proposed dataset to demonstrate the complexity and applicability of Audio Dialogues. Our code for generating the dataset will be made publicly available. Detailed prompts and generated dialogues can be found on the demo website https://audiodialogues.github.io/.
4/12/2024