Electromagnetically-Consistent Modeling and Optimization of Mutual Coupling in RIS-Assisted Multi-User MIMO Communication Systems
2404.04539

0
0
Abstract
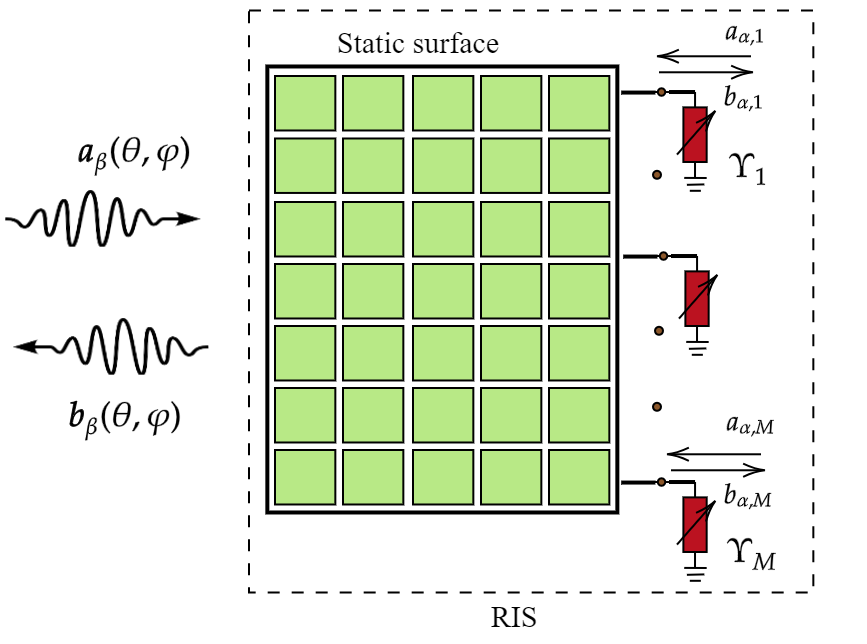
Mutual Coupling (MC) is an unavoidable feature in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs) with sub-wavelength inter-element spacing. Its inherent presence naturally leads to non-local RIS structures, which can be efficiently described via non-diagonal phase shift matrices. In this paper, we focus on optimizing MC in RIS-assisted multi-user MIMO wireless communication systems. We particularly formulate a novel problem to jointly optimize active and passive beamforming as well as MC in a physically consistent manner. To characterize MC, we deploy scattering parameters and propose a novel approach to optimize them through an offline optimization method, rather than optimizing MC on the fly. Our numerical results showcase that the system performance increases with the proposed MC optimization, and this improvement is achievable without the need for optimizing MC on-the-fly, which can be rather cumbersome.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Examines the modeling and optimization of mutual coupling in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-assisted multi-user MIMO communication systems
- Proposes an electromagnetically-consistent approach to accurately model mutual coupling effects
- Optimizes the RIS reflection pattern to minimize mutual coupling and improve system performance
Plain English Explanation
This research paper focuses on improving the performance of wireless communication systems that use Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS). RIS are devices that can dynamically control the way electromagnetic waves are reflected, allowing for more efficient and flexible wireless communication.
One key challenge with RIS-assisted systems is the issue of "mutual coupling" - the way that the different antenna elements in the system interact with each other and affect the overall signal. The authors of this paper propose a new way to model these mutual coupling effects in a physically-accurate manner. This builds on previous work on nonlocal RIS modeling and joint training of reflection patterns.
By accurately modeling mutual coupling, the researchers are then able to optimize the reflection pattern of the RIS to minimize these undesirable coupling effects. This ultimately leads to improved performance and efficiency in RIS-assisted multi-user MIMO communication systems.
The key innovation here is the use of an "electromagnetically-consistent" modeling approach, which ensures the physical reality of the system is properly accounted for. This is an important step towards realizing the full potential of RIS technology in practical wireless applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an electromagnetically-consistent modeling and optimization framework for addressing mutual coupling effects in RIS-assisted multi-user MIMO communication systems.
The authors first develop a physically-accurate model for the RIS that captures the non-diagonal structure of the mutual coupling matrix. This extends previous work on nonlocal RIS modeling by incorporating these coupling effects.
They then formulate an optimization problem to find the optimal RIS reflection pattern that minimizes the impact of mutual coupling. This builds on research into joint training of reflection patterns and power-aware sparse reflect beamforming.
The proposed approach is evaluated through simulations, which demonstrate significant performance improvements over baseline methods that neglect mutual coupling. The results highlight the importance of electromagnetically-consistent modeling for RIS-assisted cell-free massive MIMO and reconfigurable MIMO systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a rigorous and comprehensive treatment of the mutual coupling issue in RIS-assisted multi-user MIMO systems. The authors' electromagnetically-consistent modeling approach is a notable contribution, as it addresses a key limitation of previous work that overlooked these physical coupling effects.
However, the proposed optimization framework assumes perfect channel state information, which may not be realistic in practical deployments. Additionally, the simulations are conducted under idealized conditions, and further research is needed to validate the approach under more realistic wireless environments.
Another area for potential exploration is the tradeoff between the complexity of the mutual coupling model and the computational overhead of the optimization. A simplified model that captures the essential coupling dynamics may be preferable for real-time implementation.
Overall, this research represents an important step forward in ensuring the physical consistency of RIS-based communication systems. The insights and methodologies presented here can inform future work on maximizing the performance and efficiency of this emerging wireless technology.
Conclusion
This paper introduces an electromagnetically-consistent modeling and optimization framework for addressing mutual coupling effects in RIS-assisted multi-user MIMO communication systems. By accurately capturing the non-diagonal structure of the coupling matrix, the authors are able to develop an optimization approach that minimizes the impact of these undesirable physical interactions.
The results demonstrate significant performance improvements over baseline methods, highlighting the importance of physically-consistent modeling for realizing the full potential of RIS technology. While further research is needed to address practical implementation challenges, this work represents an important contribution towards the development of efficient and reliable RIS-based wireless communication systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Physically-Consistent Modeling and Optimization of Non-local RIS-Assisted Multi-User MIMO Communication Systems
Dilki Wijekoon, Amine Mezghani, George C. Alexandropoulos, Ekram Hossain

0
0
Mutual Coupling (MC) emerges as an inherent feature in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs), particularly, when they are fabricated with sub-wavelength inter-element spacing. Hence, any physically-consistent model of the RIS operation needs to accurately describe MC-induced effects. In addition, the design of the ElectroMagnetic (EM) transmit/receive radiation patterns constitutes another critical factor for efficient RIS operation. The latter two factors lead naturally to the emergence of non-local RIS structures, whose operation can be effectively described via non-diagonal phase shift matrices. In this paper, we focus on jointly optimizing MC and the radiation patterns in multi-user MIMO communication systems assisted by non-local RISs, which are modeled via the scattering parameters. We particularly present a novel problem formulation for the joint optimization of MC, radiation patterns, and the active and passive beamforming in a physically-consistent manner, considering either reflective or transmissive RIS setups. Differently from the current approaches that design the former two parameters on the fly, we present an offline optimization method which is solved for both considered RIS functionalities. Our extensive simulation results, using both parametric and geometric channel models, showcase the validity of the proposed optimization framework over benchmark schemes, indicating that improved performance is achievable without the need for optimizing MC and the radiation patterns of the RIS on the fly, which can be rather cumbersome.
6/11/2024

Joint Training and Reflection Pattern Optimization for Non-Ideal RIS-Aided Multiuser Systems
Zhenyao He, Jindan Xu, Hong Shen, Wei Xu, Chau Yuen, Marco Di Renzo

0
0
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a promising technique to improve the performance of future wireless communication systems at low energy consumption. To reap the potential benefits of RIS-aided beamforming, it is vital to enhance the accuracy of channel estimation. In this paper, we consider an RIS-aided multiuser system with non-ideal reflecting elements, each of which has a phase-dependent reflecting amplitude, and we aim to minimize the mean-squared error (MSE) of the channel estimation by jointly optimizing the training signals at the user equipments (UEs) and the reflection pattern at the RIS. As examples the least squares (LS) and linear minimum MSE (LMMSE) estimators are considered. The considered problems do not admit simple solution mainly due to the complicated constraints pertaining to the non-ideal RIS reflecting elements. As far as the LS criterion is concerned, we tackle this difficulty by first proving the optimality of orthogonal training symbols and then propose a majorization-minimization (MM)-based iterative method to design the reflection pattern, where a semi-closed form solution is obtained in each iteration. As for the LMMSE criterion, we address the joint training and reflection pattern optimization problem with an MM-based alternating algorithm, where a closed-form solution to the training symbols and a semi-closed form solution to the RIS reflecting coefficients are derived, respectively. Furthermore, an acceleration scheme is proposed to improve the convergence rate of the proposed MM algorithms. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the performance advantages of our proposed joint training and reflection pattern designs.
4/1/2024
✅
Multi-hop Multi-RIS Wireless Communication Systems: Multi-reflection Path Scheduling and Beamforming
Xiaoyan Ma, Haixia Zhang, Xianhao Chen, Yuguang Fangmand Dongfeng Yuan

0
0
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) provides a promising way to proactively augment propagation environments for better transmission performance in wireless communications. Existing multi-RIS works mainly focus on link-level optimization with predetermined transmission paths, which cannot be directly extended to system-level management, since they neither consider the interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, nor the performance balancing between different transmission paths. To address this, we study an innovative multi-hop multi-RIS communication system, where a base station (BS) transmits information to a set of distributed users over multi-RIS configuration space in a multi-hop manner. The signals for each user are subsequently reflected by the selected RISs via multi-reflection line-of-sight (LoS) links. To ensure that all users have fair access to the system to avoid excessive number of RISs serving one user, we aim to find the optimal beam reflecting path for each user, while judiciously determining the path scheduling strategies with the corresponding beamforming design to ensure the fairness. Due to the presence of interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, it is highly challenging to solve the formulated multi-RIS multi-path beamforming optimization problem. To solve it, we first derive the optimal RISs' phase shifts and the corresponding reflecting path selection for each user based on its practical deployment location. With the optimized multi-reflection paths, we obtain a feasible user grouping pattern for effective interference mitigation by constructing the maximum independent sets (MISs). Finally, we propose a joint heuristic algorithm to iteratively update the beamforming vectors and the group scheduling policies to maximize the minimum equivalent data rate of all users.
5/22/2024
🖼️
Nonlocal Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Wireless Communication: Modeling and Physical Layer Aspects
Amine Mezghani, Faouzi Bellili, Ekram Hossain

0
0
Conventional Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) for wireless communications have a local position-dependent (phase-gradient) scattering response on the surface. We consider more general RIS structures, called nonlocal (or redirective) RIS, that are capable of selectively manipulate the impinging waves depending on the incident angle. Redirective RIS have nonlocal wavefront-selective scattering behavior and can be implemented using multilayer arrays such as metalenses. We demonstrate that this more sophisticated type of surfaces has several advantages such as: lower overhead through coodebook-based reconfigurability, decoupled wave manipulations, and higher efficiency in multiuser scenarios via multifunctional operation. Additionally, redirective RIS architectures greatly benefit form the directional nature of wave propagation at high frequencies and can support integrated fronthaul and access (IFA) networks most efficiently. We also discuss the scalability and compactness issues and propose efficient nonlocal RIS architectures such as fractionated lens-based RIS and mirror-backed phase-masks structures that do not require additional control complexity and overhead while still offering better performance than conventional local RIS.
4/4/2024