The Ethics of Interaction: Mitigating Security Threats in LLMs

0
🤿
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the ethical challenges arising from security threats to Large Language Models (LLMs).
- LLMs are increasingly integrated into our daily lives, making them prime targets for attacks that can compromise their training data and the confidentiality of their data sources.
- The paper examines five major threats: prompt injection, jailbreaking, Personal Identifiable Information (PII) exposure, sexually explicit content, and hate-based content.
- The paper proposes developing an evaluative tool to guide developers and designers in fortifying backend systems and scrutinizing the ethical dimensions of LLM chatbot responses during testing.
Plain English Explanation
Large Language Models (LLMs) are powerful AI systems that can generate human-like text. As these models become more prevalent in our everyday lives, they also become vulnerable to various security threats. This paper explores the ethical implications of these security risks.
The paper identifies five main threats to LLMs: prompt injection, where attackers can manipulate the model's input to generate harmful content; jailbreaking, which allows users to bypass the model's intended use; PII exposure, where the model might inadvertently reveal personal information; and the generation of sexually explicit or hate-based content.
To address these ethical challenges, the researchers propose creating an evaluation tool that would help developers and designers strengthen the security of LLMs. This tool would also assess the ethical alignment of the models' responses during testing, comparing them to what a human would say in a moral context. The goal is to build trust in these powerful AI systems by ensuring they operate within ethical boundaries.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the ethical challenges associated with security threats to Large Language Models (LLMs). LLMs are AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data, which allows them to generate human-like responses. As these models become increasingly integrated into our daily lives, they become prime targets for various attacks that can compromise their training data and the confidentiality of their data sources.
The researchers identify and examine five major security threats to LLMs: prompt injection, jailbreaking, Personal Identifiable Information (PII) exposure, sexually explicit content, and hate-based content. They go beyond merely identifying these threats and delve into the critical ethical consequences of each, underscoring the urgency for robust defensive strategies.
To address these ethical challenges, the paper proposes the conceptualization and development of an evaluative tool tailored specifically for LLMs. This tool would serve a dual purpose: guiding developers and designers in the preemptive fortification of backend systems, and scrutinizing the ethical dimensions of LLM chatbot responses during the testing phase. By comparing LLM responses with those expected from humans in a moral context, the researchers aim to discern the degree to which AI behaviors align with the ethical values held by a broader society.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a thorough and well-researched exploration of the ethical challenges posed by security threats to Large Language Models (LLMs). The researchers' identification and analysis of the five major threats, including prompt injection, jailbreaking, PII exposure, and the generation of sexually explicit and hate-based content, are particularly valuable.
One potential limitation of the research is the lack of a detailed exploration of the technical mechanisms underlying these security threats. While the paper focuses on the ethical implications, a deeper dive into the technical aspects could have provided a more comprehensive understanding of the vulnerabilities and potential mitigation strategies.
Additionally, the paper could have delved further into the challenges of developing an effective evaluative tool for assessing the ethical alignment of LLM responses. The proposed approach of comparing AI outputs to human moral standards is an interesting idea, but the practical implementation and potential pitfalls of such a tool deserve more in-depth discussion.
Nevertheless, the paper's exploration of vulnerabilities and protections for large language models is a valuable contribution to the field, highlighting the critical need for robust security measures and ethical oversight as these powerful AI systems become increasingly integrated into our lives.
Conclusion
This paper offers a comprehensive examination of the ethical challenges arising from security threats to Large Language Models (LLMs). As these AI systems become more prevalent in our daily lives, the researchers underscore the urgent need to address the risks of prompt injection, jailbreaking, PII exposure, and the generation of sexually explicit and hate-based content.
By proposing the development of an evaluative tool to guide developers and designers in fortifying LLM systems and assessing the ethical alignment of chatbot responses, the paper presents a promising approach to cultivating trust in these powerful AI models. While the technical details and practical implementation of such a tool require further exploration, the paper's emphasis on the ethical dimensions of LLM security is a crucial step towards ensuring these systems operate within the bounds of societal values and expectations.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤿

0
The Ethics of Interaction: Mitigating Security Threats in LLMs
Ashutosh Kumar, Shiv Vignesh Murthy, Sagarika Singh, Swathy Ragupathy
This paper comprehensively explores the ethical challenges arising from security threats to Large Language Models (LLMs). These intricate digital repositories are increasingly integrated into our daily lives, making them prime targets for attacks that can compromise their training data and the confidentiality of their data sources. The paper delves into the nuanced ethical repercussions of such security threats on society and individual privacy. We scrutinize five major threats--prompt injection, jailbreaking, Personal Identifiable Information (PII) exposure, sexually explicit content, and hate-based content--going beyond mere identification to assess their critical ethical consequences and the urgency they create for robust defensive strategies. The escalating reliance on LLMs underscores the crucial need for ensuring these systems operate within the bounds of ethical norms, particularly as their misuse can lead to significant societal and individual harm. We propose conceptualizing and developing an evaluative tool tailored for LLMs, which would serve a dual purpose: guiding developers and designers in preemptive fortification of backend systems and scrutinizing the ethical dimensions of LLM chatbot responses during the testing phase. By comparing LLM responses with those expected from humans in a moral context, we aim to discern the degree to which AI behaviors align with the ethical values held by a broader society. Ultimately, this paper not only underscores the ethical troubles presented by LLMs; it also highlights a path toward cultivating trust in these systems.
Read more7/11/2024
🔍

0
Navigating LLM Ethics: Advancements, Challenges, and Future Directions
Junfeng Jiao, Saleh Afroogh, Yiming Xu, Connor Phillips
This study addresses ethical issues surrounding Large Language Models (LLMs) within the field of artificial intelligence. It explores the common ethical challenges posed by both LLMs and other AI systems, such as privacy and fairness, as well as ethical challenges uniquely arising from LLMs. It highlights challenges such as hallucination, verifiable accountability, and decoding censorship complexity, which are unique to LLMs and distinct from those encountered in traditional AI systems. The study underscores the need to tackle these complexities to ensure accountability, reduce biases, and enhance transparency in the influential role that LLMs play in shaping information dissemination. It proposes mitigation strategies and future directions for LLM ethics, advocating for interdisciplinary collaboration. It recommends ethical frameworks tailored to specific domains and dynamic auditing systems adapted to diverse contexts. This roadmap aims to guide responsible development and integration of LLMs, envisioning a future where ethical considerations govern AI advancements in society.
Read more7/1/2024

0
Deconstructing The Ethics of Large Language Models from Long-standing Issues to New-emerging Dilemmas
Chengyuan Deng, Yiqun Duan, Xin Jin, Heng Chang, Yijun Tian, Han Liu, Henry Peng Zou, Yiqiao Jin, Yijia Xiao, Yichen Wang, Shenghao Wu, Zongxing Xie, Kuofeng Gao, Sihong He, Jun Zhuang, Lu Cheng, Haohan Wang
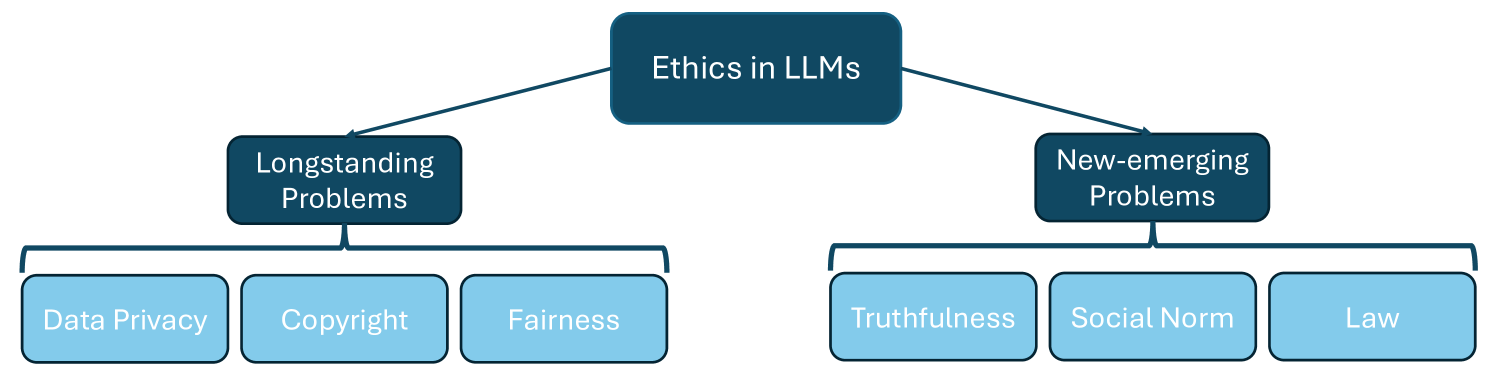
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved unparalleled success across diverse language modeling tasks in recent years. However, this progress has also intensified ethical concerns, impacting the deployment of LLMs in everyday contexts. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of ethical challenges associated with LLMs, from longstanding issues such as copyright infringement, systematic bias, and data privacy, to emerging problems like truthfulness and social norms. We critically analyze existing research aimed at understanding, examining, and mitigating these ethical risks. Our survey underscores integrating ethical standards and societal values into the development of LLMs, thereby guiding the development of responsible and ethically aligned language models.
Read more6/11/2024
👁️

0
I'm categorizing LLM as a productivity tool: Examining ethics of LLM use in HCI research practices
Shivani Kapania, Ruiyi Wang, Toby Jia-Jun Li, Tianshi Li, Hong Shen
Large language models are increasingly applied in real-world scenarios, including research and education. These models, however, come with well-known ethical issues, which may manifest in unexpected ways in human-computer interaction research due to the extensive engagement with human subjects. This paper reports on research practices related to LLM use, drawing on 16 semi-structured interviews and a survey conducted with 50 HCI researchers. We discuss the ways in which LLMs are already being utilized throughout the entire HCI research pipeline, from ideation to system development and paper writing. While researchers described nuanced understandings of ethical issues, they were rarely or only partially able to identify and address those ethical concerns in their own projects. This lack of action and reliance on workarounds was explained through the perceived lack of control and distributed responsibility in the LLM supply chain, the conditional nature of engaging with ethics, and competing priorities. Finally, we reflect on the implications of our findings and present opportunities to shape emerging norms of engaging with large language models in HCI research.
Read more4/1/2024