Exploring Human-AI Collaboration in Agile: Customised LLM Meeting Assistants

0
🔗
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This study investigates the integration of AI assistants in Agile software development meetings, specifically the Daily Scrum and a feature refinement meeting.
- It explores the critical factors for successful AI integration and the impact on team collaboration dynamics.
- The paper provides lessons learned from implementing AI in an industrial context and offers a checklist to assess a team's readiness for AI integration.
Plain English Explanation
This research paper looks at how AI assistants can be used in certain Agile software development meetings. Agile is a way of developing software that focuses on collaboration, flexibility, and quick iterations. The two meetings studied were the Daily Scrum, where the team discusses their progress, and a feature refinement meeting, where the team plans out upcoming features.
The researchers wanted to understand what makes it successful to use AI in these meetings, and how it affects the way the team works together. They tried using AI assistants in these meetings at a company and observed what happened.
The key takeaways from this study are a list of important factors for successfully integrating AI, as well as some lessons learned from doing it in a real-world setting. The researchers also provide a checklist that companies and teams can use to see if they're ready to start using AI in their Agile meetings.
The goal is to give guidance to others who want to try using AI assistants to support their Agile software development processes. The researchers hope this will help teams collaborate better and be more efficient.
Technical Explanation
This action research study investigated the integration of AI assistants in two specific Agile software development meetings: the Daily Scrum and a feature refinement meeting, which is part of the company's in-house Scaled Agile framework.
The researchers collected data through observations, interviews, and document analysis to understand the critical drivers of success for AI integration, as well as the impact on team collaboration dynamics. They used an iterative process to refine the AI assistant's capabilities based on feedback from the teams.
The key insights from the study include a set of lessons learned from implementing AI in an industrial context, as well as a readiness assessment checklist for companies and teams to evaluate their preparedness for AI integration. The researchers highlight factors such as trust, task anticipation, and the ability to adapt the AI assistant as critical for successful AI-human collaboration in Agile settings.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides valuable insights into the practical considerations for integrating AI assistants in Agile software development processes. The researchers acknowledge the limitations of their action research approach, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the study was conducted in a single industrial context, and further research would be needed to understand the broader applicability of the lessons learned.
While the paper highlights several critical success factors, it would be helpful to have a more in-depth discussion of potential challenges or risks associated with AI integration, such as issues around data privacy, transparency, or the impact on team dynamics. A more critical examination of these aspects could provide a more balanced perspective.
Overall, the paper offers a useful roadmap for teams and organizations interested in exploring the integration of AI assistants in their Agile practices. However, readers should consider the context-specific nature of the findings and engage in further research and testing to determine the best approach for their own unique circumstances.
Conclusion
This action research study provides valuable insights into the integration of AI assistants in Agile software development meetings, specifically the Daily Scrum and feature refinement meetings. The researchers identify critical success factors, such as trust, task anticipation, and adaptability, and offer a practical checklist to help teams assess their readiness for AI integration.
The lessons learned from this industrial case study can serve as a guide for other organizations and teams interested in leveraging AI to support their Agile practices. By understanding the potential benefits and challenges of AI integration, teams can make more informed decisions and develop effective strategies to enhance their collaboration and productivity.
Overall, this paper contributes to the growing body of research on the intersection of AI and Agile software development, and offers a blueprint for successfully incorporating AI assistants into these collaborative workflows.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔗

0
Exploring Human-AI Collaboration in Agile: Customised LLM Meeting Assistants
Beatriz Cabrero-Daniel, Tomas Herda, Victoria Pichler, Martin Eder
This action research study focuses on the integration of AI assistants in two Agile software development meetings: the Daily Scrum and a feature refinement, a planning meeting that is part of an in-house Scaled Agile framework. We discuss the critical drivers of success, and establish a link between the use of AI and team collaboration dynamics. We conclude with a list of lessons learnt during the interventions in an industrial context, and provide a assessment checklist for companies and teams to reflect on their readiness level. This paper is thus a road-map to facilitate the integration of AI tools in Agile setups.
Read more4/24/2024
🔍

0
Future of Artificial Intelligence in Agile Software Development
Mariyam Mahboob, Mohammed Rayyan Uddin Ahmed, Zoiba Zia, Mariam Shakeel Ali, Ayman Khaleel Ahmed
The advent of Artificial intelligence has promising advantages that can be utilized to transform the landscape of software project development. The Software process framework consists of activities that constantly require routine human interaction, leading to the possibility of errors and uncertainties. AI can assist software development managers, software testers, and other team members by leveraging LLMs, GenAI models, and AI agents to perform routine tasks, risk analysis and prediction, strategy recommendations, and support decision making. AI has the potential to increase efficiency and reduce the risks encountered by the project management team while increasing the project success rates. Additionally, it can also break down complex notions and development processes for stakeholders to make informed decisions. In this paper, we propose an approach in which AI tools and technologies can be utilized to bestow maximum assistance for agile software projects, which have become increasingly favored in the industry in recent years.
Read more8/2/2024
🤖

0
Augmenting the Author: Exploring the Potential of AI Collaboration in Academic Writing
Joseph Tu, Hilda Hadan, Derrick M. Wang, Sabrina A Sgandurra, Reza Hadi Mogavi, Lennart E. Nacke
This workshop paper presents a critical examination of the integration of Generative AI (Gen AI) into the academic writing process, focusing on the use of AI as a collaborative tool. It contrasts the performance and interaction of two AI models, Gemini and ChatGPT, through a collaborative inquiry approach where researchers engage in facilitated sessions to design prompts that elicit specific AI responses for crafting research outlines. This case study highlights the importance of prompt design, output analysis, and recognizing the AI's limitations to ensure responsible and effective AI integration in scholarly work. Preliminary findings suggest that prompt variation significantly affects output quality and reveals distinct capabilities and constraints of each model. The paper contributes to the field of Human-Computer Interaction by exploring effective prompt strategies and providing a comparative analysis of Gen AI models, ultimately aiming to enhance AI-assisted academic writing and prompt a deeper dialogue within the HCI community.
Read more4/26/2024

0
Deconstructing Human-AI Collaboration: Agency, Interaction, and Adaptation
Steffen Holter, Mennatallah El-Assady
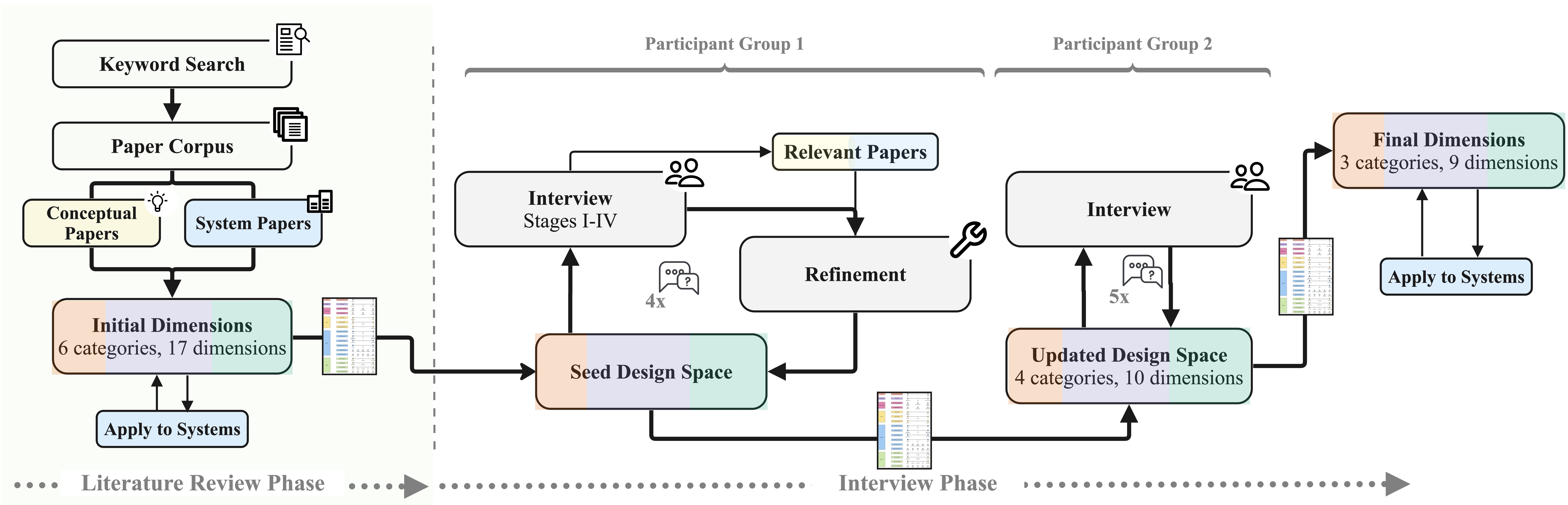
As full AI-based automation remains out of reach in most real-world applications, the focus has instead shifted to leveraging the strengths of both human and AI agents, creating effective collaborative systems. The rapid advances in this area have yielded increasingly more complex systems and frameworks, while the nuance of their characterization has gotten more vague. Similarly, the existing conceptual models no longer capture the elaborate processes of these systems nor describe the entire scope of their collaboration paradigms. In this paper, we propose a new unified set of dimensions through which to analyze and describe human-AI systems. Our conceptual model is centered around three high-level aspects - agency, interaction, and adaptation - and is developed through a multi-step process. Firstly, an initial design space is proposed by surveying the literature and consolidating existing definitions and conceptual frameworks. Secondly, this model is iteratively refined and validated by conducting semi-structured interviews with nine researchers in this field. Lastly, to illustrate the applicability of our design space, we utilize it to provide a structured description of selected human-AI systems.
Read more4/19/2024