Word2World: Generating Stories and Worlds through Large Language Models
2405.06686

0
0

Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) have proven their worth across a diverse spectrum of disciplines. LLMs have shown great potential in Procedural Content Generation (PCG) as well, but directly generating a level through a pre-trained LLM is still challenging. This work introduces Word2World, a system that enables LLMs to procedurally design playable games through stories, without any task-specific fine-tuning. Word2World leverages the abilities of LLMs to create diverse content and extract information. Combining these abilities, LLMs can create a story for the game, design narrative, and place tiles in appropriate places to create coherent worlds and playable games. We test Word2World with different LLMs and perform a thorough ablation study to validate each step. We open-source the code at https://github.com/umair-nasir14/Word2World.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces "Word2World", a system that can generate interactive stories and virtual worlds by leveraging large language models (LLMs).
- The researchers demonstrate how LLMs can be used for procedural content generation, enabling the creation of diverse and engaging narratives and environments.
- The paper explores the potential of LLMs to act as versatile content generators, going beyond traditional text generation to create more immersive, multimodal experiences.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have developed a system called "Word2World" that can use large language models (LLMs) to generate interactive stories and virtual worlds. LLMs are AI models trained on vast amounts of text data, which allows them to understand and generate human-like language.
The key idea behind Word2World is to leverage the powerful language understanding and generation capabilities of LLMs to automatically create narratives, characters, and environments for interactive experiences. This could enable the rapid development of diverse, engaging stories and virtual worlds without the need for extensive manual content creation.
For example, the system could generate a fantasy story with a detailed world, characters, and plot, all based on high-level prompts or instructions. This could be useful for creating video games, interactive fiction, or educational experiences where the content is dynamically generated rather than pre-authored.
By harnessing the capabilities of LLMs, the researchers aim to make the process of creating rich, immersive experiences more accessible and efficient, potentially opening up new possibilities for storytelling, gaming, and other interactive media.
Technical Explanation
The Word2World system utilizes large language models (LLMs) to perform procedural content generation, which is the automatic creation of game assets, levels, narratives, and other content. The researchers explore how LLMs can be leveraged as versatile content generators, going beyond traditional text generation to create more immersive, multimodal experiences.
The core of the Word2World approach involves fine-tuning a pre-trained LLM on relevant datasets, such as fantasy fiction, to imbue the model with domain-specific knowledge and capabilities. This allows the system to generate coherent stories, characters, and settings that are tailored to the target application or genre.
The researchers demonstrate several use cases, including the generation of interactive fiction, virtual world building, and even the creation of simple game levels. By providing the LLM with appropriate prompts or instructions, the system can autonomously produce narrative elements, environmental descriptions, and gameplay mechanics that can be integrated into interactive experiences.
The paper also discusses the potential challenges and limitations of using LLMs for procedural content generation, such as ensuring the generated content is consistent, diverse, and aligned with the desired narrative or gameplay objectives. The researchers suggest various techniques, such as the use of reinforcement learning and multi-task training, to address these issues and further enhance the capabilities of the Word2World system.
Critical Analysis
The Word2World research presents a compelling vision for leveraging large language models as powerful content generators for interactive experiences. The ability to automatically create narratives, characters, and virtual environments has the potential to significantly streamline the development of video games, interactive fiction, and other immersive media.
However, the paper does acknowledge several challenges and limitations that would need to be addressed. Ensuring the generated content maintains coherence, diversity, and alignment with the desired experience is a complex task that requires further research and development. Additionally, the integration of the generated content into a fully functional and engaging interactive system is not trivial and would likely require significant engineering effort.
Another potential concern is the potential for biases or inaccuracies in the generated content, which could be problematic if used in educational or other sensitive contexts. The researchers do not provide a detailed analysis of the safety and ethical implications of their approach, which would be an important consideration for wider adoption.
Despite these caveats, the Word2World research represents an important step forward in exploring the possibilities of large language models for procedural content generation. As the field of AI continues to advance, the integration of LLMs with other technologies, such as video game AI models or multimodal world models, could lead to even more sophisticated and engaging interactive experiences.
Conclusion
The Word2World research demonstrates the potential of large language models to serve as versatile content generators for interactive stories and virtual worlds. By leveraging the language understanding and generation capabilities of LLMs, the system can autonomously create narratives, characters, and environments that can be integrated into immersive experiences, potentially streamlining the development of video games, interactive fiction, and other multimedia applications.
While the approach faces some technical and ethical challenges, the paper represents an important step forward in exploring the intersection of large language models, procedural content generation, and interactive media. As the field of AI continues to advance, the integration of LLMs with other cutting-edge technologies could lead to even more sophisticated and engaging interactive experiences in the future.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
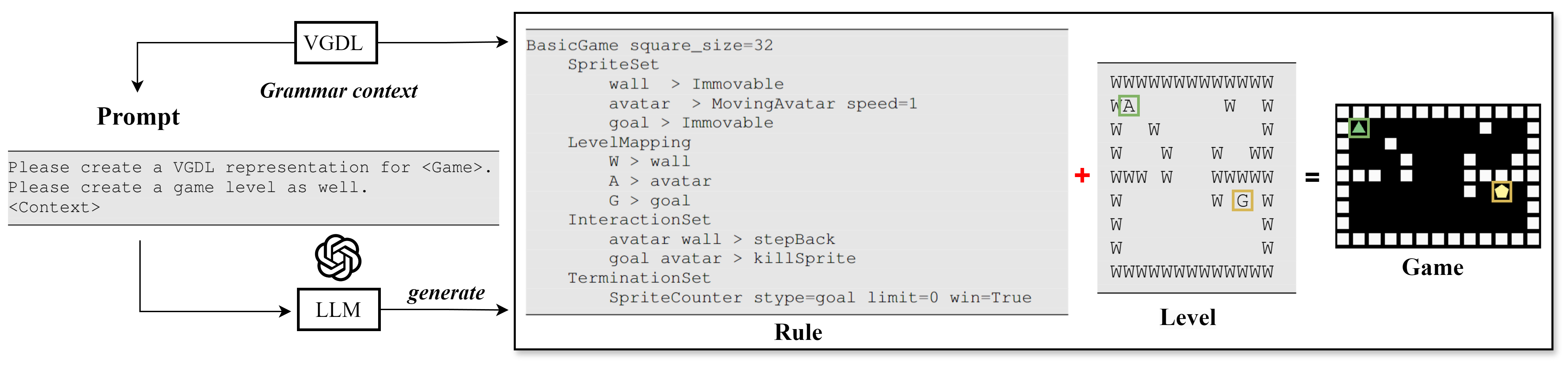
Generating Games via LLMs: An Investigation with Video Game Description Language
Chengpeng Hu, Yunlong Zhao, Jialin Liu

0
0
Recently, the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has unlocked new opportunities for procedural content generation. However, recent attempts mainly focus on level generation for specific games with defined game rules such as Super Mario Bros. and Zelda. This paper investigates the game generation via LLMs. Based on video game description language, this paper proposes an LLM-based framework to generate game rules and levels simultaneously. Experiments demonstrate how the framework works with prompts considering different combinations of context. Our findings extend the current applications of LLMs and offer new insights for generating new games in the area of procedural content generation.
5/31/2024
📈
WorldGPT: Empowering LLM as Multimodal World Model
Zhiqi Ge, Hongzhe Huang, Mingze Zhou, Juncheng Li, Guoming Wang, Siliang Tang, Yueting Zhuang

0
0
World models are progressively being employed across diverse fields, extending from basic environment simulation to complex scenario construction. However, existing models are mainly trained on domain-specific states and actions, and confined to single-modality state representations. In this paper, We introduce WorldGPT, a generalist world model built upon Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM). WorldGPT acquires an understanding of world dynamics through analyzing millions of videos across various domains. To further enhance WorldGPT's capability in specialized scenarios and long-term tasks, we have integrated it with a novel cognitive architecture that combines memory offloading, knowledge retrieval, and context reflection. As for evaluation, we build WorldNet, a multimodal state transition prediction benchmark encompassing varied real-life scenarios. Conducting evaluations on WorldNet directly demonstrates WorldGPT's capability to accurately model state transition patterns, affirming its effectiveness in understanding and predicting the dynamics of complex scenarios. We further explore WorldGPT's emerging potential in serving as a world simulator, helping multimodal agents generalize to unfamiliar domains through efficiently synthesising multimodal instruction instances which are proved to be as reliable as authentic data for fine-tuning purposes. The project is available on url{https://github.com/DCDmllm/WorldGPT}.
4/30/2024
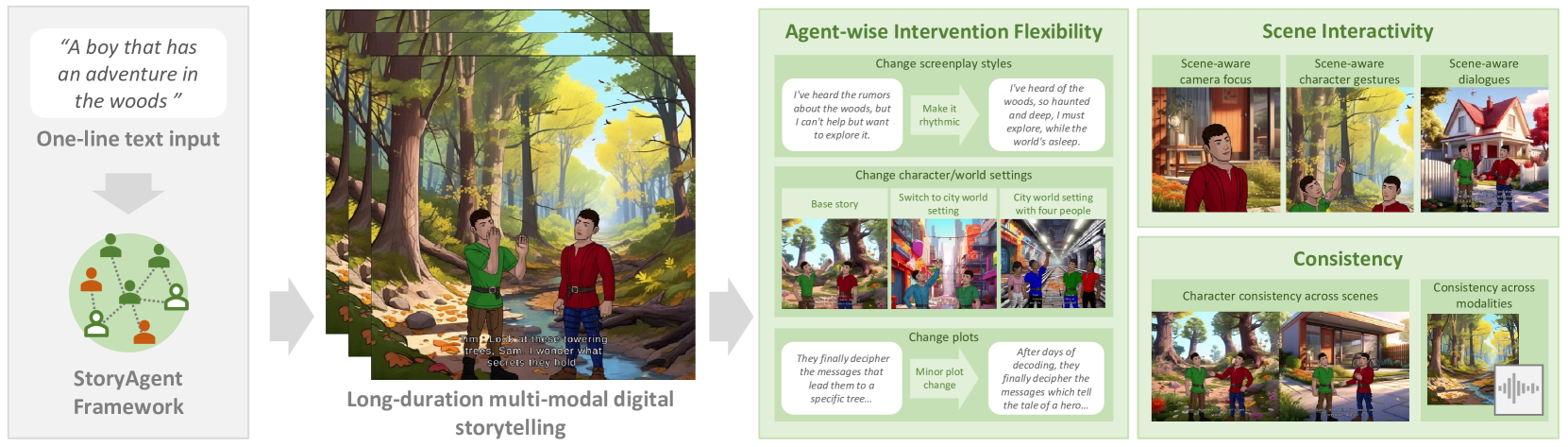
From Words to Worlds: Transforming One-line Prompt into Immersive Multi-modal Digital Stories with Communicative LLM Agent
Samuel S. Sohn, Danrui Li, Sen Zhang, Che-Jui Chang, Mubbasir Kapadia

0
0
Digital storytelling, essential in entertainment, education, and marketing, faces challenges in production scalability and flexibility. The StoryAgent framework, introduced in this paper, utilizes Large Language Models and generative tools to automate and refine digital storytelling. Employing a top-down story drafting and bottom-up asset generation approach, StoryAgent tackles key issues such as manual intervention, interactive scene orchestration, and narrative consistency. This framework enables efficient production of interactive and consistent narratives across multiple modalities, democratizing content creation and enhancing engagement. Our results demonstrate the framework's capability to produce coherent digital stories without reference videos, marking a significant advancement in automated digital storytelling.
6/24/2024
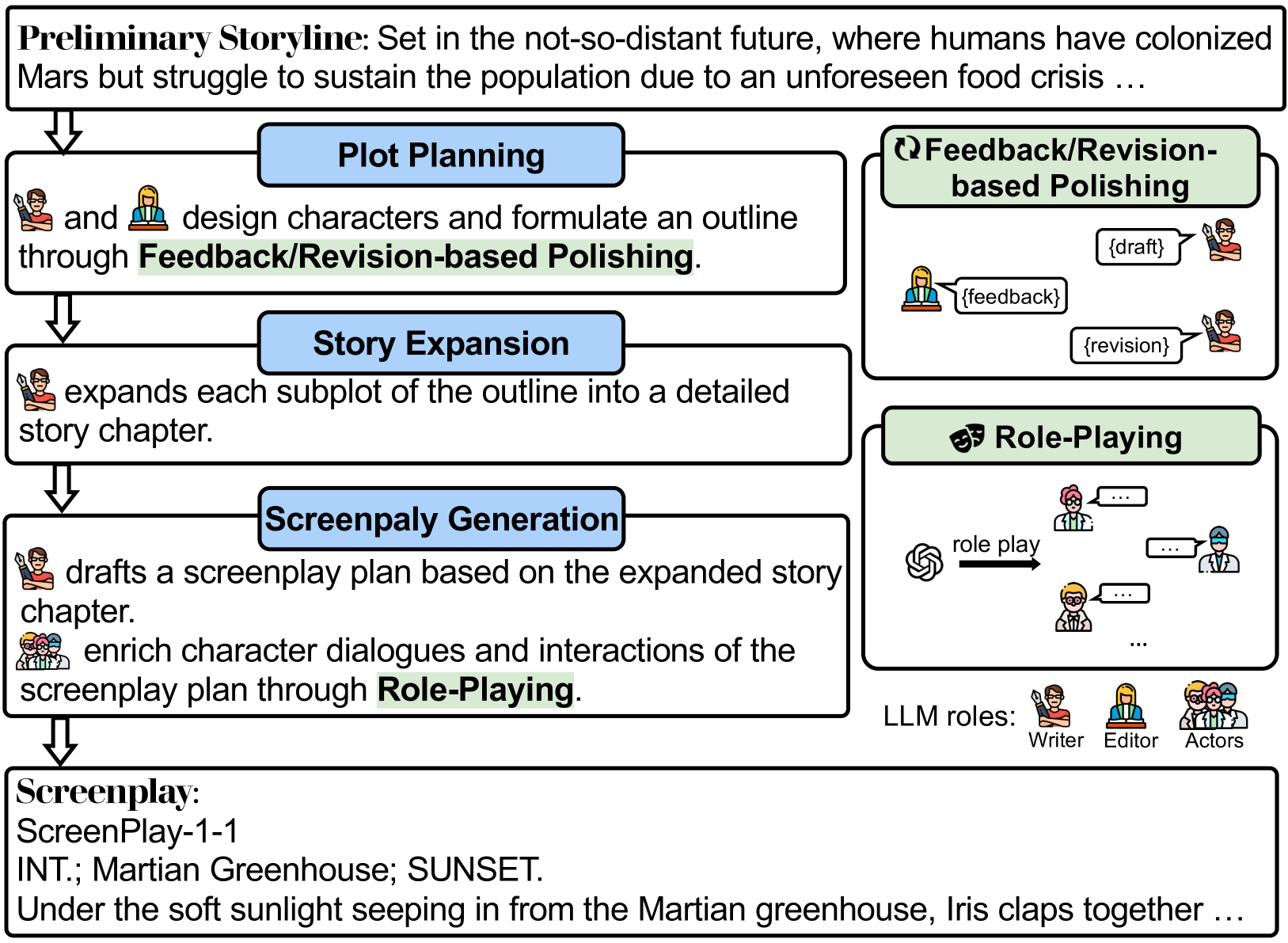
HoLLMwood: Unleashing the Creativity of Large Language Models in Screenwriting via Role Playing
Jing Chen, Xinyu Zhu, Cheng Yang, Chufan Shi, Yadong Xi, Yuxiang Zhang, Junjie Wang, Jiashu Pu, Rongsheng Zhang, Yujiu Yang, Tian Feng

0
0
Generative AI has demonstrated unprecedented creativity in the field of computer vision, yet such phenomena have not been observed in natural language processing. In particular, large language models (LLMs) can hardly produce written works at the level of human experts due to the extremely high complexity of literature writing. In this paper, we present HoLLMwood, an automated framework for unleashing the creativity of LLMs and exploring their potential in screenwriting, which is a highly demanding task. Mimicking the human creative process, we assign LLMs to different roles involved in the real-world scenario. In addition to the common practice of treating LLMs as ${Writer}$, we also apply LLMs as ${Editor}$, who is responsible for providing feedback and revision advice to ${Writer}$. Besides, to enrich the characters and deepen the plots, we introduce a role-playing mechanism and adopt LLMs as ${Actors}$ that can communicate and interact with each other. Evaluations on automatically generated screenplays show that HoLLMwood substantially outperforms strong baselines in terms of coherence, relevance, interestingness and overall quality.
6/18/2024