Integrating View Conditions for Image Synthesis

0
🖼️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a new framework for image editing that integrates viewpoint information to enhance the control and coherence of object modifications, particularly in interior design scenes.
- The researchers identify three essential criteria - consistency, controllability, and harmony - that an effective image editing method should meet.
- Through extensive experiments, the paper demonstrates the superior performance of the proposed framework compared to existing state-of-the-art methods across multiple dimensions.
- The work establishes a promising direction for advancing image synthesis techniques and enabling precise object edits while preserving the visual coherence of the entire composition.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new approach to image editing that aims to make it easier to make changes to objects within an image, especially for interior design scenes. One of the key challenges in image editing is ensuring that the changes you make to an object fit seamlessly with the rest of the image and don't look out of place.
The researchers identified three important criteria that an effective image editing method should meet:
- Consistency: The edited object should look like it naturally belongs in the image and doesn't stand out as a foreign element.
- Controllability: The user should have precise control over how the object is edited and positioned within the image.
- Harmony: The edited object should blend in with the rest of the scene and not disrupt the overall visual coherence.
The new framework proposed in the paper addresses these criteria by incorporating information about the viewpoint or camera angle of the image. This allows the system to make edits that are better aligned with the perspective of the scene, leading to more natural and harmonious results.
Through extensive testing, the researchers showed that their framework outperforms existing state-of-the-art image editing methods across a variety of metrics. This work opens up new possibilities for creating custom images and making precise object modifications while preserving the overall visual integrity of the scene.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces a novel framework for image editing that leverages viewpoint information to enhance the control and consistency of object modifications, particularly in interior design scenes. The researchers identified three key criteria that an effective image editing method should satisfy: consistency, controllability, and harmony.
Unlike previous approaches, the proposed framework addresses all three of these requirements. By incorporating viewpoint information, the system is able to make edits that are better aligned with the perspective of the scene, leading to more natural and coherent results.
The researchers conducted comprehensive experiments to evaluate the performance of their framework. This included both quantitative assessments and qualitative comparisons with state-of-the-art image editing methods, such as PolyOculus and SyncDreamer. The results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed framework across multiple dimensions.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed and thoroughly evaluated framework for addressing the challenge of image editing, particularly in the context of interior design scenes. The incorporation of viewpoint information is a novel and promising approach that helps to address the key criteria of consistency, controllability, and harmony.
However, the paper does not discuss potential limitations or areas for further research. For example, it would be valuable to understand how the framework performs on more diverse types of scenes beyond interior design, or how it handles complex occlusions and overlapping objects.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the potential biases or limitations of the training data and models used, which could impact the generalizability and fairness of the framework. Further investigation into these areas could help identify areas for improvement and inform future research directions.
Overall, this work represents a significant advancement in the field of image editing and synthesis, and the authors have demonstrated a compelling case for the effectiveness of their approach. Continued research and development in this area could lead to even more powerful and versatile tools for creating and manipulating digital imagery.
Conclusion
This paper introduces a groundbreaking framework for image editing that addresses the critical challenges of consistency, controllability, and harmony. By integrating viewpoint information, the proposed system is able to make object modifications that seamlessly blend with the surrounding scene, providing users with precise control over the editing process.
The comprehensive experiments presented in the paper convincingly demonstrate the superior performance of this framework compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. This work establishes a promising path forward for advancing image synthesis techniques and empowering users to create highly customized and visually coherent digital imagery.
The potential implications of this research extend beyond the field of image processing, as the ability to make precise and harmonious object edits could have far-reaching applications in areas such as virtual and augmented reality, interior design, and digital content creation. As the field of image editing continues to evolve, this landmark contribution is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of this transformative technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🖼️

0
Integrating View Conditions for Image Synthesis
Jinbin Bai, Zhen Dong, Aosong Feng, Xiao Zhang, Tian Ye, Kaicheng Zhou
In the field of image processing, applying intricate semantic modifications within existing images remains an enduring challenge. This paper introduces a pioneering framework that integrates viewpoint information to enhance the control of image editing tasks, especially for interior design scenes. By surveying existing object editing methodologies, we distill three essential criteria -- consistency, controllability, and harmony -- that should be met for an image editing method. In contrast to previous approaches, our framework takes the lead in satisfying all three requirements for addressing the challenge of image synthesis. Through comprehensive experiments, encompassing both quantitative assessments and qualitative comparisons with contemporary state-of-the-art methods, we present compelling evidence of our framework's superior performance across multiple dimensions. This work establishes a promising avenue for advancing image synthesis techniques and empowering precise object modifications while preserving the visual coherence of the entire composition.
Read more5/9/2024

0
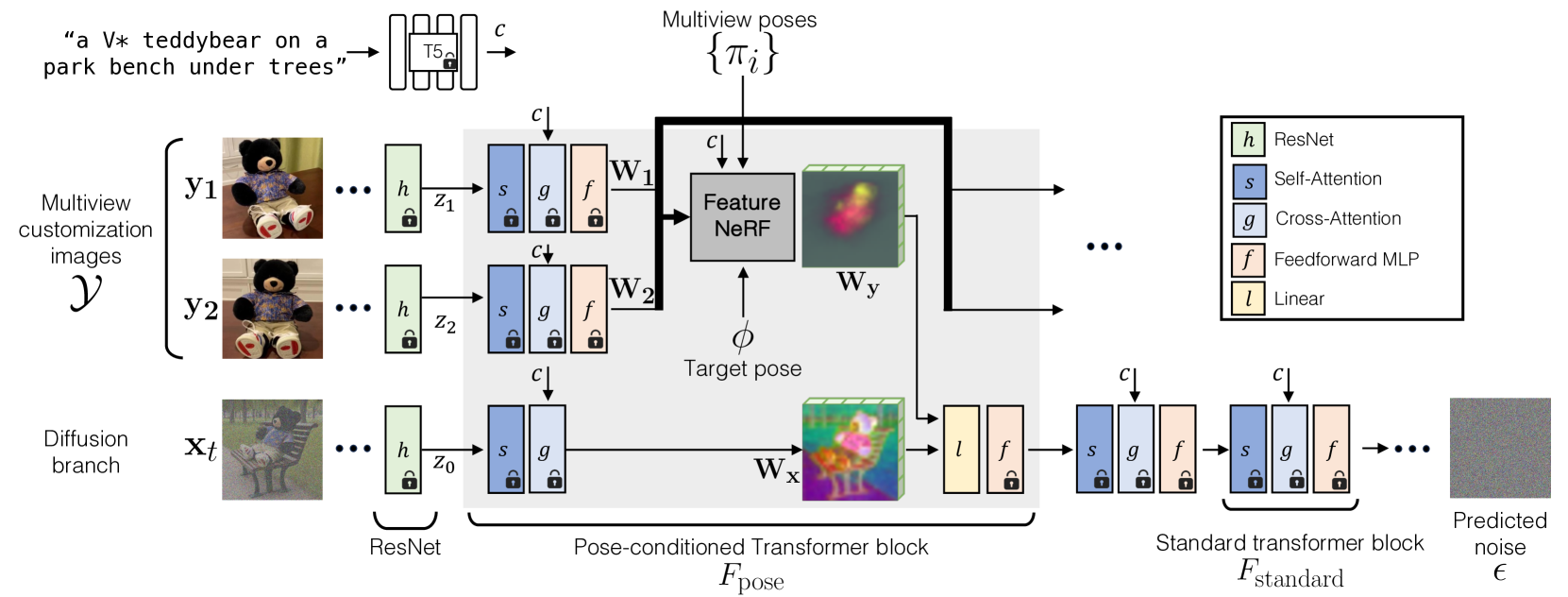
Customizing Text-to-Image Diffusion with Camera Viewpoint Control
Nupur Kumari, Grace Su, Richard Zhang, Taesung Park, Eli Shechtman, Jun-Yan Zhu
Model customization introduces new concepts to existing text-to-image models, enabling the generation of the new concept in novel contexts. However, such methods lack accurate camera view control w.r.t the object, and users must resort to prompt engineering (e.g., adding top-view) to achieve coarse view control. In this work, we introduce a new task -- enabling explicit control of camera viewpoint for model customization. This allows us to modify object properties amongst various background scenes via text prompts, all while incorporating the target camera pose as additional control. This new task presents significant challenges in merging a 3D representation from the multi-view images of the new concept with a general, 2D text-to-image model. To bridge this gap, we propose to condition the 2D diffusion process on rendered, view-dependent features of the new object. During training, we jointly adapt the 2D diffusion modules and 3D feature predictions to reconstruct the object's appearance and geometry while reducing overfitting to the input multi-view images. Our method outperforms existing image editing and model personalization baselines in preserving the custom object's identity while following the input text prompt and the object's camera pose.
Read more4/19/2024


0
3D View Optimization for Improving Image Aesthetics
Taichi Uchida, Yoshihiro Kanamori, Yuki Endo
Achieving aesthetically pleasing photography necessitates attention to multiple factors, including composition and capture conditions, which pose challenges to novices. Prior research has explored the enhancement of photo aesthetics post-capture through 2D manipulation techniques; however, these approaches offer limited search space for aesthetics. We introduce a pioneering method that employs 3D operations to simulate the conditions at the moment of capture retrospectively. Our approach extrapolates the input image and then reconstructs the 3D scene from the extrapolated image, followed by an optimization to identify camera parameters and image aspect ratios that yield the best 3D view with enhanced aesthetics. Comparative qualitative and quantitative assessments reveal that our method surpasses traditional 2D editing techniques with superior aesthetics.
Read more5/28/2024


0
An Optimization Framework to Enforce Multi-View Consistency for Texturing 3D Meshes
Zhengyi Zhao, Chen Song, Xiaodong Gu, Yuan Dong, Qi Zuo, Weihao Yuan, Liefeng Bo, Zilong Dong, Qixing Huang
A fundamental problem in the texturing of 3D meshes using pre-trained text-to-image models is to ensure multi-view consistency. State-of-the-art approaches typically use diffusion models to aggregate multi-view inputs, where common issues are the blurriness caused by the averaging operation in the aggregation step or inconsistencies in local features. This paper introduces an optimization framework that proceeds in four stages to achieve multi-view consistency. Specifically, the first stage generates an over-complete set of 2D textures from a predefined set of viewpoints using an MV-consistent diffusion process. The second stage selects a subset of views that are mutually consistent while covering the underlying 3D model. We show how to achieve this goal by solving semi-definite programs. The third stage performs non-rigid alignment to align the selected views across overlapping regions. The fourth stage solves an MRF problem to associate each mesh face with a selected view. In particular, the third and fourth stages are iterated, with the cuts obtained in the fourth stage encouraging non-rigid alignment in the third stage to focus on regions close to the cuts. Experimental results show that our approach significantly outperforms baseline approaches both qualitatively and quantitatively. Project page: https://aigc3d.github.io/ConsistenTex.
Read more8/6/2024